Introduction to Intellectual Property
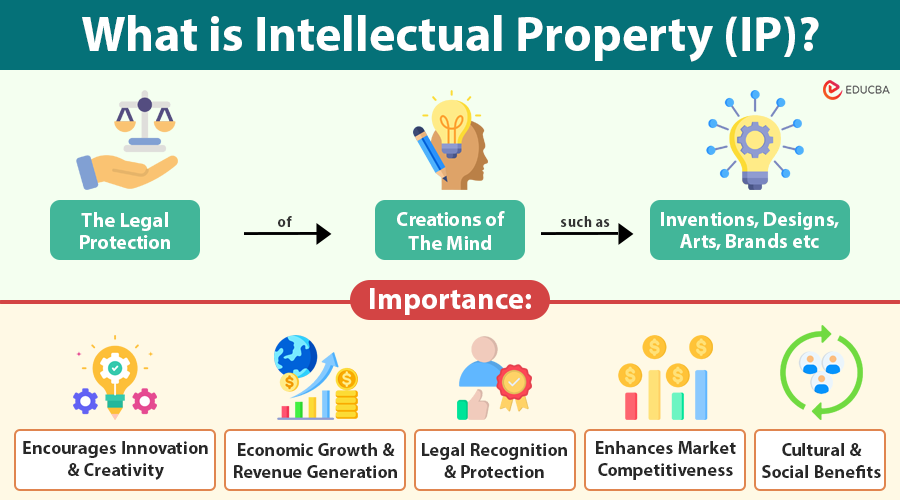
Intellectual Property (IP) encompasses creations of the mind, including inventions, artistic and literary works, designs, symbols, names, and images used in business. These intangible assets represent the intellectual effort and creativity of individuals and organizations. IP allows creators to safeguard their innovations and ideas while gaining recognition and financial rewards.
In the knowledge-driven economy, intellectual property is considered as valuable as physical assets. Technology companies, pharmaceutical firms, entertainment industries, and startups rely heavily on IP to maintain competitiveness. By protecting creative outputs, IP not only fosters innovation but also drives economic growth and promotes cultural enrichment.
IP is governed by laws and regulations that provide exclusive rights to creators for a specified period, allowing them to exploit their work and prevent unauthorized commercial use. In essence, IP acts as both a shield and a currency in the modern business and creative world.
Table of Contents
Importance of Intellectual Property
Intellectual property is important because it promotes innovation, safeguards creativity, and adds economic value. Some of the key reasons IP is critical include:
1. Encourages Innovation and Creativity
By providing legal protection, IP motivates individuals and organizations to develop new products, technologies, and creative works. For example, the patent system encourages pharmaceutical companies to invest in research and development of new drugs without fear of competitors copying their innovations.
2. Economic Growth and Revenue Generation
Intellectual property plays a key role in national and global economies. IP rights can generate income through licensing, franchising, or the sale of intellectual property. Companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Disney generate billions in revenue through patents, copyrights, and trademarks.
3. Legal Recognition and Protection
The law recognizes creators through intellectual property rights, allowing them to control how others use their work. This includes the ability to prevent unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or adaptation of their creations.
4. Enhances Market Competitiveness
Companies with strong IP portfolios enjoy competitive advantages, such as brand recognition, customer loyalty, and market differentiation. For instance, a trademarked logo or patented technology can make a company stand out in a crowded market.
5. Promotes Global Trade and Collaboration
IP protection facilitates international trade, technology transfer, and cross-border collaborations. It ensures that creators receive protection and compensation even in foreign markets, encouraging global innovation.
6. Cultural and Social Benefits
Copyrights, for instance, protect artistic and literary works, preserving cultural heritage and allowing society to access high-quality creative content. IP actively rewards creators, motivating them to continue contributing to arts, literature, and technology.
Types of Intellectual Property
We can broadly categorize intellectual property into Industrial Property, Copyrights, and Trade Secrets. Each type protects different aspects of innovation and creativity.
1. Industrial Property
Industrial property primarily focuses on commercial and industrial innovations.
A) Patents: Patents protect inventions and technological advancements. An invention can receive a patent only if it is new, original, and useful. Patents grant inventors exclusive rights for a specified period (typically 20 years) to sell or license their invention.
Example: Pharmaceutical companies patent new drugs to recover research costs and profit from innovations.
B) Trademarks: Trademarks protect brand identifiers, including logos, brand names, slogans, and symbols. They help consumers distinguish between products or services, ensuring brand recognition and trust.
Example: Nike’s “Swoosh” logo and Coca-Cola’s signature script are globally recognized trademarks.
C) Industrial Designs: Industrial designs safeguard the aesthetic and visual aspects of products, including shape, pattern, and color.
Example: Apple’s iPhone design is protected under industrial design laws to prevent replication.
D) Geographical Indications (GIs): GIs protect products associated with a specific region that possess unique qualities or reputations.
Example: Champagne from France or Darjeeling tea from India. GIs prevent misuse of the product name outside the designated region.
2. Copyrights
Copyright protects original literary, artistic, musical, and software works. It allows creators to reproduce, distribute, perform, and adapt their creations while preventing unauthorized usage. Copyright applies to books, films, paintings, music, software, and even architectural designs. Copyright duration typically lasts for the creator’s lifetime plus 60 years, though it varies by jurisdiction.
Example: J.K. Rowling holds copyrights for the Harry Potter series, controlling reproduction, adaptation, and derivative works.
3. Trade Secrets
Trade secrets encompass confidential business information, processes, formulas, and practices that provide a competitive edge. Unlike patents, companies protect trade secrets by keeping them confidential rather than disclosing them publicly. Examples: Coca-Cola’s secret formula and Google’s search algorithm. Protecting trade secrets requires NDAs, restricted access, and employee confidentiality agreements.
Intellectual Property Laws
Intellectual property laws ensure creators’ rights are protected while maintaining fair competition. Key IP laws include:
- Patent law: Defines the conditions for patentability and the rights of inventors, including exclusive rights to manufacture, sell, or license an invention.
- Trademark law: Safeguards brand identity and prevents market confusion by protecting logos, slogans, and brand names.
- Copyright law: Protects original literary, artistic, and digital works, allowing creators to control reproduction and distribution.
- Trade Secret law: Enforces confidentiality agreements, preventing unauthorized disclosure of sensitive business information.
International IP Agreements
Global treaties and organizations ensure IP protection across borders:
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO): A UN agency promoting IP protection internationally.
- TRIPS Agreement (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights): Sets minimum standards for IP regulation in WTO member countries.
- Paris Convention: Provides international protection for industrial property, including patents and trademarks.
How to Protect Intellectual Property?
Protecting intellectual property is critical for maintaining its value and enforcing rights. Steps include:
- Registration: Register patents, trademarks, copyrights, and industrial designs with national or international authorities to obtain legal protection.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): NDAs prevent unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information, particularly for trade secrets and collaborative projects.
- Monitoring and enforcement: Regularly monitor markets and digital platforms for IP infringement. Take legal action through cease-and-desist letters, lawsuits, or online takedown requests.
- Licensing and commercialization: Licensing allows others to use the IP under specific terms, earning revenue while the owner retains full rights. Example: Microsoft licenses its software to businesses worldwide.
- Digital protection: Protecting digital content through encryption, watermarking, and digital rights management (DRM) helps prevent piracy and unauthorized use of copyrighted materials.
- Employee training and awareness: Educating employees about IP policies and confidentiality helps prevent accidental leaks or misuse of sensitive information.
Challenges in Intellectual Property Management
While IP is valuable, managing it effectively presents challenges:
- Infringement and piracy: Unauthorized use of IP, including counterfeit products and digital piracy, remains a global concern.
- High costs of registration: Patents, trademarks, and legal enforcement require significant investment.
- Global enforcement issues: IP protection standards differ by country, complicating international enforcement.
- Rapid technological changes: Constant innovation demands updates to IP policies and laws, making compliance challenging.
- Awareness and education: Many creators and small businesses lack awareness of IP rights, leaving them vulnerable to infringement.
Final Thoughts
Intellectual property is a cornerstone of modern innovation, creativity, and economic growth. By understanding its types, laws, and protection strategies, creators and businesses can safeguard their intellectual assets, generate revenue, and maintain a competitive advantage. Strong IP management encourages innovation, ensures fair use, and supports a dynamic global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between intellectual property and physical property?
Answer: Intellectual property encompasses creations of the mind, such as inventions, designs, or art, whereas physical property encompasses tangible items, including land, buildings, or machinery. IP is intangible but can hold significant economic value.
Q2. Can ideas be protected under intellectual property laws?
Answer: Intellectual property protects creators’ ideas only when they express them in a tangible form, such as an invention, design, software, or written work.
Q3. Can intellectual property rights be transferred or sold?
Answer: Yes, creators or owners can transfer, sell, or license their IP rights to others. This allows businesses and creators to monetize their intellectual assets.
Q4. Are software and mobile apps protected under intellectual property laws?
Answer: Yes, creators can protect software and mobile apps with copyright for the code and with patents for unique technology or features.
Q5. How can individuals protect their IP in the digital age?
Answer: Creators can protect digital IP by using copyrights, patents, encryption, digital rights management (DRM), watermarks, NDAs, and by monitoring online platforms for unauthorized use.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on Intellectual Property helped you understand the types, importance, and protection strategies for creative and innovative works. Explore our related articles on:

