What is Data Stewardship?
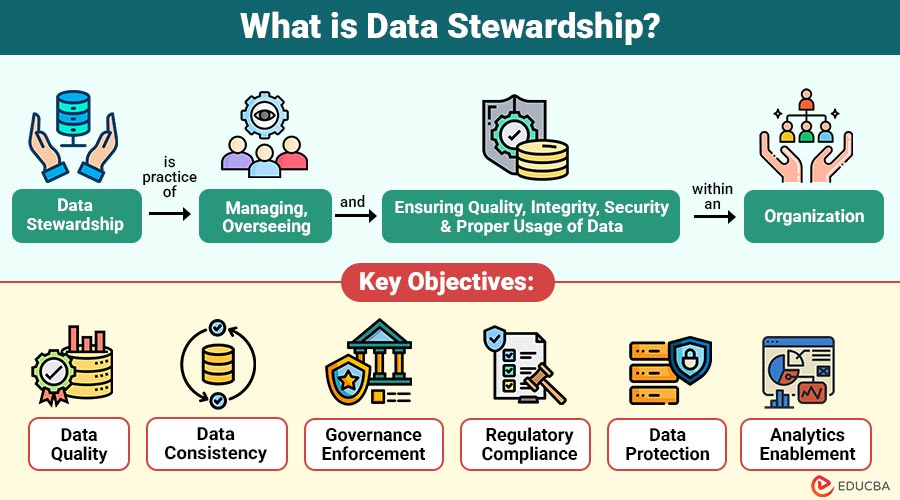
Data stewardship is practice of managing, overseeing, and ensuring the quality, integrity, security, and proper usage of data within an organization. It focuses on defining clear ownership, accountability, and standards for data assets, ensuring that data is accurate, consistent, compliant, and fit for its intended purpose.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Data stewardship ensures data quality, security, consistency, and compliance across the entire organization.
- Clear data ownership and accountability are foundational to effective data management and governance.
- Data stewards act as the bridge between business, IT, and governance teams.
- Strong stewardship improves analytics accuracy, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Importance of Data Stewardship
Effective data stewardship delivers measurable business value across the organization.
1. Improved Data Quality
Ensures data accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness, significantly reducing errors and operational rework.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Encourages adherence to industry standards and laws, including GDPR and HIPAA, by enforcing data governance procedures.
3. Better Decision-Making
Reliable, well-managed data improves confidence in analytics, dashboards, reporting, and strategic business decisions.
4. Enhanced Data Security
Protects sensitive data using classification, access controls, policies, and clearly defined data usage guidelines.
5. Operational Efficiency
Reduces data duplication, system conflicts, and manual data correction efforts across organizational platforms.
Key Objectives of Data Stewardship
The key objectives of data stewardship include:
1. Data Quality
Ensures data remains complete, reliable, timely, and accurate to support trusted decision-making across the organization.
2. Data Consistency
Maintains standardized definitions and values, reducing discrepancies across multiple systems, teams, and business units.
3. Governance Enforcement
Implements defined rules, ownership, and controls to ensure data usage aligns with organizational standards.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Helps organizations meet legal obligations by ensuring that data handling complies with applicable regulations and that audits are conducted.
5. Data Protection
Safeguards confidential data through access controls, classification, and security measures against misuse.
6. Analytics Enablement
Provides trustworthy data foundations required for accurate reporting, advanced analytics, and AI-driven insights.
Roles of a Data Steward
A data steward is accountable for managing specific data domains, such as customer, product, or financial data.
1. Data Domain Ownership
Accountable for managing specific data domains such as customer, product, financial, or operational business data.
2. Data Definitions and Rules
Defines, documents, and maintains uniform data definitions, business rules, and usage guidelines across the organization.
3. Data Quality Management
Monitors, measures, and continuously improves data quality metrics to ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
4. Issue Resolution
Identifies, investigates, and resolves data issues, discrepancies, and inconsistencies in collaboration with stakeholders.
5. Compliance and Governance
Ensures data usage complies with internal policies, regulatory requirements, and organizational data governance standards.
Types of Data Stewards
Here are the different types of data stewards, each responsible for specific aspects of data governance and management within an organization.
1. Business Data Steward
Focuses on data meaning, standardized definitions, business rules, and ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.
2. Technical Data Steward
Concentrates on data structures, system integrations, technical metadata, and maintaining overall technical data quality.
3. Operational Data Steward
Handles day-to-day data maintenance, monitoring, issue resolution, and supporting ongoing business data operations.
Data Stewardship Lifecycle
Data stewardship spans the entire data lifecycle:
1. Data Creation
Ensures accurate data definitions, standards, and validation rules are applied correctly at the source.
2. Data Storage
Manages data structures, metadata, storage locations, and access permissions to ensure secure availability.
3. Data Usage
Monitors appropriate, authorized, and compliant data usage across analytics, reporting, and operational processes.
4. Data Sharing
Governs secure internal and external data exchange while maintaining compliance, ownership, and usage controls.
5. Data Archival
Retains historical data according to organizational policies, regulatory requirements, and long-term business needs.
6. Data Disposal
Ensures secure data deletion in accordance with retention schedules, legal obligations, and approved disposal procedures.
Technologies Supporting Data Stewardship
The following technologies help organizations manage data effectively by ensuring visibility, quality, governance, and traceability across data assets.
1. Data Catalogs and Metadata Management
Provide centralized visibility into data assets, definitions, ownership, and metadata for improved discovery.
2. Data Quality Monitoring Tools
Regularly check that data is correct, complete, consistent, and up to date using automated checks and reports.
3. Master Data Management Solutions
Ensure consistent, unified, and authoritative master data across systems, applications, and business processes.
4. Data Governance and Workflow Tools
Enable policy enforcement, approval workflows, stewardship assignments, and issue tracking across data initiatives.
5. Data Lineage and Impact Analysis Tools
Challenges in Data Stewardship
Despite its benefits, organizations often face challenges when implementing data stewardship.
1. Lack of Clear Ownership
Unclear stewardship roles create accountability gaps, delaying issue resolution and reducing overall data management effectiveness.
2. Cultural Resistance
Business teams may resist governance practices, perceiving controls as restrictive, slowing the adoption of stewardship programs.
3. Siloed Data Systems
Disconnected data systems hinder consistency, visibility, integration, and end-to-end data lineage management efforts.
4. Resource Constraints
Limited time, budgets, and skilled personnel slow implementation, monitoring, and maturity of data stewardship initiatives.
5. Scaling Across the Enterprise
Growing data volumes and complexity require scalable stewardship processes, tools, and organizational alignment.
Real-World Example
Here is a real-world example illustrating how data stewardship improves data quality and business outcomes.
Retail Organization
By implementing a data stewardship program:
- Data stewards were assigned to the customer data domain
- Standard definitions and validation rules were introduced
- Data quality dashboards tracked ongoing improvements
As a result, customer data accuracy improved significantly, marketing campaigns became more effective, and reporting reliability increased.
Final Thoughts
Data stewardship is essential for ensuring accurate, secure, and compliant data. By clearly assigning responsibility, setting rules, and regularly checking data quality, organizations can trust their data. This helps them make better decisions, gain accurate insights, meet regulations, work more efficiently, and use data as a valuable asset for long-term business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is data stewardship only for large enterprises?
Answer: No. Organizations of all sizes benefit from data stewardship to improve data reliability, reduce risk, and support decision-making.
Q2. What skills are required to be an effective data steward?
Answer: Key skills include data analysis, business knowledge, communication, problem-solving, and understanding governance and compliance standards.
Q3. How does data stewardship support analytics and AI?
Answer: It ensures trusted, well-defined, and high-quality data foundations required for accurate analytics, machine learning, and AI outcomes.
Q4. What industries benefit most from data stewardship?
Answer: Industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, telecom, and government benefit significantly from regulatory and data-quality requirements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Stewardship” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.