Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2
The following article provides an outline for DB2 Version. DB2 is a relational database management system which is developed by IBM for efficiently and effectively managing, storing, retrieving and analyzing the data in the database. Most importantly, DB2 comes with the extended support for the XML which helps in implementing the non-relational database structures. DB2 also follows object-oriented style and supports many of its features. IBM had created DB2 for their personal use on their specific platform.
Later, after 1990, universal database called as UDB which is one of the DB2 server was created after deciding that the product should be able to run on any given authorized operating system such as windows, unix and linux platforms. Here we will see various versions of the DB2 and how it has evolved by adding new functionalities and supporting new programming languages over the period of time.
Various DB2 Versions
Given below are the various DB2 versions:
| Version | Code Name |
| Version 3.4 | Code language used to create this platform is Cobweb. |
| Version 8.1, Version 8.2 | Code language used to create this platform is Stinger. |
| Version 9.1 | Code language used to create this platform is Viper. |
| Version 9.5 | Code language used to create this platform is Viper 2. |
| Version 9.7 | Code language used to create this platform is Cobra. |
| Version 9.8 | Code language used to create this platform is PureScale. |
| Version 10.1 | Code language used to create this platform is Galileo. |
| Version 10.5 | Code language used to create this platform is Kepler. |
To check the version of DB2 on you LUW machine, you can type the following command on the terminal or console:
Code:
SELECT fixpack_num, service_level FROM TABLE (sysproc.env_get_inst_info()) as informationOfInstance
Output:
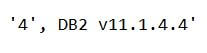
1. Viper
In between 2006 and 2007, IBM introduced a new platform called viper also called DB2 which can run o z/OS and many other distributed systems. Viper 2 proved to be the first to provide facility to store the relational data natively in XML format. Along with this, it brought many other advanced features like OLTP i.e Online Transactional Processing related improvements, data ware house and business intelligence for z/OS and many other improvements in self managing, exploitation with 64 bit data capability, self-tuning and enhancements in performance of stored procedures.
2. Viper 2
In late 2007 in the month of October IBM came up with another version of DB2 called viper2 for distributed platforms which is code name for DB2 9.5 which brought many advancements in agile XML development, simplification in management and reliability for critical business operations.
3. Cobra
IBM came up with a new version called cobra in the month of June in 2009 which is the codename for DB2 9.7 for LUW which introduced new features of temporary tables, compression of data for database indexes and storage of objects which are very large. Cobra also came up with support of various XML data partitioning techniques like range partitioning, hash partitioning and multidimensional clustering. Because of these features one can easily work with XML in environment of data warehousing.
Many additional functionalities for users working with oracle database were also introduced in DB2 which included PL/ SQL syntax, commonly used syntaxes of SQL, scripting syntax and oracle database’s datatypes. Microsoft SQL server and oracle database users find it very familiar for using DB2 because of the exhibition of behavior of concurrency model.
4. Purescale
IBM launched a new DB2 version release in 2009 in the month of October named DB2 purescale which is the cluster database mainly designed for the non-main frame platforms which is mostly suitable for OLTP transactions that is online transaction processing. The design of the DB2 purescale is based on the DB2 data sharing with parallel sysplex on the main frame platforms. The architecture of DB2 purescale is completely fault-tolerant and has the storage of shared disk. This version of DB2 provides automatic load balancing and complete availability which can be extended upto 128 servers of database.
IBM also announced in 2009 that the server of DB2 can be used as an engine in MySQL, The DB2 system can be used natively for the users using IBM I OS by using the System I platform while other operating systems can use this by using the MySQL interface. DB2 comes in-built for the users of System and all its prior versions like AS/400 and system/38 which makes the use of triggers, journaling and other features very handy.
5. Galileo
IBM introduced to a new version of DB2 in early 2012 which was DB2 10.1 and the code name for this version was Galileo which can be used for windows, Linux and Unix platforms. One of the most promising features that became available was fine-level control over the database in which we can restrict the access on row level and column level. Besides this, Galileo came up with lot many new data management capabilities like multi-temperature management of the data which helps in deciding whether the data is hot or cold which means how often the data is accessed and accordingly we can decide the storage of the data. Another feature of Galileo includes the adaptive compression capability.
6. Kepler
IBM announced a new version of DB2 named Kepler in June 2013 which is the code name for DB2 10.5.
7. Other Versions
IBM launched a new version of DB2 distribution system for hadoop in the month of April 2016 to June 2016 which was named as DB2 LUW 11.1. IBM also relaunched a version of DB2 and dashDB in the middle of 2017 year and named them to DB2. An artificial intelligence enabled DB2 version was released by IBM on June 27 in 2019 which introduced many new performance improvements in query building and execution as well as features which can help in creating the applications which are enabled with AI.
Conclusion – DB2 Version
IBM had created relational database management system which can run on any operating system which is officialized and named this DBMS as DB2. There are different versions of DB2 DBMS which are released by IBM. In each version launched by IBM, new functionalities and features have been added to make it more advanced.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 Version. Here we discuss the introduction and the various DB2 versions for the better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

