Updated March 6, 2023

Definition of DB2 LUW
Basically, DB2 is a family of database management systems, in which we manage the database operation as well as store the data in huge amounts as per the user requirement. But some database application works on the specific platform this is the disadvantage of that system but DB2 luw is a cross-platform that means it is suitable for Linux, UNIX and Windows operating systems that we called as DB2 luw.DB2 luw provides some additional features such as it supports the object-relational features and non-relational data structure that normally we called JSON and XML. The DB2 luw is the most common server that operates on different operating systems.
Syntax:
Normally DB2 luw is cross-platform and it supports the SQL statement, so there is multiple syntaxes available for multiple operations, so in this article, we generally talk about the aggregation functions because select statement works on luw platform and we here implement an aggregate function with the select statement as follows.
select specific function name(specified colm name) from specified table name;
Explanation
In the above syntax, we select a statement with an aggregate function because select supports the DB2 luw command server. Here specified function name means aggregate function name that we need to apply, specified colm name means actual column name from the specified table that means user-created table.
How DB2 luw works?
Now let’s see how luw works in DB2 as follows.
To see more about the working of DB2, we need to painstakingly contemplate and what are the various components that are helping to the working of DB2. Allow us to begin with the first, and that is table spaces. The table space is a capacity structure that contains tables, records, objects, and so forth the information in the data set is organized into a consistent gathering and it supports speedy recoverability of the information base and guarantees ideal space usage.
The following component is a schema which is a named object in the database and that is ordered sensibly. This component shapes the consistent design of the information stockpiling. Another component file, which is a bunch of pointers alluding to the columns of the table. These records can be special or non-novel or might be bunched or non-grouped.
So now we have perceived what the components are, DB2 works by recovering information through SQL questions from the table spaces. The outlines and files are the components that empower the simple recovery of information from the data set.
Now let’s see how the select statement works in DB2 luw as follows.
The select-statement is the type of query that can be straightforwardly determined in a DECLARE CURSOR statement or arranged and afterward referred to in a DECLARE CURSOR statement. It can likewise be given using dynamic SQL statements utilizing the order line processor (or comparative devices), causing an outcome table to be shown on the client’s screen. Regardless, the table indicated by a select-statement is the consequence of the fullselect.
A common table expression that we also called a typical table expression, which permits characterizing an outcome table with a table-name that can be determined as a table name in any FROM clause of the fullselect. Different normal table statements can be determined after the single WITH keyword. Every regular table expression determined can likewise be referred to by name in the FROM clause of ensuing normal table expression.
In the event that the list of columns is determined, it should comprise of however many names as there are columns in the outcome table of the fullselect. Every section name should be special and unfit. In the event that these segment names are not indicated, the names are obtained from the select rundown of the fullselect used to characterize the normal table expression.
In the event that the fullselect of a common table expression contains an information change-table-reference in the FROM condition, the regular table expression is said to alter information. A common table expression that changes information is constantly assessed when the proclamation is handled, whether or not the normal table articulation is utilized elsewhere in the explanation. On the off chance that there is, in any event, one common table expression that peruses or alters the information, all basic table articulations are handled in the request in which they happen, and every basic table articulation that peruses or changes information is totally executed, including all limitations and triggers, before any resulting regular table articulations are executed.
Examples
Now let’s see the different examples of select statement and aggregate functions as follows.
First, create a new table as follows.
create table comp_emp (cemp_id int not null, cemp_name varchar(30) not null,
cemp_address varchar(30) not null, cemp_salary int(256), primary key(cemp_id));
Explanation
Now insert some records into the comp_emp table by using insert into a statement, after insertion operation table content is shown in below screenshot as follows.
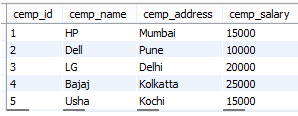
select * from comp_emp;
Now perform aggregate functions as follows.
select count(*) from comp_emp;
Explanation
In the above example, we use the select statement and count function to know the number of rows from the comp_emp table. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
![]()
Suppose we need to calculate the sum of the cemp_salary column at that time we can use the following statement as follows.
select sum(cemp_salary) from comp_emp;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement and sum function to calculate the sum of the salary column. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
![]()
So in this way, we can use different aggregate functions with select and where clauses.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Now let’s see the advantages of DB2 luw.
1. It has solid reliability.
2. It is a highly manageable database.
3. It provides a cross-platform database.
4. It supports the SQL statement.
5. It provides an automatic reporting system.
6. It provides the error handling facility to the user.
Now let’s see the disadvantages of DB2 luw.
1. There are problems with search engines.
2. It required a huge memory.
3. GUI is not user-friendly as compared to other databases.
4. We need to improve the documentation in DB2 luw.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn the DB2 luw. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of DB2 luw, as well as how it works and we also see different examples of DB2 luw. From this article, we learned how and when we use the DB2 luw.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 LUW. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, and parameters, How DB2 LUW works? examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

