Updated February 27, 2023

Introduction to Heaviside MATLAB
The following article provides an outline for Heaviside MATLAB. Heaviside function is used in Mathematics for problems involving signal processing and control theory to project signals that switch ON at specified times & stay ON indefinitely. Heaviside function represented as H (x) is discontinuous function with its value as zero if the argument is negative and 1 in case the argument is positive. The function is also referred as unit step function.
Syntax of Heaviside function in MATLAB:
Heaviside (x)
Heaviside (x) will evaluate Heaviside step at the argument value ‘x’.
Examples of Heaviside MATLAB
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Here we will compute Heaviside function of a symbolic value using Heaviside (x).
Let’s take a negative value for our first example; i.e -4. As per the definition of Heaviside function, we should get ‘0’ as output for a negative value.
Syntax:
Hs = heaviside (sym (-4)) [passing the negative argument to the Heaviside function]
Code:
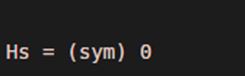
Hs = heaviside (sym (-4))
Output:
As we can see, the output of the Heaviside function is ‘0’ for the negative input, as expected by us.
Example #2
Here is an example where we compute Heaviside function for a positive argument using Heaviside (x).
Let’s take ‘5’ as our input argument. As per the definition of Heaviside function, we should get ‘1’ as output for a positive argument.
Syntax:
Hs = heaviside (sym (5)) [passing the positive argument to the Heaviside function]
Code:
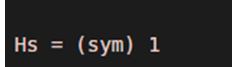
Hs = heaviside (sym (5))
Output:
As we can see, the output of the Heaviside function is ‘1’ for the positive input, as expected by us.
Example #3
Here we will compute Heaviside function for a range of values using heaviside (x) and will plot them to see the output.
Let’s take a range of numbers from 0 to 5 as our input argument. As per the definition of Heaviside function, we should get ‘1’ as output for all these values. So, Mathematically, our output will be a straight line parallel to x-axis at y = 1.
Syntax:
syms x [Initializing the variable]
fplot (heaviside (x), [0, 5]) [passing the input range as argument and plotting the output]
Code:
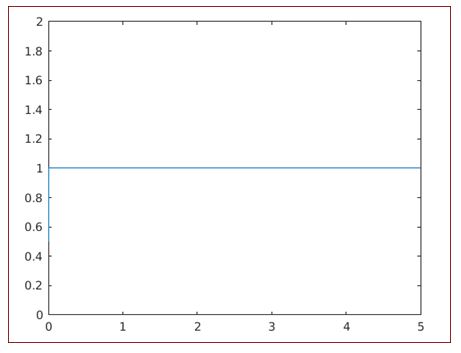
syms x
fplot (heaviside (x), [0, 5])
Output:
As we can see, the output of the Heaviside function is ‘1’ for the positive range of values, as expected by us.
Example #4
Here we will compute Heaviside function for a range covering both positive and negative values using heaviside (x) and will plot them to see the output.
Let’s take a range of numbers from -5 to 5 as our input argument. As per the definition of Heaviside function, we should get ‘1’ as output for all the positive values and ‘0’ for all the negative values. So, Mathematically, our output will be 2 straight lines, one parallel to x-axis at y = 1 and the other one along the x-axis; i.e at y = 0.
Syntax:
syms x [Initializing the variables]
fplot (heaviside (x), [-5, 5]) [passing the input range as argument and plotting the output]
Code:
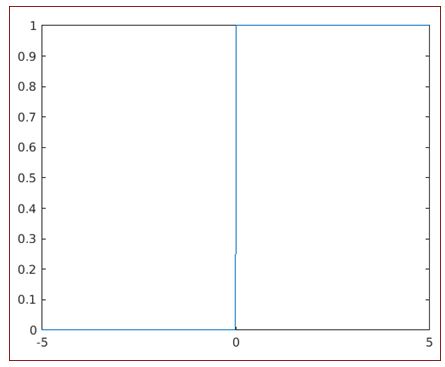
syms x
fplot (heaviside (x), [-5, 5])
Output:
As we can see, the output of the Heaviside function is ‘1’ for the positive range of values and ‘0’ for the negative range of values, as expected by us.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Heaviside MATLAB. Here we discuss the introduction to Heaviside MATLAB along with examples to calculate the unit step. We can calculate the Heaviside function for both positive and negative values. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –