Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of DB2 List Databases
DB2 provides the different kinds of commands to the user, list databases is one of the commands that are provided by the DB2. By using DB2 list databases command we can list all databases from the local server. Basically, the database directory is used by many people every day. The database directory stores the information for connecting to databases. Sometimes users need to list all databases from the local system or remote system. At that time we used the DB2 list databases command. When we create the database then all details about the database, storage devices, configuration file, and tables are stored in the database directory.
Syntax:
db2 list database directory
Explanation:
In the above syntax, we use the list database command to list all databases from the local system.
How to list databases in DB2?
Now let’s see how the list command works in DB2 as follows.
Basically, the list database command is used to list all content of the system database directory that we need. If we specify the path then it returns the content of the local database directory. When we need to list the content of the database at that time we need to consider some parameters as follows.
- Scope
On the off chance that this command is given without the ON path boundary, the framework data set registry is returned. This data is something similar at all data set allotments.
On the off chance that the ON path boundary is indicated, the nearby data set index on that way is returned. This data isn’t something very similar at all data set parts.
- Authorization
We don’t require any authorization; we directly fetch the content from the system database directory because directory operation works locally only.
- Database Alias
The database alias is used when we create a database or cataloged it. If we don’t specify the alias then the list database command uses the database name parameter when the database was recorded.
- Database name
This is used to database name when we created a database or we can say that when the database was recorded.
- Local database directory
The local database directory means where we stored the database. This field is filled in just if the framework database index has been checked.
- Database directory
The database directory specifies where the database is stored. This field is filled in just if the local database directory has been filtered.
- Node name
This name is used for remote nodes. This name compares to the value entered for the node name parameter when the data set and the hub were listed.
- Database release level
The release level of the database manager can work on the information base.
- Comment
Any remarks related to the database that was entered when it was indexed.
- Directory entry type
The specified location of the database:
- A Remote entry is used to show where the database is located.
- An Indirect entry is used to show the database is stored on the local system. Databases that are placed on a similar node as the system database directory are thought to in an indirect way reference the home section (to a nearby data set registry) and are viewed as backhanded passages.
- A Home entry demonstrates that the database directory is in a similar way as the neighborhood information base registry.
- An LDAP entry shows that the database location records are put away on an LDAP server.
All entries of the system database directory are either remote location off or backhanded. All entries from the local database indexes are recognized in the system database set registry as aberrant sections.
Authentication
The validation means authentication type listed at the client-side.
Catalog database partition number
Determines which hub is the catalog database partition. This is the data set parcel on which the CREATE DATABASE order was given.
Database partition number
Determines the number that is relegated in db2nodes.cfg to the hub where the order was given.
Alternate server hostname
Determines the hostname or the IP address for the substitute worker to be utilized when there is correspondence disappointment on the association with the information base. This field is shown distinctly for the system database directory.
Alternate server port number
Indicates the port number for the alternate server to be utilized when there is correspondence disappointment on the association with the database. This field is shown distinctly for the system database directory.
Alternate server node name
On the off chance that the registry section type is LDAP, indicates the node name for the alternate server to be utilized when there is correspondence disappointment on the association with the database.
Alternate server gateway node name
On the off chance that the directory entry type is LDAP, indicates the entryway hub name for the substitute door to be utilized when there is correspondence disappointment on the association with the database.
Utilization notes
Despite the DB2 LDAP CACHE random variable setting, if utilizing the LIST DATABASE DIRECTORY or the LIST NODE DIRECTORY commands, the list of specified local database set and node entries are read from the LDAP worker.
There can be a limit of eight opened database catalog examines per measure. To beat this limitation for a cluster record that issues in excess of eight LIST DATABASE DIRECTORY commands inside a solitary Db2, convert the clump document into a shell script. The “db2” prefix creates another Db2 meeting for each order.
Examples
Now let’s see the examples of list commands in DB2 as follows.
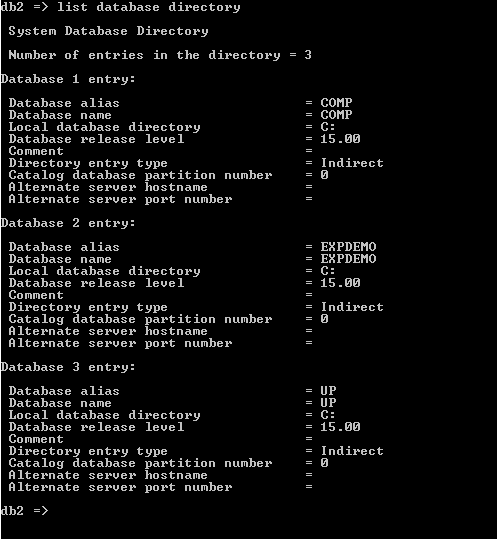
list database directory
Explanation
In the above example, we use the list database command to list out the all content from the system directory. After executions of the above command, it shows all databases one by one that is recorded. It shows all detailed information about the database. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn the DB2 list database. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of DB2 list database command, as well as how it works and we also see different examples of DB2 list database. From this article, we learned how and when we use the DB2 list database command.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 List Databases. Here we discuss definition, syntax, and parameters, How to list databases in DB2? examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –