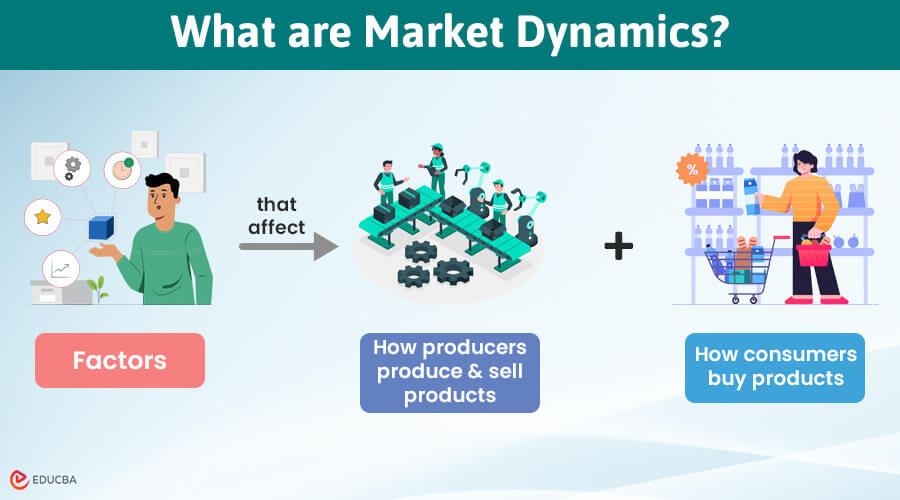
Market Dynamics Definition
Market dynamics are the factors in a market that affect how businesses and consumers behave. For instance, how businesses set their product prices, how individuals choose a product to buy, etc.
The factors that affect the market, include:
- Supply
- Demand
- Government Rules
- Technological Advancements
- International Trade
- Consumer Behavior & Preferences
- Competition
- Business Regulations
Table of Contents
How Does it Work?
Let’s understand how all the factors influence the market dynamics. We will use an example of a company that manufactures tractors.
What causes prices to increase:
- Suppose there is a shortage of raw materials needed to make tractors. The supply will decrease, and prices might increase.
- Government subsidies for farmers to purchase new machinery can increase demand. This increase in demand can affect the prices.
- The company might experience high demand during specific seasons, such as the rainy season, when farmers urgently require tractors for agricultural activities.
- If several companies produce similar tractors (high competition), they must compete on price, features, and quality, often leading to better deals for consumers.
What causes prices to decrease:
- If the company uses new technology, it makes it cheaper to build tractors, so prices could decrease.
- Favorable international trade agreements that reduce tariffs or import costs on tractor components can lower overall production costs. This reduction in costs can decrease the final price of tractors in the market.
- During economic downturns, farmers might buy fewer tractors, so companies might lower prices to sell more.
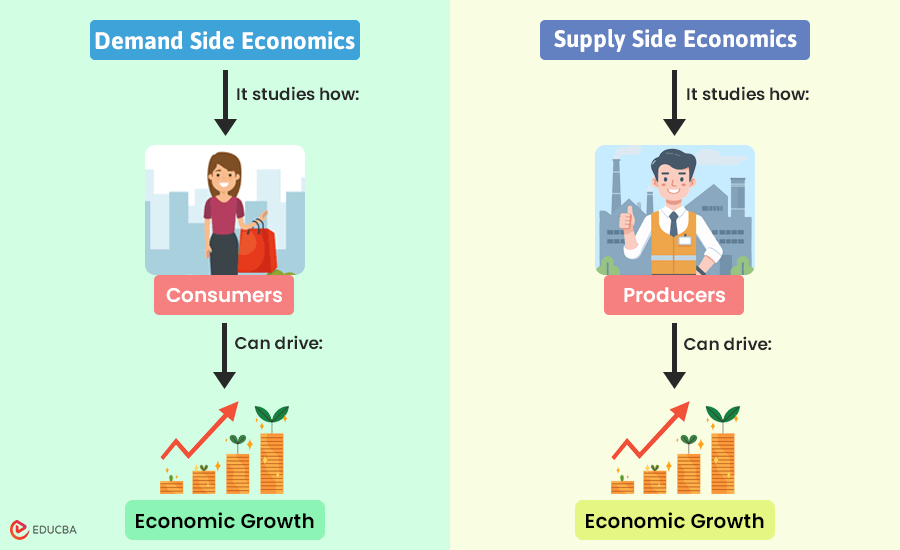
Market Dynamics in Economic Models
The concepts of demand side and supply side refer to different perspectives on how goods and services are influenced in the marketplace:
1. Demand Side Economics
Demand-side economics studies how consumer behavior and purchasing decisions affect economic activity and lead to growth. It highlights the crucial role of consumer demand in shaping the economy.
For instance, during the rainy season, the demand for umbrellas and raincoats increases. In response, stores increase their stock of these items, and manufacturers may hire additional workers to meet the demand. It shows how businesses adapt to changes in consumer preferences, thereby influencing economic activities.
2. Supply Side Economics
Supply-side economics studies how producers and their ability to create goods and services contribute to economic growth. It highlights the importance of production and business incentives in shaping the economy.
For instance, if the government lowers taxes on businesses, companies have more money to invest in new machinery, hire more workers, and produce more goods. This increase in production can lead to more products in stores and possibly lower prices. It shows how encouraging businesses to produce more can directly affect economic activities and growth.
Example
Suppose a coffee company specializes in producing gourmet coffee. It sources its coffee beans from another nation renowned for its high-quality produce.
However, due to political unrest in this coffee-producing nation, the company’s imports of raw coffee beans are severely disrupted.
It results in:
- The shortage of coffee beans has caused the company’s production capacity to decrease by 40%.
- Surge in the global price of coffee beans by 45%.
As a result, the coffee company increases its prices to maintain profitability. Therefore, consumers will face higher costs for their preferred coffee brand.
It demonstrates how political instability can disrupt supply chains and influence both business operations and consumer prices.
Final Thoughts
It’s important to note that market dynamics not only influence how companies set prices but also impact how consumers react to price changes and how suppliers respond to shifts in demand. If businesses can understand this, they can keep up with developments and stay profitable. For this, they must control their business environment and quickly adapt to changes. By doing this, they can compete with rivals by offering competitive prices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the causes of market dynamics?
Answer: Government has significant influence over free markets. The monetary and fiscal policies like changing interest rates, tax rates, and the money supply greatly impact the financial sector.
The flow of money between countries impacts the strength of an economy and its currency. When more money leaves a nation than enters, both its economy and currency weaken.
Consumers, investors, and politicians have varying opinions on the future direction of the economy, which affects their current behavior. It influences both present and future trends.
The supply and demand for goods, services, investments, and currencies cause prices to fluctuate. When demand for an item increases and supply decreases, prices go up. On the other hand, if supply grows faster than demand, prices go down.
Q2. How to do a market dynamics analysis?
Answer: Follow these steps to analyze market dynamics:
- Start by reviewing industry reports to understand the market’s growth rate, consumer spending patterns, and your firm’s position relative to competitors.
- Compare your business with others producing similar goods or services to gauge your standing in the market.
- Evaluate the demand conditions in the industry, including barriers to exit and the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.
- Look for potential threats such as new entrants, substitute products, and the level of competition.
- Stay updated on changes in technology and consumer preferences by collaborating with customers and channel partners.
- Understand how consumers might react to price changes by analyzing the psychological effects of different price points on demand and the interaction of pricing dynamics.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on “Market Dynamics” helped you learn about supply, demand, prices, and their effects on consumers and producers. For more such economics-related articles, refer to the posts below: