What is Federated Learning?
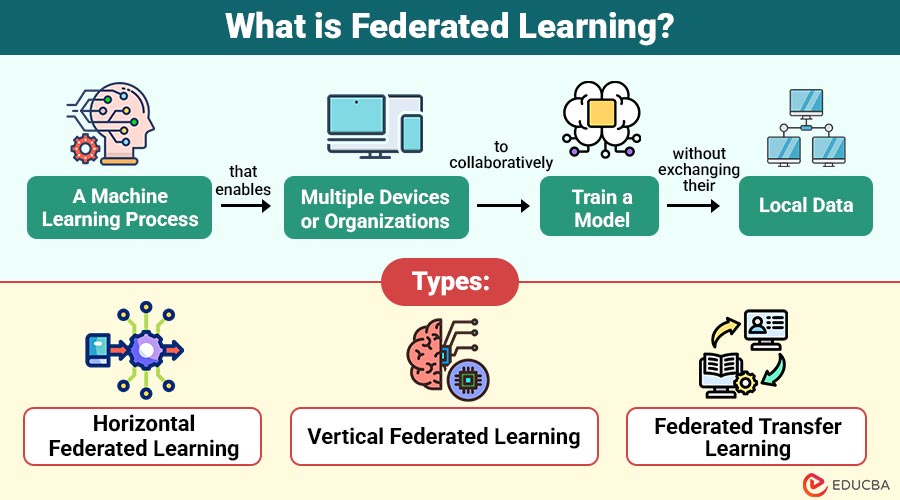
Federated Learning (FL) is a machine learning process that enables multiple devices or organizations to collaboratively train a model without exchanging their local data.
Instead of sending user data to a central server, the learning occurs locally on the device. Only the trained model updates (like weights or gradients) are sent back to a central server, which aggregates them to improve a global model.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Federated Learning enables model training across devices without sharing raw, sensitive data centrally.
- It ensures privacy, reduces bandwidth, and complies with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Real-world applications span healthcare, banking, mobile, retail, and autonomous vehicle industries.
- Despite benefits, FL faces challenges like communication overhead, data heterogeneity, and security threats.
How Does Federated Learning Work?
Let us break down the step-by-step process of how Federated Learning typically works:
1. Initialize a Global Model
A central server creates an initial machine learning model and distributes identical copies to all participating client devices for local training.
2. Local Training
Each device uses its private data to locally train the model locally, ensuring personal data never leaves the device and stays secure.
3. Send Updates
After training, devices send only the learned updates—such as gradients or model weights—to the server, without sharing their actual raw data.
4. Aggregate Update
The server collects updates from all devices and aggregates them, often using Federated Averaging, to refine and enhance the global model’s accuracy.
5. Repeat the Process
The server sends the improved global model back to the devices, and the training cycle repeats until the model achieves the desired performance across all participants.
Why is Federated Learning Important?
Here are the key reasons why FL is important:
1. Privacy Preservation
Federated Learning is perfect for industries where data sensitivity is a big concern, like healthcare and finance, because it preserves user privacy by keeping personal data on the user’s device.
2. Reduced Bandwidth Usage
Only model updates—not raw data—are sent to the server, significantly reducing network bandwidth usage and avoiding large-scale data uploads typically required in centralized machine learning systems.
3. Faster Personalization
Training models locally on user data enables them to quickly adapt to individual behavior, providing more accurate and customized results without compromising personal privacy or requiring central data storage.
4. Compliance with Data Regulations
Federated Learning supports legal compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by eliminating the need for centralized data storage, thus reducing regulatory risk for organizations.
Types of Federated Learning
Federated Learning can be distinguished into three types based on how data is distributed:
1. Horizontal Federated Learning
Data has the same feature space across devices but different user samples, enabling collaboration among institutions with similarly structured datasets.
2. Vertical Federated Learning
Data shares common users but has different feature spaces across parties, allowing organizations with distinct data types on the same users to collaborate.
3. Federated Transfer Learning
Used when both features and samples differ across parties, combining transfer learning and FL to enable collaboration with minimal data overlap.
Technologies and Frameworks for Federated Learning
Several open-source frameworks are available to experiment with FL:
1. TensorFlow Federated
An open-source framework by Google for simulating and experimenting with machine learning on decentralized data.
2. PySyft
Developed by OpenMined, PySyft enables privacy-preserving machine learning through Federated Learning, differential privacy, and encrypted computation.
3. Flower
A user-friendly framework supporting diverse platforms, ideal for both academic FL research and scalable production deployment.
4. FedML
A collaborative library supporting cross-device and cross-silo FL with tools for benchmarking, simulation, and deployment at scale.
Real World Examples
Let us look at some practical examples:
1. Smartphones
Google uses FL to improve services like Gboard, their keyboard app. It learns how users type without sending their keystrokes to the cloud.
2. Healthcare
Hospitals can collaborate on training models for disease detection (e.g., cancer prediction) without sharing sensitive patient records.
3. Finance
Banks can train fraud detection models on local transaction data, maintaining customer privacy.
4. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars can improve object recognition by learning from data captured locally on the road and then sharing improvements across a fleet.
Challenges of Federated Learning
Despite its benefits, FL is not without hurdles:
1. Communication Overhead
Frequent data exchange between many devices and the central server can cause latency, bandwidth consumption, and synchronization issues during model training.
2. Data Heterogeneity
Data varies across devices in size, quality, and distribution, making it difficult to build a well-generalized model that performs consistently.
3. Device Limitations
Edge devices often have limited CPU, memory, and battery life, which can restrict their ability to perform intensive local training tasks effectively.
4. Security Risks
Federated Learning remains vulnerable to model poisoning, backdoor attacks, and data inference if proper encryption and security protocols aren’t implemented.
Final Thoughts
Federated Learning offers a smart and secure way to train machine learning models while keeping data private and local. By allowing devices to collaborate without compromising user information, it represents a significant shift from traditional centralized AI approaches. Whether you are a developer, data scientist, or just a tech enthusiast, understanding federated learning helps you appreciate where the future of AI is heading—towards smarter, safer, and more responsible intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is Federated Learning safe?
Answer: Yes, it is safer than traditional learning, as data stays on the device. However, it must be combined with other security measures for full protection.
Q2. Do users need to approve federated learning?
Answer: It depends on the implementation. In many cases, it is done in the background with privacy protections in place.
Q3. Can Federated Learning work without the internet?
Answer: Not really. It requires a network to facilitate the exchange of model updates with the central server.
Q4. Which companies use Federated Learning?
Answer: Google, Apple, Nvidia, and OpenMined are prominent adopters of this technology.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Federated Learning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.