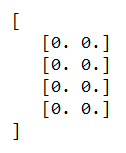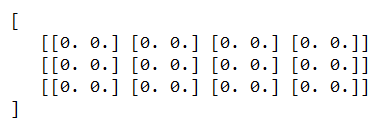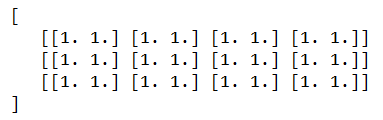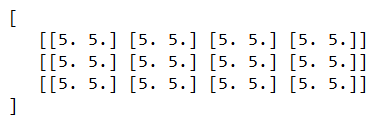Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to Keras Layers
Keras layers form the base and the primary blocks on which the building of Keras models is constructed. They act as the basic building block for models of Keras. Every layer inside the Keras models is responsible for accepting some of the input values, performing some manipulations and computations, and then generating the appropriate output containing the required transformed information. Also, it is a repetitive structure where the computed information that is the output of the particular layer acts as the values of input for other models.
In this article, we will learn about the basics of Keras layers and try to understand the Keras layers and the Keras layer’s basic concept.
What are Keras layers?
To gain insights into the input structure, the layers of Keras need some input_shape, which is the input shape. Further, we need an initializer to assign the weights to every input. Lastly, we will need an activator to convert the achieved output into a non-linear format.
The specification of the value of the range between which all the input data must have their weights for the generation and the restrictions to be put on them are specified by the constraints. There is one more component named regularizer that proves to be helpful for the process of optimization. It tries to make the model and layer as optimized as possible by dynamically putting some penalties on the model’s weights in the optimization process.
In short, the Keras layers need to be provided with the following minimum information for the completion of layer –
• Constraints
• Regularizers
• Input shape
• Activators
• Initializers
• Count the units or neurons that are present inside the layer
Keras layers Basic Concept.
Now, we will try to understand every concept inside the Keras layer and look at how Keras supports that concept.
Input shape
Whenever you create any machine learning program, the model takes the input into videos, text, images, or others and converts them into an array containing numbers that are then supplied to the algorithm as input. The value of input numbers can be a one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or multi-dimensional array that is a matrix. The shape of input is used for the specification of its dimensions which is just a tuple or pair of integers. Let us take one example; if we say input shape id (4,2), the input matrix will contain two columns and four rows.
Let us consider some examples to understand input shape –
Example #1
import numpy as np
sampleInputShape= (4, 2)
educbaInput = np.zeros(shape)
print(educbaInput)
Output if the above code snippet after execution is –
Example #2
import numpy as np
sampleInputShape= (3, 4, 2)
educbaInput = np.zeros(shape)
print(educbaInput)
Output if the above code snippet after execution is –
To create the first input layer, we need to specify the input shape of the model’s input data.
Initializers
We can assign the weights to all the inputs while creating a machine learning model. Initializers make the provision of various functions available for the initial weight assignation. Let us discuss some of the available functions provided by initializers –
- Zeros – For giving the value 0 for all the input data during generation. We had a look at its implementation above two examples.
- Ones – It helps assign one value for all the input data that will eb generated. Let us consider one example,
from Keras.sampleEducbaModels import Sequential
from Keras.layers import Activation, Dense
from Keras import initializers
assignOneAsInitialValue = initializers.Ones()
sampleEducbaModel.add(Dense(512, activation = 'relu', input_shape = (3, 4, 2),
kernel_initializer = assignOneAsInitialValue))
which results in the following output –
Constant
We can assign a particular constant value specified by the user to all the input values of the data. Let us take the same kind of example code snippet but with the specification of 5 as the constant number to initialize the input data –
from Keras.models import Sequential
from Keras.layers import Activation, Dense
from Keras import initializers
sampleEducbaConstantInitializer = initializers.Constant(value = 5) model.add(
Dense(512, activation = 'relu', input_shape = (3, 4, 2), kernel_initializer = sampleEducbaConstantInitializer)
)
Whose output is –
The other functions we have are RandomNormal, RandomUniform, TruncatedNormal, VarianceScaling, lecun_normal, lecun_uniform, glorot_normal, glorot_uniform, he_normal, he_uniform, orthogonal, and identity that is used for assigning initial values to inputs and are functions provided by the initializer.
Constraints
We can set the constraints on the weights or parameters in the machine learning models when in the optimization phase. The constraints module provides various functions for setting the Keras model’s constraints. Let’s have a look at some of them in the below tabular structure –
| Function | Purpose/ Description |
| NonNeg | It helps apply constraints on the weights so that they should have non-negative values. |
| UnitNorm | It helps apply the constraints on the weights to the unit norm value. |
| MaxNorm | Helps for the specification that the weights should have a value equal to or less than the specified value. |
| MinMaxNorm | Applies the constraints on the weight that the norm value on the weight should be between the specified minimum and maximum values of the range.
|
Regularizers
They are used in the optimization phase for applying certain penalties on the layer’s parameters during optimization. Note that the process of regularization is applied on an individual layer only. The functions provided by the regularizer of Keras for penalty application on layers are as mentioned below in table –
| Function | Description |
| L1 regularizer | Used for the application of L1-based regularization. |
| L2 regularizer | Application of the L2-based regularization can be made by using this function. |
| L1 and L2 regularizer | We can apply both the regularizations of L1 and L2 by using this method. |
Activations – This is the component to determine whether a specific neuron inside the machine learning network or model is activated or deactivated.
Besides this, there are various Keras layers: Dense layer, Dropout layer, Flatten layer, reshape layer, permute layer, repeat vector layer, lambda layer, convolution layer, pooling locally connected layer, merge layer, an embedding layer.
Conclusion
Each Keras layer takes certain input, performs computation, and generates the output. Basic concepts of the Keras layers include input shape, initializers, regularizers, constraints, and activations.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Keras Layers. Here we discuss the introduction What is Keras layers, the Basic Concept, and examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –