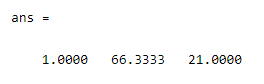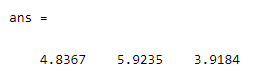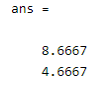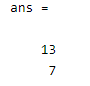Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of Matlab Variance
Matlab provides different kinds of functionality to the user; in Matlab variance, we can return the first array element whose size does not equal 1. Basically, variance is used for financial time series. Variance we can use in a multidimensional array to return the first element of the array, which does not equal 1 as a vector. If we observe that the array is a vector, then we can consider variance as a scalar. By default, the size of variance is 1. If we have a matrix in which each column is a random variable and all rows in observation at that time a row vector containing the variance that corresponds to every column from the matrix.
Syntax:
There are multiple syntaxes of variance as follows.
variance = var (Array)
variance = var (Array, weight)
variance = var (Array, weight, all)
variance = var (Array, weight, dimension)
Explanation
In the above syntaxes, we use different parameters as follows.
In the first syntax, we specify the variance is equal to an array which means it returns the first array dimension whose size is not equal to the 1. If the array is in an observation state, then the variance is scalar.
In syntax, we pass the two parameters that are array and weigh; if weight = 0, then the variance is normalized, and it requires -1 observation, and if weight =1, then variance normalized by observation number. Basically, weight is a vector, and it contains the non-negative elements.
In the third syntax, we pass the three different parameters such as an array, weight, and all, as shown in the above syntax. Here all is used to compute the all element when weight is 0 or 1, and this syntax is suitable for only specific versions of Matlab.
In the fourth syntax, we pass the three different parameters that are array, weight, and dimension. In this syntax, we pass the array with weight and dimension. It is used to maintain the normalization of array dimensions.
How does variance work in Matlab?
Now let’s see how variance works in Matlab as follows.
Now let’s see what are the input arguments required for the variance as follows.
We use different parameters as input. First is that Array, The array may be a vector or it may be a matrix or it may be a multidimensional array and it uses the single or double data types.
The next input parameter is that weight, and we can specify either 0 or 1; when weight is 0, then the required number of observations is -1, and when weight is 1, then it is the required number of observations. It also uses the single or double data type.
The next parameter is that dimension, by using the dimension, we can specify the positive integer scalar. Suppose there is no value for dimension, then it takes the default value of array dimension. It uses the single, double, int8 and int16, etc data types.
The next input parameter is that vector dimension; it also specifies the positive integer vector and it represents each dimension input array. The length of the output parameter is that 1 and it remains the same for other dimensions.
The next input parameter is that reset port, the reset port is used to specify the transaction that causes the interrupt during the execution to reset the running variance. Normally RST time is always a positive integer.
Now let’s see the output argument for the variance as follows.
If the Running variance option is not selected, the block computes the variance in each row or column of the input, or along vectors of a given input dimension. It also has the ability to compute the variance of the full input at each sample period. The variance of the associated column, row, or complete input is represented by each member in the output array y. The Find the variance value over parameter determines the size of the output array y.
There are other properties we may also consider when we need to perform the variance in Matlab.
Examples
Now let’s see the different examples of variance in Matlab for better understanding as follows. Let’s see how we can implement the variance in matrices as follows.
First, we need to create the matrix by using the following statement.
M = [3 -9 2; 2 6 -4; 1 4 5];
Explanation
By using the above statement, we created a 1 by 3 matrix. Now execute the following statement to compute the variance of the matrix as follows.
var(M)
Explanation
The final output we illustrated by using the following screenshot is as follows.
Now let’s see how we can compute the variance for weight vectors as follows.
First, we need to create the matrix by using the following statement as follows.
M = [3 -1 8; 4 5 7; -2 2 3];
wm = [0.4 0.15 0.15];
var(M.wm)
Explanation
By using the above statement, we created a matrix, and we also provide the weight to compute the variance with respect to the weight. After that, we write the var statement to compute the variance of the matrix as shown in the above example. The final output we illustrated by using the following screenshot is as follows.
Now let’s see how we can specify the dimension for the variance as follows.
M = [2 -3 4; 8 4 3];
var(M,1,2)
Explanation
In the above example, we first created a matrix, and after that, we specify the weight with dimension as shown in the above example, here we assign the weight as 1. The final output we illustrated by using the following screenshot is as follows.
When we specify the weight is 0, then see the output as follows.
So in this, we can perform the different operations with help of different input parameters with variance, here we can also perform the different operations as per our requirement for financial series.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn Matlab variance. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of variance, and we also see different examples of variance. From this article, we learned how and when we use Matlab variance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Variance. Here we discuss the Definition, syntax, How variance works in Matlab? examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –