Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of DBMS 3 tier Architecture
DBMS is a very important tool to efficiently organize data in the database which provides simplified data access. The DBMS reduces redundancy and aids in data consistency. DBMS design is based on its architecture which is basically named as client/server architecture is applied to an agreement with an enormous number of PCs, database servers, web servers, and few other modules which are connected with networks.
DBMS architecture can be considered for types as a single-tier or multiple tiers but logically this architecture of database is defined to be of two types i.e. 2-tier architecture as well as 3-tier architecture. In 3-tier DBMS architecture, it includes an additional layer concerning the client and server where the client may not directly connect with the server.
DBMS 3 tier Architecture
The DBMS strategy is dependent on its client/server architecture to connect much quantities of PCs, database servers, web servers, and also other constituents available on the networks. Here, the client/server architecture includes several PCs with a workstation that are associated through the network. The DBMS architecture is determined by how users are related to the database to receive their request accomplished.
This design architecture assists in the scheme, develop, deploy and maintain the DBMS tool where it permits classifying the database software into distinct modules which may be self-reliantly improved, reformed, substituted, or altered. This process aids to comprehend the components of a database.
Since a database keeps serious information and also supports access data swiftly and firmly. Hence, choosing the accurate DBMS architecture benefits easy and efficient data management.
The DBMS can be normally considered to be of the following types:
1. 1-tier architecture: In this type of architecture, the database is made directly available to the user where it can be implemented and changes made here will directly get reflected on the database itself. It does not offer any convenient tool for the end operators.
This 1-tier architecture is applied for the creation of the native application, where program writers can directly link with the databases for a swift response.
2. 2-tier architecture: In this type of architecture can be said similar to the first one architecture as the normal client-server type where applications on the client-side can connect to the database directly at the server-side. The APIs like JDBC, ODBC are applied for this kind of 2-tier architecture. Here, the application programs and the user interfaces are executed on the client side.
Here, the server-side is intended to deliver the functionalities such as transaction management and query processing. For communicating with the DBMS, a connection is to be established by the client-side application with the server-side.
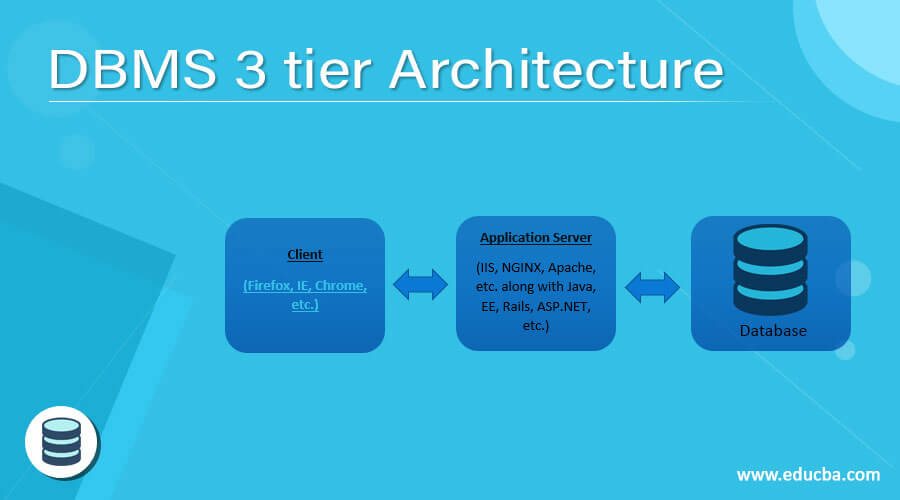
3. 3-tier architecture: Generally, there is another layer present in between the server and the client in the 3-tier architecture of DBMS where a direct connection with the server is made available. The application on the user end works together with an application server that additionally connects with the database system.
The end-user does not have any concern about the prevalence of the database further than the application server where even the database has no clue about the end-user outside the application. This type of 3-tier architecture is applied for a huge number of web applications.
Let us discuss some more details on the 3-tier architecture of DBMS:
DBMS 3-tier architecture is known to be the utmost prevalent client-server design in DBMS where the improvement and maintenance of logic, functional procedures, user interface, and data storage is performed autonomously as distinct modules. This 3-tier architecture includes a database server, an application layer, and a presentation layer which separates each other depending on the complexity of users and how the data available in the database is implemented.
We can say that 3-tier DBMS architecture is an extension lead of the 2-tier client-server architecture consisting of the following layers:
Presentation Layer: This is also called as User Tier layer because of the end-users function on this architectural layer of DBMS where they have no knowledge about any prevalence of the database outside this layer. Multiple views of the DBMS at this layer can be delivered by the application. Here, all views are produced by applications that exist in the application tier. Multiple-tier DBMS architecture is greatly modifiable since all of its modules are independent and maybe also altered similarly. For instance Tablet, PC, Mobile, etc.
Application Layer: This is a middle-tier layer where the application server resides along with the programs which access the database. This application layer at the tier offers an abstracted view of the database for a user so that the users at the end are not aware of the presence of the database away from the application. On the other end, the database tier does not have any idea of another user operator outside the application layer tier. Therefore, the application layer assembles in the mid and performs as a mediator between the database and the end-user.
This layer is also called the business logic layer processing functional logic, rules, and constraints before transitory data to the operator or down to the DBMS.
Database server: This is the Data-tier layer where the database is located along with its query handling languages. Here, we can further have the relations which define the data and their associated constraints at this tier level.
Following is a diagram illustrating the 3-tier architecture in DBMS:

Fig. DBMS 3-Tier Architecture
The aim to design a 3-tier architecture is as follows:
- For independence of program data
- Supporting features of DBMS
- Assisting multiple views of the data
- For not connecting the physical database and the user applications.
One of the biggest examples of 3-tier architecture in DBMS includes any huge websites on the internet.
Conclusion
The 3-tier DBMS architecture is implemented when there are big web application cases. As this architecture comprises an extra layer between the server and the client, therefore, the end operator has no knowledge about the presence of the database outside the application server. The application on the client end cooperates with this application server that additionally interconnects with the database system.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DBMS 3 tier Architecture. Here we discuss the definition, types, and layers of DBMS3 architecture. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

