Updated July 24, 2023

Definition of Interest Coverage Ratio
The term “interest coverage ratio” (ICR) refers to the financial ratio that assesses a business’s ability to pay off its financial costs using its operating profit.
In other words, it measures how well a company can cover the interest payment on its debt. Please note that the calculation does not include principal repayment obligations.
Formula
The formula can be expressed as operating profit or earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by the interest expense. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Examples of Interest Coverage Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
Let us take the example of a manufacturing company to illustrate the computation of the (ICR). The company achieved revenue of $35.5 million in 2018, while it incurred raw material and direct labor costs of $12.2 million and $5.5 million, respectively. The rental expense, depreciation, and salaries for the period are $0.7 million, $1.5 million, and $3.7 million, respectively. Calculate the company’s interest coverage ratio if its annual interest expense was $2.2 million.
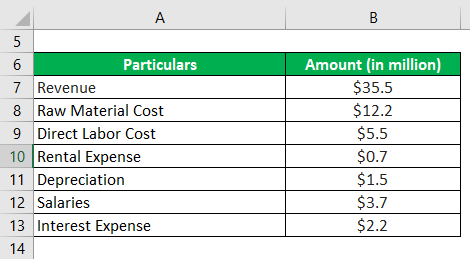
Solution:
COGS is calculated using the formula given below
COGS = Raw Material Cost + Direct Labor Cost
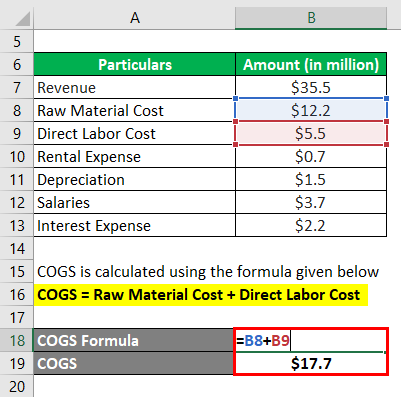
- COGS = $12.2 million + $5.5 million
- COGS = $17.7 million
Operating Expenses is calculated using the formula given below
Operating Expenses = Rental Expense + Depreciation + Salaries
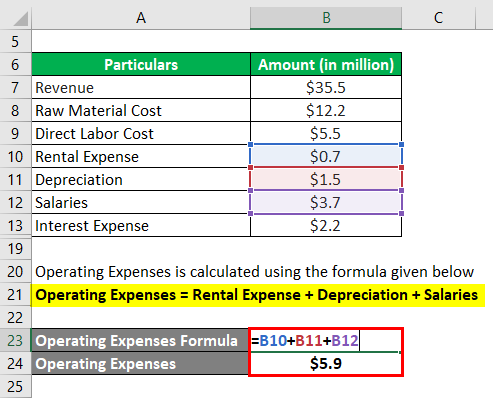
- Operating Expenses = $0.7 million + $1.5 million + $3.7 million
- Operating Expenses = $5.9 million
Operating Income (EBIT) is calculated using the formula given below
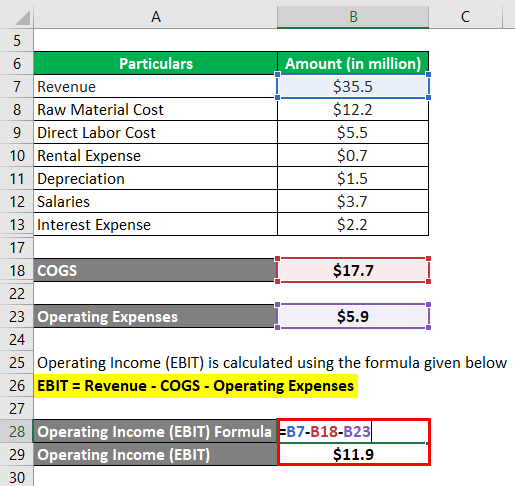
- Operating Income (EBIT) = $35.5 million – $17.7 million – $5.9 million
- Operating Income (EBIT) = $11.9 million
It is calculated using the formula given below
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense
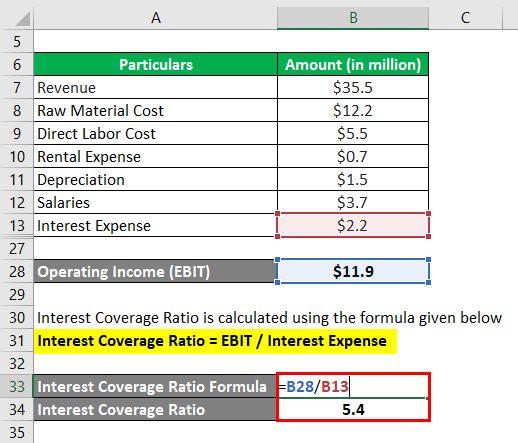
- = $11.9 million / $2.2 million
- = 5.4x
Therefore, the company’s (ICR) for 2018 was 5.4x.
Example #2
Let us now take Apple Inc.’s example to explain the calculation of (ICR). During 2018, Apple Inc. booked $70.90 billion as operating income, while it incurred $3.24 billion as interest expense. Compute Apple Inc.’s interest coverage (ICR) based on the information.
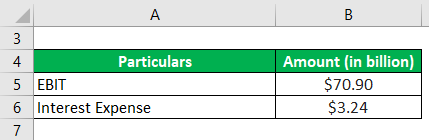
Solution:
It is calculated using the formula given below
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense
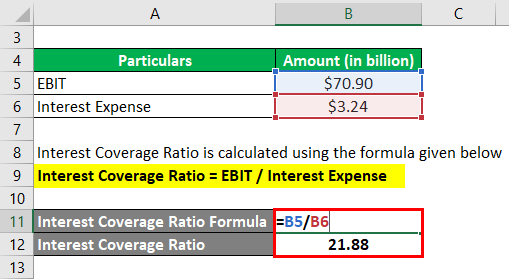
- = $70.90 billion / $3.24billion
- = 21.88x
Therefore, Apple Inc.’s (ICR) for 2018 was 21.9x.

Source Link: Apple Inc. Balance Sheet
Example #3
Now, let us take the example of Walmart Inc. and compute it (ICR). The company recorded an operating income of $20.44 billion during 2018. Compute Walmart Inc.’s interest coverage ratio for 2018 if the interest expense incurred was $1.98 billion.
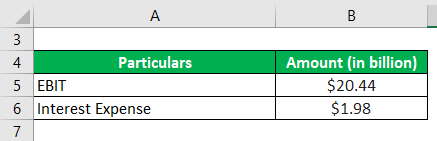
Solution:
Interest Coverage Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense
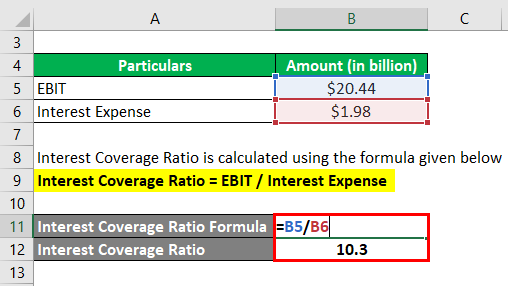
- = $20.44 billion / $1.98 billion
- = 10.3x
Therefore, Walmart Inc.’s (ICR) for 2018 was 10.3x.
Source: Walmart Annual Reports (Investor Relations)
Example #4
Now, let us take the example of Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.’s annual report for the year 2018. As per the annual report, the year’s operating profit and financial expenses were $53.52 billion and $7.82 billion, respectively. Compute Samsung’s interest coverage ratio for the year 2018.
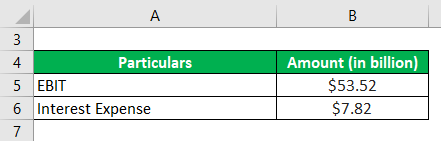
Solution:
The interest Coverage Ratio calculates using the formula given below
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense

- = $53.52 billion / $7.82 billion
- = 6.8x
Therefore, Samsung’s (ICR) for the year 2018 was 6.8x.

Source Link: Samsung Inc. Balance Sheet
Explanation
The formula derives by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the operating profit booked by the company during the given period, usually a year, which is available as a separate line item in the income statement. If not, EBIT can be computed by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses from revenue.
EBIT = Revenue – COGS – Operating expenses
Step 2: Next, determine the company’s interest expense on its debt. It is either available as interest expense or financial cost in the income statement.
Step 3: Finally, the formula for (ICR) derives by dividing the operating profit (step 1) by the interest expense (step 2) as shown below.
Relevance and Use of Interest Coverage Ratio
The concept of (ICR) is very important as it assesses a company’s capability to pay its interest obligations. A higher value (more than 2.0x) indicates that the company can comfortably meet its interest expenses. On the other hand, a lower value (less than 1.0x) of (ICR) indicates that the company is not generating adequate operating profit to meet interest payments, which exposes it to the risk of bankruptcy.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Interest Coverage Ratios. Here we discuss how to calculate (ICR) along with practical examples. We also provide an Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


