Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2 Date Functions
DB2 date functions are the scalar functions provided by IBM to handle and manipulate the date values in the DB2 database. The availability of these date and time functions in DB2 makes it very effective and easy to manipulate the date and time-related values. In this article, we will have a look at some of the date functions that are available in DB2 and which can be used for our convenience. Firstly, we will have a look at the basic handling of the current date and time retrieval in DB2. Further, we will study different readymade functions related to date available in the DB2 database.
Retrieve current date and time values in DB2 –
There are certain in-built DB2 registers that help us to retrieve the date-related values for the current period. For example, if we want to retrieve the current value of date then it can be retrieved by using the following query statement –
SELECT current date as "Today's date" FROM sysibm.sysdummy1 ;
The output of the execution of the above query statement gives out the following resultant value of the current date value as shown in the below image –

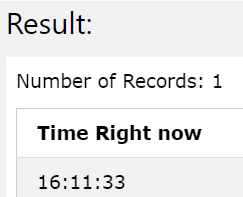
Now, we will try to retrieve the current time value which can be retrieved in DB2 by using the following query statement –
SELECT current time as "Time Right now" FROM sysibm.sysdummy1;
The output of the execution of the above query statement gives out the following resultant value of current time value as shown in the below image –
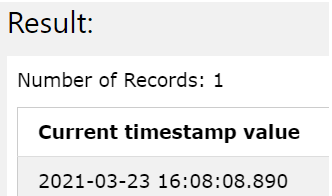
We can make use of the following query statement to get the current timestamp value in DB2 –
SELECT current timestamp as "Current timestamp value" FROM sysibm.sysdummy1;
The output of the execution of the above query statement gives out the following resultant value of the current timestamp value as shown in the below image –
Let us now have a look at some of the additional date-related functions that are available in DB2. The purpose and description for each of the functions are also specified in the following table showing date functions of DB2.
| Function | Description | Example | Output |
| ADD_MONTHS | This function is used to add the certain number of months in the expression and returns the value that is in datetime format having newly added months as specified in arguments. | SELECT DATE_ MONTHS (“2021-01-15”, 10) as “ADD_MONTHS output”;
|
|
| ADD_DAYS | This function is used to add a certain number of days in the specified expression and returns the value that is in datetime format having newly added days as specified in arguments. | SELECT ADD_DAYS(“2021-01-15”, 50) as “ADD_DAYS output”;
|
|
| ADD_MINUTES | This function is used to add certain number of minutes in the specified expression and returns the value that is in datetime format having newly added minutes as specified in arguments. | SELECT ADD_ MINUTES (“2021-01-15”, 1500) as “ADD_MINUTES output”;
|
|
| ADD_HOURS | This function is used to add certain number of hours in the specified expression and returns the value that is in datetime format having newly added hours as specified in arguments. | SELECT ADD_HOURS (“2021-01-15”, 55) as “ADD_HOURS output”;
|
|
| ADD_YEARS | This function is used to add certain number of years in the specified expression and returns the value that is in datetime format having newly added years as specified in arguments. | SELECT ADD_YEARS (“2021-01-15”, 5) as “ADD_YEARS output”;
|
|
| ADD_SECONDS | This function is used to add certain number of seconds in the specified expression and returns the value that is in datetime format having newly added seconds as specified in arguments. | SELECT ADD_ SECONDS (“2021-01-15”, 50000) as “ADD_SECONDS output”;
|
V |
| DAY | This function is used to retrieve the day value from the specified date-time value. | SELECT DAY(‘2021/03/15’) AS ” Day value of month”;
|
|
| AGE | This function is used to retrieve the age calculated between the current timestamp value and the specified argument and is returned in terms of years. Months and the total number of days between the two timestamps. |
SELECT AGE (‘2011/03/15’) AS “age”;
|
|
| DATE_PART | This function helps us to retrieve a particular portion of the data from the passed date time value argument. | SELECT DATE_PART (yy,’2017‑01‑28′) AS DatePartValue;
|
|
| DAYOFMONTH | This function helps us to retrieve the integer value ranging between 1 to 31 which stands for the day of the month from the specified datetime value. | SELECT DAYOFMONTH ( ‘2017/09/18’) AS DayofMonth; | |
| DAYNAME | This function helps us to retrieve the name of the day for the specified timestamp in form of the character string. The day portion from the specified expression is based on the locale name. The day portion can also be specified by using the CURRENT LOCALE LC_TIME which is a special register. | SELECT DAYNAME(“2021-03-15 02:30:22”) as “Day of the date” ;
|
|
| DAYOFYEAR | This function is used to retrieve the day value of the year which is specified. | SELECT DAYOFYEAR( ‘2021/03/12 08:36’) AS “day of year”;
|
|
| DAYOFWEEK | This function helps to retrieve the day value between 1 to 7 where 1 stands for the first day of the week, 2 for Tuesday, and so on. | SELECT DAYOFWEEK (“2021-01-15”) as “Week of the date”;
|
|
| DAYOFYEAR | It helps to retrieve the day of the year as specified in the arguments. | SELECT DAYOFYEAR (“2021-01-15”) as “Day of the date”;
|
|
| DAYOFWEEK_ISO | It helps to retrieve the day of the year passed in the specified arguments which returns an integer value ranging between 1 to 7 where 1 stands for Monday while 7 for Sunday. | SELECT DAYOFWEEK(“2021-03-15 09:34:21”) as “Day of week in integer”;
|
|
| DAYS | This function helps to get the integer value of the specified date format. | SELECT DAYS(‘2021/03/12 08:36’) AS “current days”;
|
|
| HOUR | It helps in retrieving only the hour part from the specified value. | SELECT HOUR( ‘2021/03/12 08:36’) AS “current hour”;
|
|
| MINUTE | This function retrieves the minute value from the specified date value. | SELECT MINUTE(‘2021/03/12 08:36’) AS “current minutes”;
|
|
| NOW | This function returns the timestamp value that depends on the execution of that timestamp function and the SQL statement which is executed by the currently specified parameter. | SELECT NOW() as “current timestamp value”;
|
|
| MONTHS_BETWEEN | This function helps to retrieve the number of months that are estimated between the two expressions specified in the arguments. | SELECT MONTHS_BETWEEN ( ‘2021/03/15’, ‘2011/03/15’) AS “Month difference” ;
|
|
| QUARTER | This date function retrieves the quarter in which the specified date is present. | SELECT QUARTER (‘2021/03/15’, ‘2011/03/15’) AS “Date interval in quarters”;
|
|
| TIMESTAMP_FORMAT | This function helps to retrieve any particular value of the timestamp in any format that we wish. | SELECT TIMESTAMP_FORMAT(“2021-03-15”, “%Y”) as “Year of the date”;
|
|
| TO_DATE | This function is used to get the timestamp value from the specified character string. | SELECT TO_DATE(“2021-01-15”) as “Date value”;
|
|
| TO_CHAR | This function helps in getting the character representation of the timestamp value that is passed as the argument. It is also used for avoiding implicit conversions in some cases. | select to_char(“2021-01-15″,”YYTH MONTH YEAR”) as “modified date”; | |
| TIMESTAMPDIFF | This function is used to retrieve the difference between the two timestamp values in the format which is specified in the first argument and the difference between the two timestamp values is specified in the second argument that is converted to CHAR value. | SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF (quarter,’2021/03/15′, ‘2011/03/15’) AS “Date interval in quarters”;
|
Conclusion
There are many date functions available in DB2 RDBMS provided by IBM which can be used to handle date and time efficiently and effectively.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 Date Functions. Here we discuss introduction, syntax, and many date functions available in DB2 RDBMS. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

