Updated June 1, 2023
Difference Between MySQL Float vs Decimal
MySQL offers various data types to users, including float and decimal data types. We use the float data type in MySQL to represent approximate numeric values. Single-precision values are stored using four bytes, while double-precision values require eight. On the other side, we have a decimal data type that comes under the numeric data types; we can use DEC as a decimal. To store fixed values in a database, we commonly utilize the decimal data type. The decimal point precision and float data types must be defined in decimal. There is no need to specify the precision point.
Head to Head Comparison between MySQL Float vs Decimal (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 differences between MySQL Float vs Decimal:
Key Differences between MySQL Float vs Decimal
Let’s see the critical difference between MySQL’s float and decimal data types.
- Floating and decimal data types are the same; this confuses the float and decimal. This similarity of float and decimal data types is based on mathematics. But the key difference between them is memory and precision.
- Confusion can arise when floating-point numbers are approximated and not stored as precise, exact values. A floating-point value, as written in a SQL statement, may not be equivalent to the internal representation of an SQL statement. Endeavors to treat floating-point numbers as accurate in correlations may prompt issues. They are likewise dependent upon the stage of execution conditions. The FLOAT and DOUBLE data types are dependent upon these issues. For DECIMAL sections, MySQL performs activities with an accuracy of 65 decimal digits, which should tackle most basic incorrectness issues.
- The DECIMAL data types store precise numeric values commonly known as “Fixed-Point” or “Exact Value” types. They are frequently used when it is crucial to preserve decimal precision with precise values, such as storing financial information like product cost. In MySQL, the NUMERIC data type is implemented as DECIMAL.
- While pronouncing a DECIMAL or NUMERIC segment, the accuracy and scale can be determined as DECIMAL (P, S) or NUMERIC(P, S), where P is the exactness, and S is the scale. The accuracy of a data type refers to the maximum number of digits (including digits after the decimal point) that can be stored in the column. On the other hand, the scale represents the number of digits that can be explicitly stored after the decimal point. For instance, the value DECIMAL (8, 2) segment can store any worth with eight digits and two decimals, for example, from – 222222.22 to 222222.22.
- In other words, we can say that the decimal data type has a higher precision point and is used in financial software to avoid rounding errors in mathematics. But the decimal type’s performance is slower than the float data type. But one more important thing about the decimal is that it provides the 100 % correct representation of numbers, and the other side float data types cannot accurately represent numbers even if numbers are in a specified format. The float data type is primarily utilized in graphic libraries.
- Now let’s see the different examples of float and decimal data types to understand the key difference between them using MySQL statement.
Example
First, we need to create a new table using the following table.
create table sample_F_D (sample_id int, Sample_Float float, Sample_Decimal decimal (4,2));
Explanation: By using the above statement, we created a new table name sample_F_D with different attributes such as sample_id with the integer data type, Sample_Float with the float data type, and Sampl_Decimal with the decimal data type, and here also we specify the precision point as shown in the above statement. We illustrate the final out of the above statement by using the following screenshot.
Now insert some value to identify the basic difference between the float and decimal data type.
Insert into sample_F_D(sample_id, Sample_Float, Sample_Decimal) values(1, 2.1, 2.1), (2, 2.1, 2.1), (3, 2.1, 2.1) ;
Explanation: Here, we insert a statement of the floating and decimal values into the sample table.
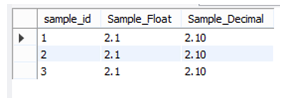
Now see inserted records as follows.
select * from sample;
Explanation: In the above statement, we use the select statement to display the rows from the sample table. It shows the floating number as well as the decimal number. We illustrate the final out of the above statement by using the following screenshot.
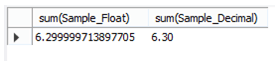
Now perform the sum of both columns and see the difference between them as follows.
select sum(Sample_Float), sum(Sample_Decimal) from sample;
Explanation: After executing the above statement, the screenshot below illustrates the difference between the float and decimal data types.
The final output is different; the Sample_Deciamal column is more precise here.
MySQL Float vs Decimal Comparison Table
Let’s see the comparison table of float and decimal data types on MySQL as follows.
| Float | Decimal |
| Float data types are used to store the approximate precision point. | We can store the same precision point in decimal data type. |
| We can make the changes in the floating-point number after the decimal point. | In decimal data type, we can make such kinds of changes. |
| There is no need to define the precision point in the float data type. When we specify the float data type to store the six digits, then it is capable to store the 25.32 and 43.365 | In decimal data type, we need to define precision points. For example, 25.32 and 45.364 should use decimal precision points. |
| By default range of floating data types is 24 places | By default, the range of decimal data types corresponds to one byte. |
| The floating data type is a single-precision, which uses the 32-bit floating-point data type. | In decimal data type, we can use a 128-bit floating-point data type. |
Conclusion
We hope from this article; you learn the MySQL float vs. decimal. From the above article, we have learned the float vs decimal in MySQL, and we also see different examples of MySQL float vs decimal. This article taught us how and when to use the MySQL float vs decimal.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Float vs Decimal” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.