Updated May 24, 2023

Introduction to MySQL CURDATE
Manier times while inserting the values in MySQL tables with date columns, we have to insert the date column that is the date at that particular time of insertion, or even set the default value of the date column to the date on which that record is inserted. In all such cases, we need to retrieve the value of the date at that particular instance when the operation is being performed. For this, Mysql has provided the functionality to use the CURDATE function to retrieve the current date.
In this article, we will learn how to use the CURDATE function, its syntax and example, alternatives of the CURDATE function in MySQL, and the difference between the NOW() functionality and the CURDATE() functionality.
Syntax
string/number CURDATE();Explanation: The CURDATE() function returns the value of the current date or the date at that particular instance when the function is being called. The date format depends upon the context in which the function is being called. For example, when string context is used, the retrieved data’s format is in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format. At the same time, in the case of numeric context, the format of the fetched date changes to YYYY-MM-DD format.
How does MySQL CURDATE work?
Let us retrieve the value of the CURDATE() function using the simple SELECT statement as follows:
Code:
SELECT CURDATE();Output:
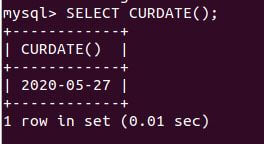
Explanation: that is the date when the article is being written in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format. As we can see, the default format used is the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’, and the return type is a string. Let us convert the retrieved value in the numeric context value by adding 0 or 1 value or some other number to convert the returned value implicitly to the numeric value. We will use the following query statements.
Code:
SELECT 0 + CURDATE();Output:
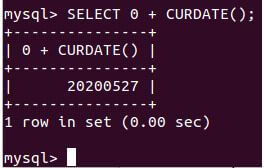
Explanation: Execution of the above query statement gives the following output with today’s date value in YYYY-MM-DD format.
Code:
SELECT 1 + CURDATE();Output:
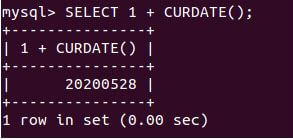
Explanation: Execution of the above query statement gives the following output with tomorrow’s date value as it is equivalent to today’s date plus one day in YYYY-MM-DD format.
Examples to Implement MySQL CURDATE
Below are some examples mentioned:
Example #1
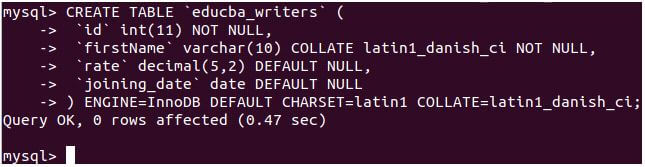
Let us see how we can use it in the table to insert the date column to today’s date. We will create a table named educba_writers with a joining_date column with date data type with the help of the following query statement:
Code:
CREATE TABLE 'educba_writers' (
'id' int(11) NOT NULL,
'firstName' varchar(10) COLLATE latin1_danish_ci NOT NULL,
'rate' decimal(5,2) DEFAULT NULL,
'joining_date' date DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 COLLATE=latin1_danish_ci;Output:
Example #2
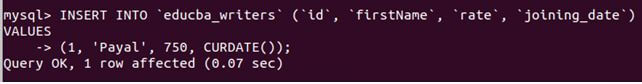
We will insert the values in the educba_writers table with today’s date as the joining_date value using the CURDATE function. For this, we will use the following insert query statement. Let us insert some more rows with non-null rate and joining date value:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate', 'joining_date') VALUES
(1, 'Payal', 750, CURDATE());Output:
Example #3
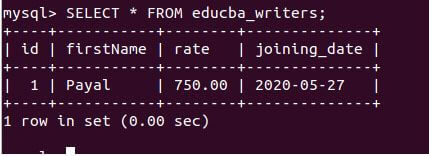
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
Example #4
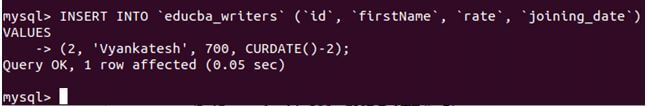
We can see that the value of today’s date, 2020-05-27, in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format is inserted in the joining_date column. We can even insert the dates concerning today’s date using the CURDATE() function. Like for example, we can add the joining date as two days prior or three days later than today by reducing that many days from the CURDATE() function. Suppose we have to insert a writer record named Vyankatesh, whose joining was two days prior to today. Then we can make use of the following query statement to insert this record:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate', 'joining_date') VALUES
(2, 'Vyankatesh', 700, CURDATE()-2);Output:
Example #5
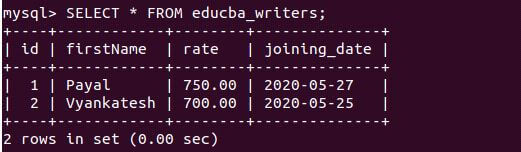
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
Example #6
Suppose we have to insert a writer record named Omprakash, whose joining is after four days. Then we can use the query statement as follows:
Code:
INSERT INTO 'educba_writers' ('id', 'firstName', 'rate', 'joining_date') VALUES
(3, 'Omprakash', 600, DATE_FORMAT((CURDATE() + 4), "%Y-%m-%d"));Output:

Example #7
Let us retrieve the record and view the inserted value in the educba_writers table using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_writers;Output:
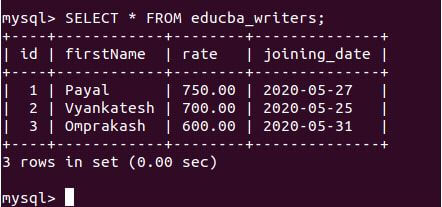
Alternatives of CURDATE() function
We can use the CURRENT_DATE and CURRENT_DATE() functions instead of the CURDATE() function, as both of them work in the same way and return the same value as that of the CURDATE() function. Let us confirm the working of all three functions by executing a simple query of SELECT that will retrieve the value of all three functionalities as follows:
Code:
SELECT CURDATE(), CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_DATE();Output:
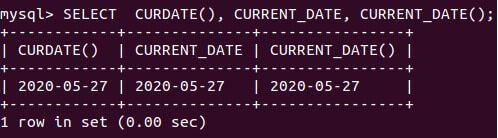
Explanation: We can see that all three functions and statements retrieved the same value on 2020-05-27, which is today’s date.
Difference between NOW() function and CURDATE()
Now() function retrieves the whole timestamp that includes the current date and time, while the CURDATE() function retrieves only the current date. The date part of the NOW() function is equivalent to the CURDATE() function’s output. Let us see the result by using the following query statement:
Code:
SELECT CURDATE(), DATE(NOW()), NOW();Output:
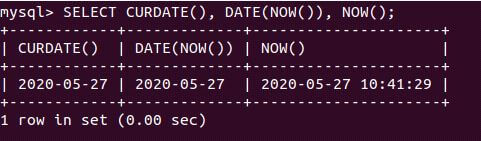
Explanation: We can observe that the value of the CURDATE() and DATE(NOW()) expressions is equivalent.
Conclusion
We can use MySQL’s CURDATE() function to retrieve the current date and manipulate it according to our necessity.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL CURDATE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

