What is Delivery Trading?
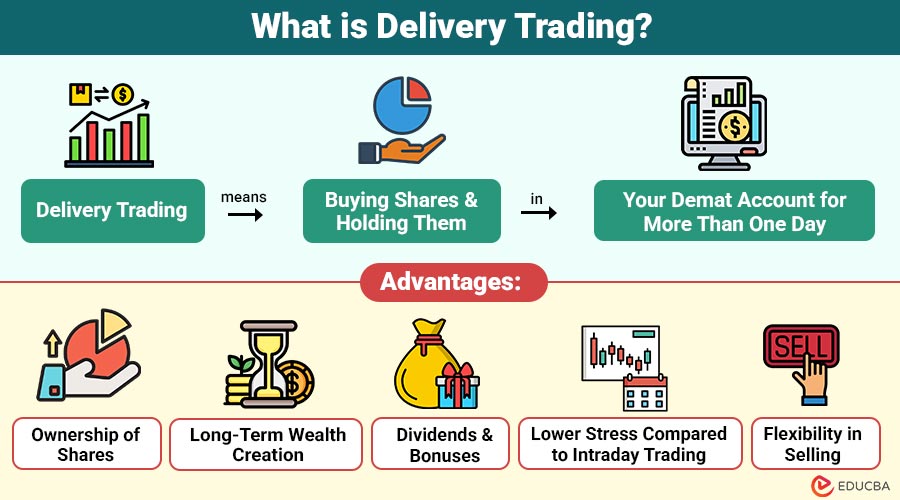
Delivery trading means buying shares and holding them in your demat account for more than one day. In this type of trading, you become the actual owner of the shares until you decide to sell them.
For example, if you buy 50 shares of TCS today and keep them for a few months, it is considered delivery trading because the shares are delivered to your demat account and not sold the same day.
Table of Content:
- What is Delivery Trading?
- How Delivery Trading Works?
- Advantages
- Delivery Trading vs. Intraday Trading
- Risks and Limitations
- Taxation and Regulatory Aspects
- Best Practices
- Common Mistakes
Key Takeaways
- Delivery trading allows investors to buy and hold shares for the long term, providing true ownership and potential wealth growth.
- Profits come from price appreciation, dividends, and bonus shares, while risks include market volatility and capital lock-in.
- Successful delivery trading requires proper research, portfolio diversification, and a disciplined, long-term approach.
- Avoid common mistakes, such as chasing trends, overexposure, and neglecting company fundamentals, to maximize returns and protect investments.
How Delivery Trading Works?
Delivery trading is a simple process where you buy shares and hold them in your demat account for as long as you wish. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Open Demat and Trading Account: To start delivery trading, you need both a trading account (for buying and selling shares) and a demat account (for storing the shares you own digitally).
- Choose the Shares to Buy: Research companies and select the shares you want to invest in based on performance, growth, and stability.
- Place a Buy Order: Log in to your trading platform and place a buy order for the chosen shares. Ensure you have sufficient funds in your trading account.
- Trade Settlement (T+2 Days): Once you purchase the shares, they will be credited to your demat account within two working days, following the T+2 settlement rule.
- Hold or Sell Anytime: After the shares are delivered, you can keep them for weeks, months, or years, and sell them later when the price increases.
Advantages of Delivery Trading
Delivery trading offers investors long-term growth opportunities and true ownership of shares, making it a reliable investment method.
- Ownership of Shares: When you buy shares through delivery trading, they are transferred to your demat account, giving you complete ownership. You can hold them as long as you want.
- Long-Term Wealth Creation: By holding shares for months or years, you can benefit from price appreciation and the power of compounding, building substantial wealth over time.
- Dividends and Bonuses: Shareholders in delivery trading receive dividends and bonus shares declared by companies, adding extra income and value to their investment.
- Lower Stress Compared to Intraday Trading: Delivery trading does not require constant monitoring or quick decisions, reducing the pressure and risk of daily market fluctuations.
- Flexibility in Selling: You can sell your shares whenever the market conditions are favorable, giving you control over your investment timing.
Delivery Trading vs. Intraday Trading
| Aspect | Delivery Trading | Intraday Trading |
| Definition | Buying shares and holding them in your demat account for more than one day. | Buying and selling shares on the same day to make quick profits. |
| Ownership | You become the actual owner of the shares. | Shares are not owned; trades are squared off the same day. |
| Timeframe | Can hold shares for months or years. | Must close positions before the market closes on the same day. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to long-term holding. | Higher risk due to market volatility in short-term trading. |
| Profit Source | Profit from price appreciation, dividends, and bonuses. | Profit comes only from short-term price movements. |
| Stress Level | Less stressful; no constant monitoring needed. | More stressful; requires active tracking and quick decisions. |
Risks and Limitations
While delivery trading is safer than intraday trading, it still comes with certain risks and limitations that investors should be aware of.
- Market Volatility: The value of your investment may decrease as share prices can vary due to market conditions, economic shifts, or the performance of the company.
- Capital Lock-In: Money invested in shares is tied up until you sell them, which can limit liquidity if you need cash urgently.
- Risk of Loss: Holding shares for an extended period does not guarantee a profit; poor company performance or market downturns can result in losses.
- Brokerage and Charges: Buying and selling shares involves brokerage fees and account maintenance charges, which can slightly reduce overall returns.
- Time Required for Research: Effective delivery trading requires proper analysis of companies and sectors, which can be time-consuming for investors.
Taxation and Regulatory Aspects
While delivery trading is safer than intraday trading, it still comes with certain risks and limitations that investors should be aware of.
- Market Volatility: The value of your investment may decrease as share prices can vary due to market conditions, economic shifts, or the performance of the company.
- Capital Lock-In: Money invested in shares is tied up until you sell them, which can limit liquidity if you need cash urgently.
- Risk of Loss: Holding shares for an extended period does not guarantee a profit; poor company performance or market downturns can result in losses.
- Brokerage and Charges: Buying and selling shares involves brokerage fees and account maintenance charges, which can slightly reduce overall returns.
- Time Required for Research: Effective delivery trading requires proper analysis of companies and sectors, which can be time-consuming for investors.
Best Practices for Successful Delivery Trading
Following best practices can help investors maximize profits and reduce risks in delivery trading.
- Conduct Proper Research: Analyze company fundamentals, financial performance, management quality, and industry trends before investing. Research helps in selecting reliable stocks for long-term gains.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Distributing investments among various sectors and companies can help minimize the risk of losing money due to a decline in a single stock or the overall market.
- Adopt a Long-Term Perspective: Delivery trading works best when you hold shares for months or years, allowing compounding and price appreciation to work in your favor.
- Monitor Performance Periodically: Keep track of company updates, quarterly results, and market news, but avoid reacting to short-term price fluctuations.
- Manage Risks Wisely: Set investment limits, avoid overexposure, and maintain a balance between safe and high-growth stocks to protect your capital.
- Use Reliable Trading Platforms: Select trustworthy brokers with user-friendly apps, low fees, and excellent customer support to ensure seamless trading and account management.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding mistakes can help investors protect their capital and achieve better long-term results in delivery trading.
- Chasing Short-Term Gains: Many traders attempt to capitalize on quick profits by tracking daily price movements. Delivery trading is for long-term investment, so focusing on short-term trends can lead to losses.
- Ignoring Fundamental Analysis: Investing without verifying a company’s financial health, management, and growth prospects can lead to suboptimal stock choices. Always research before buying.
- Overexposure to a Single Stock or Sector: Investing all your money in a single stock or sector increases risk. Diversification reduces potential losses if one stock performs poorly.
- Selling in Panic During Market Fluctuations: Price drops are normal in markets. Selling immediately during minor dips can result in missing long-term gains.
- Neglecting Tax and Regulatory Rules: Not considering capital gains tax, STT, or SEBI regulations can create legal issues and reduce net profits.
- Ignoring Brokerage and Charges: High transaction fees or account maintenance costs can erode profits if not closely monitored.
Final Thoughts
Delivery trading is a reliable method for building long-term wealth by owning shares and benefiting from price growth, dividends, and bonuses. While it involves some risks, such as market fluctuations and capital lock-in, careful research, diversification, and patience can help investors succeed. By following best practices and avoiding common mistakes, delivery trading offers a disciplined approach to investing, making it an ideal choice for those seeking stable and sustainable returns over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can delivery trading be done in the commodity or forex market?
Answer:- No, delivery trading is specific to stocks and shares, not commodities or forex.
2. Do delivery traders need to pay upfront for the full share price?
Answer:- Yes, the full amount is required to buy shares in delivery trading.
3. Is margin trading allowed in delivery trading?
Answer:- Typically, delivery trading requires full payment, and margin trading is generally not used.
4. Can delivery shares be pledged for loans?
Answer:- Yes, shares in a demat account can be pledged as collateral for loans.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on Delivery Trading helped you understand long-term investing. For more stock market tips, explore these related articles below:
