Updated March 21, 2023
Introduction to Distinct Keyword in SQL
Distinct command in SQL is used along with the Select command in order to retrieve only distinct or dissimilar values from a table. It is mainly used as a method to filter duplicate records and fetch only unique records from a given table, where there is a possibility of fields having multiple duplicate records. The Distinct keyword in SQL is used in the Select statement as ‘Select Distinct * from table_name’.
Syntax with Explanation
Let’s look at the distinct keyword syntax with an example:
Let’s have an employee table with three columns: empId, empname, and city, as shown below:
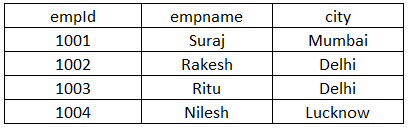
Select DISTINCT(column_name) from table_name;In our example above, we can see that the city is the column that has repetitive values, so we will put the city in place of column_name and employee in place of table_name. On running, it will return the unique city names, which are Mumbai, Delhi, Lucknow. If we remove a distinct keyword, it will retrieve four values instead of three.
Parameters used for Distinct Keyword in SQL
Let’s now look at the various parameters present in a distinct keyword. Below is the syntax for a distinct keyword.
Syntax:
Select DISTINCT(expressions) from tables [where conditions];- Expressions: In this, we provide the column names or calculations that we want.
- Tables: We provide the table names from which we want the records. One thing to note is that there should be at least one table name after from clause.
- Conditions: This is purely optional; we provide conditions when we want the data to first satisfy a particular condition for the records to get selected.
How to Use Distinct Keyword in SQL?
As we have already discussed the parameters. Let’s now learn where to use distinct keyword with the help of examples.
Let’s create a table CUSTOMER using DDL statements(data definition language) and then populate them using DML( Data manipulation language).
DDL (creating table):
CREATE TABLE customer ( customer_id int NOT NULL, name char(50) NOT NULL, city varchar2, state varchar2);This will create a table having four columns customer_id, name, city, and state. Now we will use DML statements to enter data in the table.
Insert Statements to enter data:
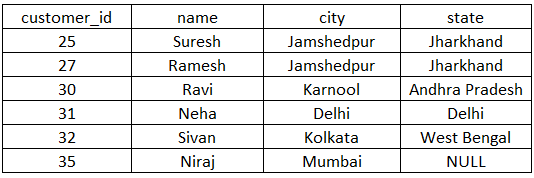
INSERT INTO customer (customer_id, name, city, state) VALUES (25, 'Suresh','Jamshedpur','Jharkhand');INSERT INTO customer (customer_id, name, city, state) VALUES (27, 'Ramesh', 'Jamshedpur','Jharkhand');INSERT INTO customer (customer_id, name, city, state) VALUES (30, 'Ravi', 'Karnool', 'Andhra Pradesh');INSERT INTO customer (customer_id, name, city, state) VALUES (31, 'Neha', 'Delhi', 'Delhi');INSERT INTO customer (customer_id, name, city, state) VALUES (32, 'Sivan', 'Kolkata', 'West Bengal');INSERT INTO customer (customer_id, name, city, state) VALUES (35, 'Niraj', 'Mumbai', 'Maharashtra');On executing the above statements, we get the below customer table.

Now let’s execute some queries using distinct queries to learn how to use distinct keyword.
1. First, we will find unique values in a column.
Query:
select DISTINCT state from customer order by state;We will get 5 values on executing the query as we have only five distinct states as Jharkhand is repeated twice. Since we have used ORDER BY so the result set will be sorted in ascending order. Below is the result set we should get on executing the query.

2. Secondly, we will unique values from multiple columns.
Query:
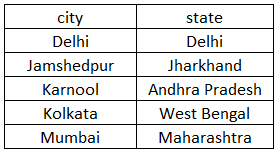
select DISTINCT city, state from customer order by city, state;The above query will return each unique city and state combination. In the above case, distinct applies to each field which is written after the distinct keyword. So we will have five pairs of city and state as there Jamshedpur city, which has been repeated twice. So we will have Jamshedpur along with Jharkhand once. The city will be ordered in ascending order. The result set on executing the query is shown below.
3. We will now see how the distinct keyword handles null values.
First of all, we will update a field in the state column as NULL and then use a distinct keyword to obtain the result set.
The update query to set NULL value in one of the fields of the customer table.
Query:
update customer set state=”” where customer_id = 35;This will insert a NULL value in the last field of the state column. The table will be updated as below.
Now, let’s execute a distinct keyword using a select query.
Query:
select DISTINCT state from customer order by state;On executing the above query, we will set five values as the distinct keyword considers NULL also a unique value. Jharkhand being repeated twice will only have one value in the result set. Since we have used the ORDER BY clause so the result set will be sorted in ascending order. Below is the result set we should see on executing the above query.

Conclusion
To conclude this article, we can say that a distinct keyword is a very powerful and useful keyword that is used in SELECT statements based on different conditions depending on business requirements to retrieve UNIQUE/DISTINCT values from a column or columns.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Distinct Keyword in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

