What Is a Flash Loan?
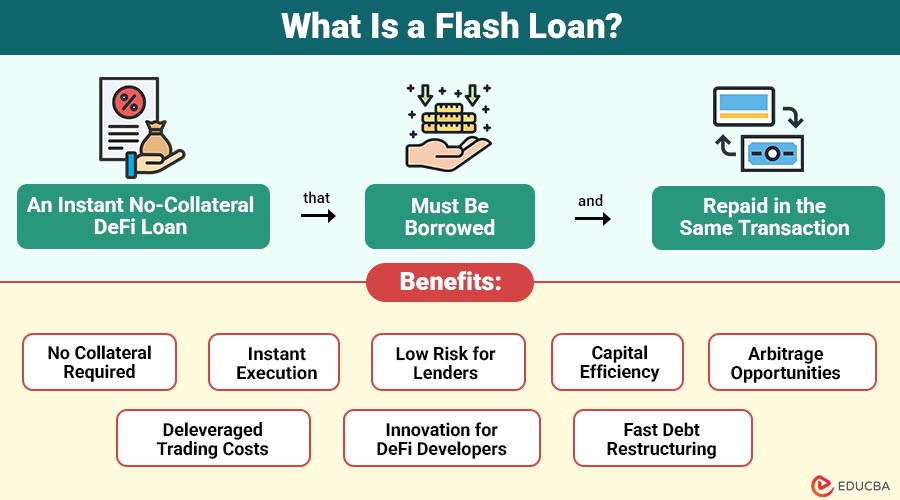
A flash loan is a type of instant, no-collateral loan in DeFi that must be borrowed and repaid within the same blockchain transaction. If the borrower does not repay, the system automatically cancels the entire transaction.
For example, a trader borrows $50,000 through a flash loan, uses it to buy a token at a low price on one exchange, sells it for a higher price on another exchange, repays the loan in the same transaction, and retains the profit.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Characteristics
- How Does it Work?
- Example
- Benefits
- Use Cases
- Platforms
- Risks Associated
- Attacks
- How to Stay Safe?
- Flash Loan vs. Traditional Loan
- Future Trends
Key Characteristics
- Atomicity: All steps (borrowing, executing actions, and repayment) occur in a single atomic transaction, enforced by smart contract logic.
- Capital efficiency: Users can access large liquidity pools instantly without locking their own funds.
- Programmability: Developers can create arbitrage bots, automated strategies, and custom smart contract operations.
- Democratized access: Anyone with technical expertise can utilize flash loans, regardless of financial background.
How Does a Flash Loan Work?
The mechanism relies on smart contracts programmed to enforce strict execution conditions. Below is a detailed explanation of the process.
1. Initiating the Flash Loan
A user, or more commonly, a smart contract, initiates the loan request with a DeFi protocol such as Aave, dYdX, or Uniswap.
The request specifies:
- The asset (e.g., USDT, ETH, DAI)
- The amount required
- The borrower specifies how they will use the borrowed funds.
No credit checks, collateral, or approvals are needed, as the atomic nature of blockchain transactions guarantees repayment.
2. Executing the Financial Operations
After approval, the user can execute the planned strategies.
Common operations include:
- Arbitrage across decentralized exchanges
- Swapping collateral on lending platforms
- Refinancing debt positions for lower interest rates
- Liquidating undercollateralized positions
- Rebalancing yield farming portfolios.
Developers must tightly program each of these steps within the same transaction.
Smart contracts ensure that any deviation or failure triggers a complete reversion.
3. Repayment
By the end of the transaction, the borrowed funds, plus the flash loan fee, typically ranging from 0.03% to 0.09%, must be returned to the liquidity pool.
If the borrower successfully repays the loan, the system finalizes the transaction.
If not, the blockchain cancels the transaction entirely, meaning:
- No assets move
- No loss occurs to the lender
- No partial execution takes place
- All actions revert to the initial state.
Flash Loan Example
Imagine a trader notices that Token A is priced at $100 on Exchange X but $105 on Exchange Y. To profit from this difference, the trader:
- Takes a flash loan of 1,000 Token A without providing collateral.
- Buys Token A on Exchange X at $100 each using the borrowed funds.
- Sells the same tokens on Exchange Y at $105 each.
- Makes a profit of $5 per token (total $5,000).
- Uses a portion of the profit to repay the flash loan plus fees within the same transaction.
- Keeps the remaining profit once the transaction batch completes.
If any step fails, like the price difference disappearing, the entire transaction automatically reverses, and the loan is never issued.
Benefits of Flash Loans
Here are the key benefits:
- No collateral required: Borrowers can access large amounts of capital instantly without having to pledge assets.
- Instant execution: The entire loan, strategy, and repayment happen within a single blockchain transaction.
- Low risk for lenders: Smart contracts enforce immediate repayment; if the borrower fails to repay, the entire transaction is automatically reversed.
- Capital efficiency: Traders and developers can execute high-value strategies without needing upfront funds.
- Arbitrage opportunities: Borrowers can profit from price gaps across exchanges using borrowed funds.
- Deleveraged trading costs: Users perform complex operations (such as refinancing or swapping collateral) without incurring interest over time.
- Innovation for DeFi developers: It enable the creation of advanced financial products, bots, and automated systems.
- Fast debt restructuring: Users can quickly refinance loans, swap collateral types, or close positions in a single atomic action.
Use Cases of Flash Loans
It supports a wide range of use cases within the decentralized finance sector.
1. Flash Loan Arbitrage
Arbitrage remains the most common application. Traders exploit price discrepancies across AMMs (Automated Market Makers) such as Uniswap, SushiSwap, Curve, and Balancer.
Types of Arbitrage
- DEX-DEX Arbitrage
- DEX-CEX Arbitrage
- Triangular Arbitrage involving multiple tokens
- Stablecoin Arbitrage in volatile pools.
Professionally developed bots execute arbitrage strategies within milliseconds, capitalizing on market inefficiencies.
2. Collateral Swapping
It enables borrowers to modify their existing collateral without requiring additional funds. For example, a user can replace volatile collateral with stable assets to reduce liquidation risk.
Protocols such as Aave offer built-in support for collateral swapping using flash loans.
3. Debt Refinancing
Users can refinance loans across multiple lending protocols to obtain lower interest rates or restructure obligations.
For example:
- Repay a loan on MakerDAO
- Transfer the position to Aave with a lower APY
- Utilize flash loan funds to complete the transition in a single transaction.
This automated refinancing mechanism offers strong financial optimization for borrowers.
4. Liquidations in DeFi
Liquidators use it to repay loans of undercollateralized borrowers and receive liquidation rewards.
This process strengthens the security and stability of lending protocols.
5. Yield Farming Optimization
It supports complex strategies such as:
- Rebalancing liquidity across pools
- Entering or exiting farming positions without new capital
- Optimizing APY by shifting assets dynamically.
Institutional-grade DeFi funds often incorporate flash loans into automated yield strategies.
Flash Loan Platforms
Several DeFi platforms provide flash loan services, each with unique features and liquidity capabilities.
1. Aave Flash Loans
Aave pioneered flash loans and remains the most widely used platform for this purpose. It offers:
- High liquidity
- Advanced developer documentation
- Flash Loan V2 and V3 frameworks
- Multi-chain support (Ethereum, Polygon, Avalanche, Optimism, etc.).
2. dYdX
dYdX operates as a decentralized margin trading platform with flash loan functionality, favored by developers and arbitrageurs who require quick and efficient execution.
3. Uniswap V3
Uniswap enables flash swaps, allowing users to withdraw assets and repay them in the same transaction.
Popular among high-frequency arbitrage traders.
4. Balancer
Balancer pools offer multi-token flash loans, making them well-suited for complex, multi-asset arbitrage strategies.
Risks Associated With Flash Loans
Despite their efficiency, they carry critical risks.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Hackers can exploit bugs in smart contracts, resulting in the loss of funds or enabling them to manipulate the protocol.
- Flash Loan Attacks: Hackers can use it to manipulate prices, exploit liquidity pools, or trigger protocol weaknesses within a single transaction.
- High Technical Complexity: Executing them requires advanced coding and blockchain knowledge, making them inaccessible to beginners.
- Market Manipulation: It can temporarily distort asset prices, affecting other users and creating instability in decentralized finance (DeFi) markets.
- Dependency on Liquidity: If liquidity pools lack sufficient funds, users may be unable to borrow the amount needed for arbitrage or strategies.
- Transaction Failure Risks: Any step that fails in the transaction process causes the entire transaction to revert, resulting in wasted gas fees.
- Network Congestion and Gas Fees: High network activity can cause such transactions to be slow or expensive, thereby reducing profitability.
- Protocol-Specific Risks: Different DeFi platforms have unique rules; misconfigurations or unfamiliar mechanisms can lead to unexpected losses.
Flash Loan Attacks
Flash loan attacks are a significant concern in DeFi because they enable attackers to manipulate the market on a large scale with minimal capital requirements.
Example: Oracle Manipulation Attack
- Attacker takes a flash loan to acquire a large volume of a token.
- Manipulates the token’s price in a low-liquidity pool.
- Uses inflated price data to borrow or drain another protocol.
- Repays the flash loan.
- Keeps the profit, often measured in millions.
Defensive measures include robust oracle design, improved liquidity safeguards, and advanced smart contract audits.
How to Stay Safe When Using Flash Loans?
Flash loan security necessitates adherence to best practices across development, operational execution, and risk mitigation.
- Prefer audited flash loan platforms such as Aave or Uniswap
- Avoid low-liquidity pools vulnerable to manipulation
- Test smart contract logic thoroughly using frameworks like Hardhat or Foundry
- Implement circuit breakers and slippage limits
- Monitor gas fees to prevent transaction failure
- Use MEV protection tools such as Flashbots or private mempools.
Flash Loan vs. Traditional Loan
| Feature | Flash Loan | Traditional Loan |
| Collateral Requirement | None | Mandatory |
| Repayment Period | Same transaction | Months/Years |
| Speed | Seconds | Days/Weeks |
| Accessibility | Open to all developers | Restricted, requires approval |
| Primary Use Case | Arbitrage, automation | Personal or corporate finance |
| Risk Type | Smart contract risk | Credit/default risk |
The Future of Flash Loans
Flash loans are poised to expand significantly as DeFi matures.
- Cross-chain: Enabled by interoperability protocols
- Layer-2: Lower fees, faster execution (Arbitrum, Optimism)
- Institutional APIs: For automated treasury management
- AI-Powered Arbitrage Engines: Dynamic execution using real-time data
- Insurance: New product categories to mitigate smart contract risk
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Do flash loans require any credit checks?
Answer: No. It do not require credit checks because repayment happens within the same transaction, eliminating credit risk for lenders.
Q2. Can beginners use flash loans?
Answer: Technically yes, but flash loans are complex and require strong knowledge of smart contracts, Web3 development, and DeFi platforms.
Q3. Are flash loans legal?
Answer: Yes. It is legal, but some flash loan attacks may exploit protocol weaknesses. These attacks are unethical but often fall into a regulatory gray area.
Q4. Do flash loans affect token prices?
Answer: They can. Large transactions can cause sudden price fluctuations in low-liquidity pools, potentially impacting market stability.
Q5. Do flash loans work in bull and bear markets?
Answer: Yes. Price discrepancies, liquidations, and refinancing opportunities exist in both market conditions, although arbitrage margins may vary.
Final Thoughts
Flash loans represent one of the most advanced innovations in decentralized finance, enabling instant, collateral-free borrowing and sophisticated financial operations. Their programmable, atomic structure makes them a powerful tool for arbitrage, debt restructuring, liquidation, and yield optimization. However, the complexity and risks associated with flash loans require strong technical expertise, robust security practices, and a deep understanding of DeFi mechanisms.
As the DeFi ecosystem continues to evolve, flash loans will remain central to liquidity optimization, automated trading, and financial engineering, shaping a future where capital efficiency and smart contract automation redefine global finance.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on flash loans helps you understand how instant, no-collateral borrowing works in DeFi and why it has become a powerful tool for traders and developers. Check our related articles to learn more about DeFi, basic blockchain concepts, and useful crypto trading strategies.
