Updated May 29, 2023

Introduction to MySQL Split
MySQL split concept is to split the string-related data. For example, we could sometimes be willing to separate the column values, which consist of a delimiter. For such cases, we use the split concept. This concept comes into the picture if you are intended to split the string. In MySQL, we use SUBSTRING_INDEX() to split the string. It usually consists of three arguments, i.e., string, delimiter, and position. The string value will be split based on the position. It returns the substring of the string from the occurrence count.
In this session, we will learn how to split the string by mentioning the position for the split and the example.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax for the SUBSTRING_INDEX (): –
SUBSTRING_INDEX( <STRING>, <DELIMITER>, <OCCURRENCE_COUNT> );Here we are specifying the string, delimiter, and count. Based on the count occurrence, the substring will be returned. If the count is negative, it returns the value from the right to the final delimiter. If the count value is positive, it returns it from the left to the last delimiter.
How does MySQL Split work?
Now let us see how to split the columns using the SUBSTRING_INDEX ().
select substring_index ("ABC| BGF| TYH ",'|',1) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC| BGF| TYH ",'|',2) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC| BGF| TYH ",'|',3) AS STRING ;Output:
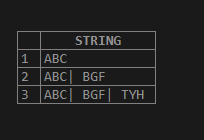
Here in the above example, the delimiter is ‘|’.
select substring_index ("ABC
BGF
TYH ",'\n',1) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC
BGF
TYH ",'\n',2) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC
BGF
TYH ",'\n',3) AS STRING ;Output:

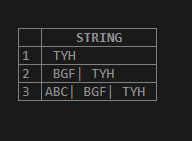
Negative value:
select substring_index ("ABC| BGF| TYH ",'|', -1) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC| BGF| TYH ",'|', -2) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC| BGF| TYH ",'|', -3) AS STRING ;Output:
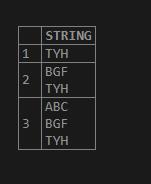
select substring_index ("ABC
BGF
TYH ",'\n', -1) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC
BGF
TYH ",'\n', -2) AS STRING
UNION
select substring_index ("ABC
BGF
TYH ",'\n', -3) AS STRING ;Output:
Example
Now let us create the table and split the string by applying the SUBSTRING_INDEX (). Let us create the below table:
create table Employee_Address
(
E_ID int,
E_NAME varchar(20),
E_LOCATION varchar(20),
E_ADDRESS varchar(100)
);
Insert the below data into the table: -
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (1, 'Sam', 'MP', '12-1-26; Seoul; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (2, 'Sohan', 'Bangalore', '11-26; Busan; South korea' );
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (3, 'Will', 'Tamilnadu', '91-27; Seoul; South korea' );
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (4, 'Ben', 'UP', '10-34; Seoul; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (5, 'Hamington', 'UP', '126-09; Busan; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (6, 'Ji eun', 'Bangalore', '167-4; Seoul; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (7, 'Jimin', 'UP', '234-0; Busan; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (8, 'Jk', 'Bangalore', '166-0; Busan; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (9, 'V', 'AP', '12-89-26; Busan; South korea');
insert into EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS values (10, 'Jhope', 'Bangalore', '189-1-26; Seoul; South korea');Output for the above table is as below: –
select * from EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS;Output:
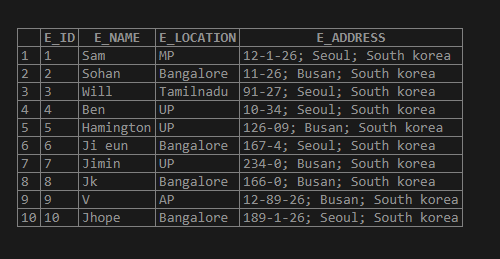
Now let us split the column values of “E_ADDRESS” using the SUBSTRING_INDEX ();
SELECT E_ID,
E_NAME,
E_LOCATION,
SUBSTRING_INDEX(E_ADDRESS,';',1) AS ADDRESS1, /* -- substring declare-*/
SUBSTRING_INDEX(E_ADDRESS,';',2) AS ADDRESS2, /* -- substring declare-*/
SUBSTRING_INDEX(E_ADDRESS,';',3) AS ADDRESS3/* -- substring declare-*/
FROM EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS;Output:
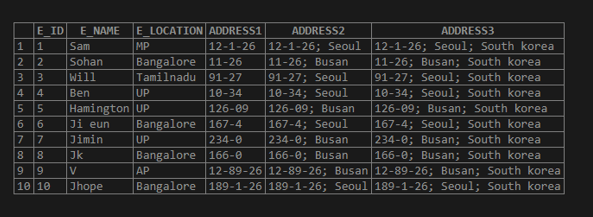
Now we can split into an individual instead of the above output;
SELECT E_ID,
E_NAME,
E_LOCATION,
SUBSTRING_INDEX((SUBSTRING_INDEX(E_ADDRESS,';',1)),';',-1) AS ADDRESS1,
/* -- nested substring declare-*/
SUBSTRING_INDEX((SUBSTRING_INDEX(E_ADDRESS,';',2)),';',-1) AS ADDRESS2,
/* -- nested substring declare-*/
SUBSTRING_INDEX((SUBSTRING_INDEX(E_ADDRESS,';',3)),';',-1) AS ADDRESS3
/* -- nested substring declare-*/
FROM EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS;Output:
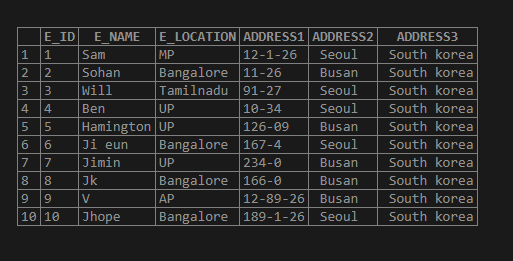
Conclusion
- MySQL split concept is to split the string-related data. For example, we could sometimes be willing to separate the column values, which consist of a delimiter.
- For such cases, we use the split concept. The MySQL Split concept comes into the picture if you are intended to split the string. In MySQL, we use SUBSTRING_INDEX() to split the string.
- It usually consists of three arguments, i.e., string, delimiter, and position. The string value will split based on the position.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Split” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

