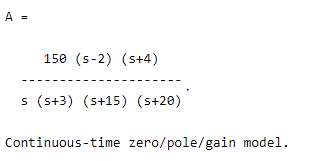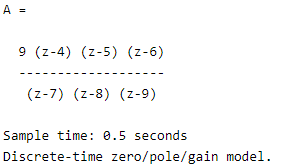Updated March 14, 2023
Introduction to Matlab zpk
The following article provides an outline for Matlab zpK. Matlab provides different types of functions to the user; the zpk is one of Matlab’s functions. Basically, it is used to create the zero–pole–gain models, or we can say that it is used to convert the dynamic system models into the zero-pole-gain form. So, for example, in the zpk () function, we can directly use poles, gains, and zero to create a zero–pole – gain form. Similarly, another way to convert the zero–pole–gain form is that state-space model that we can also call SS, so by using this method, we can also convert the zero pole gain form.
Syntax
There are multiple syntaxes available for the zpk () function in Matlab here; we write only three as follows.
Variable_Name = zpk(zeroes, poles, gain)
Variable_Name = zpk(zeroes, poles, gain,time)
Variable_Name = zpk(zeroes, poles, gain, sample time)
Explanation
In the above syntax, we used the different parameters as follows.
In the first syntax, we use Varible_Name that means the actual name of a variable that depends on the user. After that, we use the zpk function to create zero – pole – gain form by using the vector and scalar values. The output of the zpk () function is that model data and that store in any specified variable. After getting the output, we need to set the zero and pole value to [ ], and there is no specific condition that means these two inputs may be different or equal.
In the second syntax, we perform the step to gain the zero – pole – gain form, but here the only difference is that by using the second syntax, we can create the discrete-time zero – pole – gain form by simply adding the time parameter as shown in the above syntax. In this syntax, the time should be -1 or [ ].
In the third syntax, we can inherit the properties of dynamic systems by including the sample time as shown in the above syntax.
How zpk works in Matlab?
Now let’s see how the zpk () function works in Matlab as follows.
Basically, in the zpk () function, we need to consider the different parameters for execution as follows.
Input Argument as follows:
In the zpk () function, we have a different type of input argument as follows.
- Zero – pole- gain model from zeros
In which we use row vectors for SISO models. For example we can consider [2, 3+j, 3-2] and we need to create a model with zeros such as v=2, v=3+j and v= 3-2.
In this method, we can use the array vector that is Ny-by-Nu-cell. It is also useful to create the discrete-time zero–pole – gain model.
- Poles of zero – pole- gain model from poles:
It is also specifying the two different vectors, such as the row vector and the Ny-by-Nu-cell vector. Therefore, in this method, we can create the SISO zero – pole- gain model by using a row vector, and by using a Ny-by-Nu-cell vector, we can create the discrete-time MIMO SISO zero–pole–gain model.
- Gains zero – pole- gain model from gains:
It specified the scalar and Ny-by-Nu-cell vector cell array to gain the zero – pole – gain form. This method uses a scalar vector for the SISO time zero – pole – gain model and Ny-by-Nu-cell vector cell array for MIMO zero – pole – gain mode.
- Sample time:
Sample time is used to specify the scalar, and by using the argument, we can initiate the initial value of sample time.
- Dynamic system:
This argument is also used to specify the SISO and MIMO model but in a dynamic nature.
- Static gain:
It is used to specify the scalar or matrix, and it represents the ratio of output.
Now let’s see the Output Argument in zpk as follows.
In the output argument, we used different objects such as the genss model object, uss model object, and zpk model object. Genss model object returns when input contains the tunable parameters, model object returns when input includes an uncertain parameter, and zero model object returns when input contains the numeric values.
Examples of Matlab zpk
Now let’s see the different examples of the zpk () function in Matlab for better understanding as follows.
Now let’s see a very simple example of the zpk () function as follows.
A = zpk ([2, -4], [0, -3, -15, -20], 150)
Explanation
By using the above example, we try to create the SISO zero–pole–gain model. Here we specify all zeros, poles, and gain values as shown in the above statement. The final result of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see the example of the discrete-time SISO model as follows.
zeros = [4 5 6];
poles = [7 8 9];
gain = 9
ts = 0.5
A = zpk(zeros, poles, gain, ts)
Explanation
In the above example, we use the sample time to create the discrete SISO model. The final result of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see how we can concatenate the SISO model and generate the MIMO model as follows.
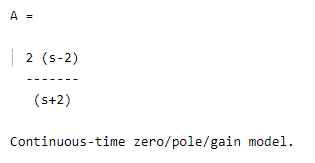
zeros_1 =2;
poles_1 = -2;
gain = 2;
A = zpk(zeros_1, poles_1, gain)
Explanation
By using the above code, we created the first SISO model. The final result of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now create one more SISO model by using the following code as follows.
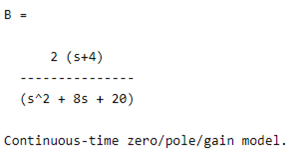
zeros_2 = -4;
poles_2 = [-4+2i -4-2i];
B = zpk(zeros_2,poles_2,gain)
Explanation
The final result of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now merge both SISO models and create a MIMO model as follows.
Z = [A;B]
Explanation
In the above statement, we just concatenate both SISO models. The final result of the above statement we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
So in this way, we can use the zpk () function in Matlab as per our requirement with different syntax.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn Matlab zpk. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of zpk and different examples of zpk. From this article, we learned how and when we use Matlab zpk.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab zpk. Here we discuss how and when we use zpk along with the different examples of Matlab zpk. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –