Updated July 18, 2023

Definition of Deferred Tax Asset
Deferred tax asset refers to the company that is created when there arises a difference in the timing of tax payment due to different accounting treatments by other laws, or it can also occur when an organization has overpaid the taxes by way of advance tax or tax deductions which results in less tax liability in future. The same is the opposite of deferred tax liability.
Explanation
A company must follow different laws like income tax, company law, etc. There might be differences in the accounting treatment under other laws, so while assessing under income tax law, the companies must follow the regulations and accounting treatment under income tax laws. So, the tax difference arises due to differences in accounting treatment. The tax difference may result in tax savings or tax increments, ultimately settling in the future. The deferred tax asset arises when the company has paid more taxes or some items resulted in lowering the tax in the future, for example, advance tax paid, prepaid rent, income due but not received, etc.
How to Create Deferred Tax Assets?
It is the tax difference that arises due to timing differences. For example, income as per books is $ 5,000, and income as per income tax laws is $ 6,000 difference is due to different depreciation policies by income tax and company law. So, the organization has to pay tax as per income tax laws as assessed in income tax, i.e., the organization has to pay more taxes now, the benefit of which is available to the organization in the form of deferred tax assets in the future. In short, if positive, the difference between tax as per income tax and as per books resulted in the creation of deferred tax assets.
Deferred tax asset is shown on the asset side of the balance sheet under-current assets.
Examples of Deferred Tax Assets
Following examples are given below:
Income as per Income Statement
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Net income before depreciation | $5,000 | $6,000 |
| Depreciation | $1,000 | $500 |
| Net Income after Depreciation | $4,000 | $5,500 |
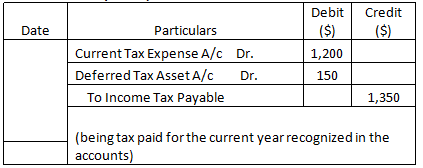
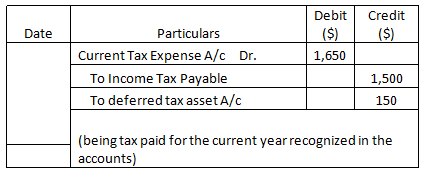
| Tax @ 30% | $1,200 | $1,650 |
Income As Per Tax Calculations
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Income before Depreciation | $5,000 | $6,000 |
| Depreciation | $500 | $1,000 |
| Income after Depreciation | $4,500 | $5,000 |
| Tax @ 30% | $1,350 | $1,500 |
Calculate the deferred Tax Assets and pass the journal entries for the same.
Solution:
Deferred Tax Assets are the difference between tax as per accounts and as per income tax calculation.
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
| Tax as per Income Tax Laws | $1,350 | $1,500 |
| Tax as per Accounts | $1,200 | $1,650 |
| Deferred Tax Asset | $150 | ($150) |
Journal Entries:
Journal Entries (Year 1)
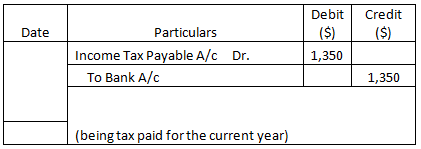
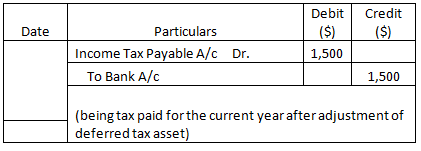
Journal Entries (Year 2)
Deferred Tax Assets Recognition
If an organization is currently in a loss-making position and has carried forward losses, it can offset these losses against future income. Therefore, the creation of a deferred tax asset is contingent upon the organization’s confidence in its ability to generate adequate profits in the future, enabling the utilization of the deferred tax asset.
Deferred Tax Assets Journal Entries
Journal entries for deferred tax assets.
- Creation of deferred tax asset.
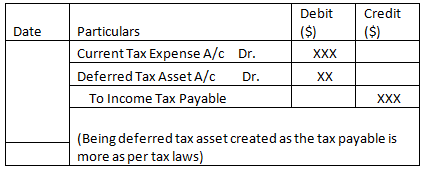
- Utilization of deferred tax in the future.
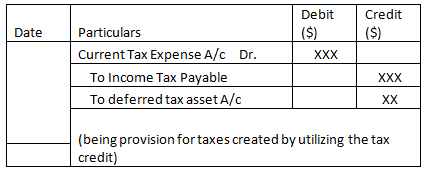
Importance of Deferred Tax Assets
- Deferred tax assets can be used to set off liability for the future.
- The benefit of overpaid taxes can be availed through deferred tax assets.
- It assures the organization that overpaid taxes can be utilized in the future.
- Arises only through the temporary difference; hence the liability remains unaffected.
- It helps to reduce future tax liabilities.
Deferred Tax Assets vs Deferred Tax Liability
- A deferred tax asset is a credit for the taxes already paid and to be less settled in the future, whereas a deferred tax liability is a credit availed or created for the taxes to be paid in the future.
- Deferred tax asset helps reduce future tax liability, whereas deferred tax liability increases future tax liability.
An example of a deferred tax asset is high depreciation per income tax and low per book.
An example of deferred tax liability recognizes reserves for doubtful debts as per income tax, whereas there is no recognition in accounts.
Advantages of Deferred Tax Assets
- Reduce future tax liability.
- Improves the transparency of calculation.
- The benefit of the overpaid tax credit can be availed.
- Calculations and credits ensure legal compliance as per different laws.
- Temporary imbalances can be settled legally.
Disadvantages of Deferred Tax Assets
- Lots of calculations, assumptions, and legal procedures are involved.
- There is no proof of virtual certainty that credit can be utilized in the future due to unpredictable positions.
- This creates complexity in the accounts as every year, two sets of books of accounts are to be maintained.
Conclusion
When a company has overpaid taxes or when temporary timing differences lead to the payment of excessive taxes in the current period, deferred tax assets can be created. The deferred tax asset differs from deferred tax liability as deferred tax liability results in the payment of more taxes in the future. The calculation also involves lots of complexities.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Deferred Tax Asset. Here we also discuss the definition and how to create deferred tax assets with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


