Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2 alter column.
DB2 Alter Column is used to modify the definition and the structure or behavior of the column that already exists in one of the tables of the database. Most of the time, the business requirement keeps changing, and with new changes that need to be incorporated, we may need to add or modify the existing columns present in the table. The modification of the column is also possible in case if the datatype of the column or the size of the column is incompatible or incapable of storing the type and size of value that we want to store in it. In other cases, we may need to change the default value that is assigned to the particular column of the table.
For all these scenarios, we can make use of the ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN statement to modify the definition of the column. In this article, we will study the general syntax of the ALTER COLUMN statement in DB2 and also study with the help of examples to see how we can update the columns in the database.
Syntax
The syntax of ALTER COLUMN statement is as shown below –
ALTER TABLE name of the table
ALTER COLUMN name of the column
SET type of modification to be made
In the above syntax, we have three different things to specify in the ALTER COLUMN statement. The following list gives a detailed description of all the three things to be mentioned inside the ALTER COLUMN statement –
Name of the table – This is the table name inside which the column to be modified exists in the database.
Name of the column – This is the column name which we wish the definition to be modified. This column can be of any data type and size and can have or not have the default value assigned to it.
Type of modification of table – The column may be modified for multiple reasons, like updating the records with a default value and having the new value as the default value for the column. We can also change the data type, size of the column, and the data type of the existing column in our D/b2 database.
Examples
Let us now study how we can make use of the ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN command statement in DB2 with the help of certain examples.
Consider a table named customers, which has the following columns in it, and the structure of the table and the types and names of the columns are as shown below after describing it –

Example #1 – Increasing the size of the column
Now suppose that we modify the column email_id and try to increase its size to 100. For this, we will require to use the ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN command, and our query statement will now look somewhat as shown below –
ALTER TABLE customers ALTER COLUMN email_id SET DATATYPE VARCHAR(100);
The execution of the above query statement will change the structure and definition of the email_id column to VARCHAR datatype with the size of 100. If we now try to describe the table customers, it will give the following output as shown in the below image –

We can observe from the above image that the email_id column has now got extended its size to 100 characters and has the VARCHAR data type.
Example #2 – Change the datatype of the column
Now, there is a requirement that we need to store the mobile number in the column with the name mobile_number, but the data type of that column should be an integer and not the characters or varchar. This can also be done by using the ALTER COLUMN statement along with the SET DATATYPE modification clause. Our query statement will become somewhat as follows as we want the new datatype of the mobile number column as an integer –
ALTER TABLE customers ALTER COLUMN mobile_number SET DATATYPE NUMBER(10);
The execution of the above query statement gives out the following output after describing the customer tables, which shows that the mobile number column has changed its datatype from varchar to number, which will now store an integer and not the string –
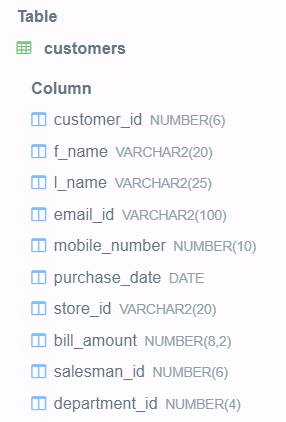
The above example demonstrates that we can convert the datatype of the column from the existing datatype to any of the alternative datatypes. In such a case, we have to make sure that the data type in which we are converting the column should be compatible with the original one so that all the existing values of that column can be easily converted and stored in the same column with the compatible datatype.
Example #3
We can even change the AUTOINCREMENT property or the column’s DEFAULT value by using the ALTER COLUMN command. Let us consider the same example of the customer’s table, which contains the column name purchase date. Suppose that we have to change the default value of that column to the current timestamp value. In such a case, we can make the use of following query statement –
ALTER TABLE customers ALTER COLUMN purchase_date SET DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE;
The output of the above query statement is as shown below –
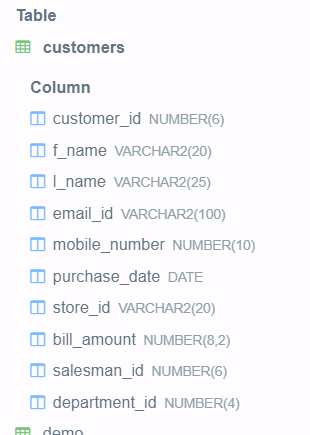
Conclusion – DB2 alter column
Due to changing business requirements, there might be a need to extend the size of the particular column stored in the database or change the type of value stored in that column. There is often a necessity to provide the default value or modify it later so that the NULL value does not get stored in the column if a value is not specified while insertion. All this can be done by using the ALTER COLUMN statement.
We can make the use of ALTER COLUMN command along with the ALTER TABLE statement that is present in DB2 to modify and change the structure and definition of the particular column that exists in the table. We can either change the column’s datatype to the size of the column or even the default value assigned to the particular column, which can be its modifying type of column. All this can be done by using the ALTER COLUMN statement in DB2 RDBMS. We have to specify the table name column name and the modification required for that column in the query statement of ALTER COLUMN.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 alter column. Here we discuss the general syntax of the ALTER COLUMN statement in DB2 and also study with the help of examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

