Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to Euler Method Matlab
To analyze the Differential Equation, we can use Euler’s Method. A numerical method to solve first-order first-degree differential equations with a given initial value is called Euler’s method. Euler’s method is the simplest Runge – Kutta method. The error to step corresponds to the square of the step size, and the error at a given time is corresponding to the step size is nothing but a first-order technique of an Euler’s method. Euler’s method is the most basic emphatic method for the numerical integration of ordinary differential equations. In this topic, we are going to learn about the Euler Method Matlab.
When we have a hard time-solving differential equation with approximating behavior Euler’s Method is used.
Syntax
The syntax for Euler’s Method Matlabisas shown below:-
T1=a:g:b;
(y(j+1) = y(j) + g * f(x(j),y(j)))
E=[T1' Y']
where –
a and b are the start and stop points, g is step size, E=[T1′ Y’] where T is the vector of abscissas and Y is the vector of ordinates.
How Does Euler Method Work in Matlab?
Steps for Euler method:-
Step 1: Initial conditions and setup
Step 2: load step size
Step 3: load the starting value
Step 4: load the ending value
Step 5: allocate the result
Step 6: load the starting value
Step 7: the expression for given differential equations
Examples
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1
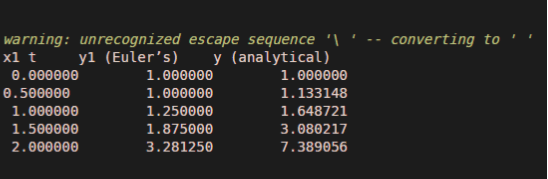
Let see an example for an initial condition of Euler’s rule; now we first we define the function has two variable so we should have two arguments. We have the first or initial condition, the value of y1 at x1 sub 0. Step size is 0.5, so we define the step for side edge, and since we have a tabular representation of the solution, we define the header of the table so we have here x1 of the left column, we will have the Euler’s solution in the middle and the analytical solution. We define the first row of the table because we know the initial value of the domain or initial start point of the domain; we have the initial value of y1, and we can compute the initial or the value of the solution function at the start of the domain. Now we take a loop that normally starts at the first point to compute z1 next points step size is h1, and also, we have the increment, or we all go through the solution up to the x1 and minus edge. Now inside the loop, we have this is Euler’s formula we have y1 of the current solution, and we have differential equation multiplied by an edge to compute the value of the next step, and here we compute bx1 as the next step. Finally, we print the result of the next step to take the loop for the other values, and finally, we end the loop.
Matlab code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
dy1 = @(x1, y1) x1*y1;
f1 = @(x1) exp (x1^2/2);
x0 = 0;
xn1 = 2;
y1 = 1;
h1 =0.5;
fprintf ('x1\ t\t y1 (Euler’s) \t y (analytical) \n')
fprintf (' %f \t %f \t %f\n', x0, y1, f1(x0));
for x1= x0 : h1 : xn1-h1
y1 = y1 + dy1(x1, y1)*h1;
d1 = x1 + h1;
fprintf ('%f \t %f \t %f \n ', d1,y1,f1(d1))
end;
Output:
Figure 1
So this is the solution at step size (h1) is 0.5; we notice that there is a big difference, especially in the final row. We can change a step size (h1) to see other better results.
Example #2
We take an example for plot an Euler’s method; the example is as follows:-
dy/dt = y^2 - 5t y(0) = 0.5
1 ≤ t ≤ 3 ∆t = 0.01
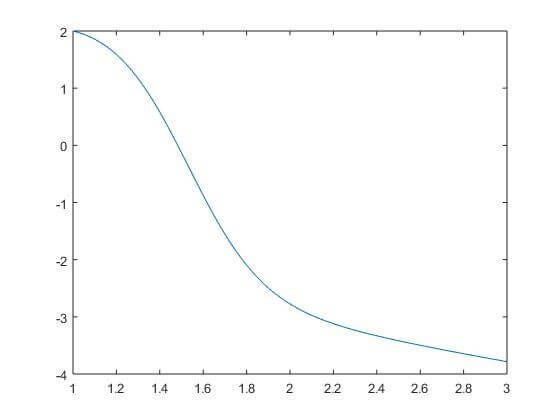
We have solved it in be closed interval 1 to 3, and we are taking a step size of 0.01. So we can take 200 points to reach 1 to 3 at a difference of 0.01. So let’s give it the value of t is equal to zeros from 201 to 1, we will compute y also at the corresponding points, points from 201 to 1. Now, we know that our initial points are 1 2, so we will say let us take our first value 1. Then for y, we are going to take the first value is 1. Now we just set variable I, we just take a loop, for I equal to 1 to 200, inside the loop for each subsequent value of t after the i-th value we add 0.01. Then for y take i plus 1 equals to we want previous y value ( y(i) ) and add the 0.01 in it, and we are going to look at an array of values, so I had put a dot before that multiplication sign y(i) then I have put a dot to the power of 2 then we are subtracting 4 times t(i) and then finally end the loop. Now we take a plot t y that is a plot(t, y).
Matlab code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
t = zeros (201,1);
y = zeros (201,1);
t(1) = 1;
y(1) = 2;
for i= 1 : 200
t(i+1) = t(i) + 0.01;
y(i+1) =y(i) + 0.01 .* (( y(i).^2) - 5.*(t(i)));
end
plot(t, y);
Output:
Figure 2
Conclusion
In this article, we saw the concept of the Euler method; basically, the Euler method is used to solve first-order first-degree differential equations with a given initial value. Then saw syntax related to Euler method statements and how it works in MatLab. Also, we saw some examples related to the Euler method statement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Euler Method Matlab. Here we discuss the concept of the Euler method; basically, the Euler method is used to solve the first order first-degree differential equation with a given initial value. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –