What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
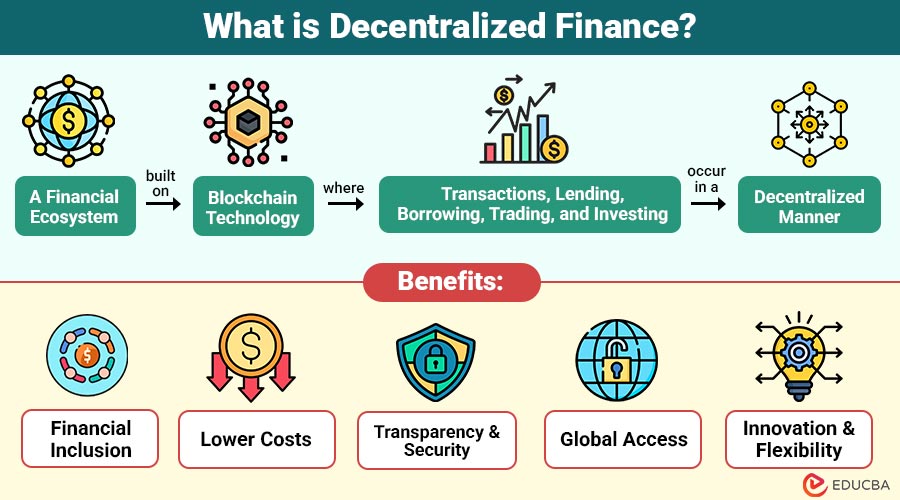
Decentralized Finance refers to a financial ecosystem built on blockchain technology, where transactions, lending, borrowing, trading, and investing occur in a decentralized manner. In contrast to conventional finance, which relies on centralized authorities, DeFi leverages smart contracts—self-executing contracts with terms of an agreement directly written into code.
Key features of DeFi include:
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Users do not need middlemen to conduct business.
- Transparency: A public blockchain records every transaction.
- Accessibility: Involvement is open to anyone with an internet connection.
- Programmable Finance: Smart contracts automate processes like lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Decentralized Finance enables global financial participation by removing intermediaries and empowering individuals with autonomous control over assets.
- Smart contracts automate transactions, lending, and trading, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and reduced reliance on traditional banks.
- Decentralized finance users must manage their private keys carefully, as losing access can result in permanent loss of funds.
- Continuous blockchain innovation and wider adoption suggest a promising future with accessible, secure, and innovative financial opportunities.
How Decentralized Finance Works?
DeFi operates on blockchain networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Solana, and Polygon. The ecosystem relies on smart contracts, which are automated protocols that execute predefined rules when certain conditions are met.
Here is a simplified workflow of DeFi:
- Users deposit cryptocurrency into a DeFi protocol.
- The protocol’s smart contracts manage these funds automatically.
- Users can lend or borrow assets, earn interest, or trade without relying on traditional banks.
- All transactions are transparent and immutable, ensuring security and trust.
Key Components of Decentralized Finance
Here are the main key components that make up the DeFi ecosystem:
1. Decentralized Exchanges
Platforms like Uniswap and SushiSwap enable direct crypto trading without centralized intermediaries, ensuring transparency, control, and accessibility.
2. Lending & Borrowing Protocols
Platforms like Aave and Compound let users lend for interest or borrow using crypto collateral, improving liquidity.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins like DAI, USDC, and USDT keep their value steady, making transactions in DeFi more reliable and less risky.
4. Yield Farming & Liquidity Mining
Users contribute liquidity to protocols, earning tokens or rewards that incentivize participation and stimulate decentralized finance ecosystem expansion.
5. Synthetic Assets & Derivatives
Platforms facilitate tokenized assets mirroring real-world instruments like stocks, commodities, or fiat, expanding decentralized financial market accessibility.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance
Here are the key benefits that DeFi offers:
1. Financial Inclusion
DeFi democratizes finance, enabling anyone with internet access to participate, even in regions with limited banking infrastructure.
2. Lower Costs
By removing intermediaries, transaction fees, and overhead costs are significantly reduced, benefiting both users and service providers.
3. Transparency and Security
All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, reducing fraud risk. Smart contracts ensure automated execution without human intervention.
4. Global Access
Users can access DeFi platforms 24/7, regardless of geographical restrictions. Cross-border transactions are faster and cheaper than traditional methods.
5. Innovation and Flexibility
DeFi lets developers build financial apps on blockchain, like lending platforms, decentralized insurance, and digital tokens.
Challenges of Decentralized Finance
Despite its promise, DeFi faces several challenges:
1. Smart Contract Risks
Vulnerabilities or bugs in smart contracts may cause fund losses, requiring secure protocols, thorough code audits, and continuous monitoring.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments worldwide continue developing decentralized finance regulations, creating significant legal ambiguities, compliance challenges, and uncertainties for platforms, users, and investors.
3. Scalability Issues
Networks like Ethereum experience high transaction fees and congestion, limiting participation, reducing efficiency, and discouraging widespread adoption of decentralized financial systems.
4. Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets remain inherently volatile, exposing DeFi users to high risks, unpredictable losses, and unstable investment returns across varying conditions.
5. User Responsibility
Decentralized Finance users manage their private keys independently; losing access permanently eliminates funds, contrasting traditional banks, which offer recovery options.
Real-World Examples
Here are some prominent examples demonstrating the power of decentralized finance:
1. Uniswap (DEX)
Bypassing conventional exchanges, Uniswap enables users to trade cryptocurrencies straight from their wallets using liquidity pools..
2. Aave (Lending & Borrowing)
Aave enables crypto holders to lend assets for interest or borrow funds using collateral, fully governed by smart contracts.
3. MakerDAO (Stablecoin Platform)
MakerDAO issues DAI, a decentralized stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, enabling users to borrow and trade without relying on traditional banking institutions.
4. Yearn.Finance (Yield Optimization)
Yearn.Finance automatically moves funds across lending protocols to maximize user yield, showcasing the potential of automated finance.
Future Trends
Here are some key trends shaping the future of Decentralized Finance:
1. Interoperable Blockchain Networks
Cross-chain protocols let assets move easily between different blockchains, making DeFi more flexible, liquid, and widely used.
2. Integration with Traditional Finance
Banks and financial institutions can integrate DeFi solutions, creating hybrid systems that strike a balance between decentralization, regulatory compliance, and enhanced financial services.
3. AI-Driven Smart Contracts
AI can improve DeFi smart contracts by enhancing investments, spotting fraud, and tailoring products for users.
4. Tokenization of Real-World Assets
Real estate, stocks, and commodities could be tokenized on DeFi platforms, offering innovative investment opportunities and expanding market accessibility.
5. Regulatory Clarity
Governments are expected to establish clear DeFi regulations that protect users while supporting innovation and ensuring sustainable, long-term growth within decentralized finance.
Final Thoughts
Decentralized Finance is transforming global finance by removing intermediaries, enhancing transparency, and providing worldwide access. It empowers individuals to manage finances independently. Although challenges like smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, and market volatility persist, continuous blockchain advancements and increasing adoption of DeFi solutions suggest a promising future, offering innovative, secure, and accessible financial opportunities for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is DeFi safe to use?
Answer: DeFi is generally secure if you use well-audited protocols and take personal security measures. However, risks from smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility remain.
Q2. Do I need cryptocurrency to use DeFi?
Answer: Yes. Most DeFi platforms require cryptocurrency like Ethereum or stablecoins to interact with their services.
Q3. Can DeFi replace banks completely?
Answer: Not entirely yet. While DeFi offers many banking alternatives, regulatory oversight and stability provided by traditional banks remain critical.
Q4. How do I start with DeFi?
Answer: Start by setting up a crypto wallet, acquiring cryptocurrency, and exploring popular DeFi platforms like Uniswap, Aave, or MakerDAO.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Decentralized Finance” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
