What is Data Lineage?
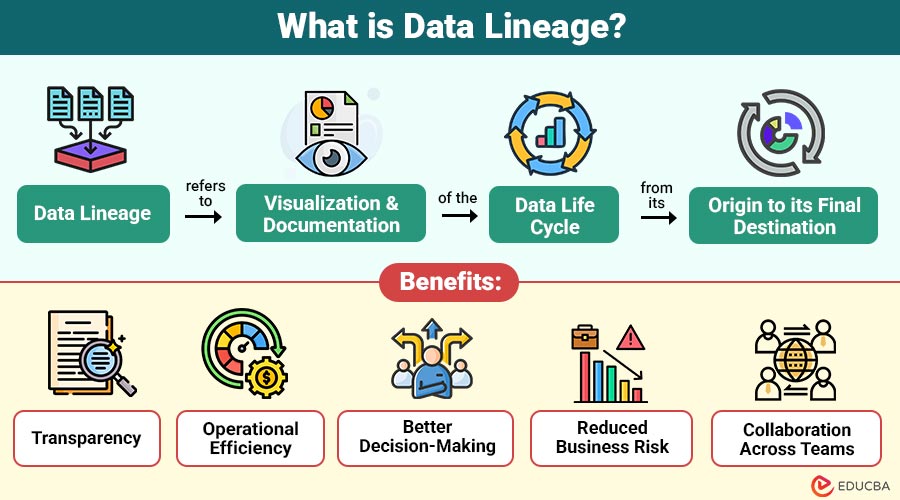
Data lineage refers to the visualization and documentation of the data life cycle—from its origin to its final destination. It includes all the touchpoints, transformations, processes, and systems that the data interacts with along the way.
In simple terms, data lineage answers three fundamental questions:
- Where does the data come from? (Source)
- How does it change during processing? (Transformation)
- Where does it end up? (Destination)
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Data lineage traces a data’s complete journey, accurately documenting its origins, transformations, systems, and final destinations.
- It enhances organizational data trust by identifying inconsistencies, errors, and transformation issues early in the pipeline.
- Regulatory compliance becomes easier through clear traceability required by GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and similar standards.
- Lineage accelerates root cause analysis by quickly revealing the exact source of reporting or data issues.
Why is Data Lineage Important?
Organizations face growing pressure to maintain data integrity, meet compliance requirements, and support complex analytical needs. Data lineage addresses these challenges through:
1. Improved Data Trust and Quality
Lineage helps data teams identify inconsistencies, errors, and transformation issues, leading to improved data quality and reliability.
2. Stronger Regulatory Compliance
Industries with strict rules (like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX) need to clearly track their data. Data lineage helps them follow these rules by showing exactly how data is handled.
3. Faster Root Cause Analysis
When problems arise—such as incorrect reports—lineage maps enable the quick identification of the source of the issue.
4. Better Impact Analysis
Before making system changes, lineage helps teams assess the potential downstream effects.
5. Enhanced Governance and Accountability
Lineage forms the backbone of any robust data governance framework by documenting data stakeholders and processes.
How Data Lineage Works? (Step-by-Step Process)
Here are the step-by-step stages that clearly explain how data lineage functions in any organization:
Step 1: Metadata Collection
The tool automatically collects important details from databases, SQL code, data pipelines, APIs, and BI dashboards.
Step 2: Transformation Mapping
The system reads the rules to understand how data is cleaned, filtered, combined, summarized, improved, or changed.
Step 3: Data Flow Visualization
A visual interface displays end-to-end data movement, clearly showing every source, transformation, pipeline stage, and final destination.
Step 4: Impact and Dependency Analysis
The tool highlights downstream dependencies, showing which tables, reports, dashboards, or models rely on specific data elements.
Step 5: Continuous Monitoring
Lineage automatically updates in real time, ensuring accurate tracking as pipelines evolve, change, expand, or undergo modifications.
Types of Data Lineage
Here are the primary types of data lineage that organizations use to understand data flow at different levels:
1. Horizontal Data Lineage
Tracks how data moves across multiple systems and layers, showing its flow from source to destination throughout the architecture.
2. Vertical Data Lineage
Traces data relationships within a single system, detailing how tables, columns, and internal transformations interact and connect.
3. Fine-grained (Column-level) Lineage
Provides precise, detailed visibility into column-to-column data transformations, enabling deeper analysis and accurate impact assessment.
Use Cases of Data Lineage
Data lineage is becoming an increasingly necessary enterprise requirement. Below are major use cases:
1. Regulatory Compliance & Auditing
Industries like finance, healthcare, and government need clear records to stay transparent and accountable. Data lineage helps by showing exactly where data comes from and how it changes, making it easier to meet regulatory rules.
2. Data Quality Management
By identifying inconsistencies and broken pipelines, lineage supports proactive quality assurance.
3. Data Migration & Modernization
Understanding dependencies is crucial for cloud migration, schema redesign, and system upgrades.
4. Business Intelligence & Reporting
Lineage enhances report accuracy, which is critical for executive dashboards and analytics.
5. Impact Analysis
Before modifying a pipeline or deleting a column, lineage helps evaluate the number of downstream processes that will be impacted.
6. Machine Learning & AI
ML models depend on high-quality, traceable data. Lineage improves model reliability, auditability, and explainability.
7. Data Governance Frameworks
Lineage integrates with catalogs, stewardship tools, glossaries, and governance policies.
Benefits of Data Lineage
Here are the key benefits that it offers to organizations across analytics, governance, and operational workflows:
1. Transparency
Provides complete visibility into data pipelines, showing sources, transformations, and destinations, and builds stronger trust.
2. Operational Efficiency
Reduces troubleshooting time and ETL failures while streamlining pipeline management for improved overall operational efficiency.
3. Better Decision-Making
Teams gain higher confidence in analytics outputs because lineage ensures accurate, reliable, and trustworthy data-driven insights.
4. Reduced Business Risk
Lineage helps reduce business risks by spotting mistakes and missing information early, so problems can be fixed before they cause failures.
5. Collaboration Across Teams
Data engineers, analysts, and business users collaborate effectively because lineage provides shared visibility into data flows.
Challenges in Implementing Data Lineage
Despite its advantages, implementing enterprise-wide lineage has challenges, such as:
1. Complex Data Environment
Hybrid architectures that combine on-premises systems, cloud platforms, and diverse tools make automated lineage extraction extremely challenging.
2. Metadata Inconsistencies
Different technologies store metadata in varied formats, creating significant compatibility challenges for unified lineage interpretation.
3. Manual Effort for Legacy Systems
Legacy systems lacking documentation force teams to rebuild lineage manually, increasing workload, time, and potential errors.
4. High Implementation Cost
Comprehensive lineage tools, integrations, governance frameworks, and skilled resources often demand substantial financial investment.
5. Data Volume & Velocity
Continuous high-speed data streams complicate real-time lineage tracking, particularly in large-scale, distributed processing environments.
Real-World Examples
Here are some industry-specific examples that show how organizations rely on data lineage in practical scenarios:
1. Banking
Banks trace the origin, transformation, and destination of every transaction to ensure accurate fraud detection, audit compliance, and adherence to regulations.
2. E-commerce & Retail
Retailers track inventory, customer behavior, order flows, and analytics pipelines to optimize their operations and make informed decisions.
3. Telecom
Telecom companies map data usage, billing details, and network analytics to support accurate reporting and regulatory compliance.
Tools Used for Data Lineage
Some of the leading tools include:
1. Apache Atlas
Apache Atlas is an open-source governance framework providing metadata management, data cataloging, and automated lineage tracking for complex Hadoop and cloud ecosystems.
2. Collibra
Collibra is an enterprise data intelligence platform offering robust data governance, automated lineage visualization, cataloging, and compliance management across large organizations.
3. Alation
Alation is a leading data catalog solution enabling metadata discovery, lineage mapping, governance workflows, and collaborative data usage across business and technical teams.
4. Informatica EDC
Informatica Enterprise Data Catalog automatically scans systems, extracts metadata, builds lineage, and offers AI-driven insights for enterprise-wide data governance and management.
5. Microsoft Purview
Microsoft Purview helps you keep all your data organized. It shows where your data comes from, how it changes, and where it goes. It also labels data automatically and makes sure your company follows all rules—whether the data is in Azure, on your own servers, or in multiple clouds.
6. Talend
Talend offers data integration, quality, governance, and automated lineage capabilities through its unified platform for managing modern cloud and hybrid data ecosystems.
7. Manta
Manta specializes in deep automated lineage, scanning SQL, ETL, and BI systems to provide detailed, transparent flow maps for complex data pipelines.
Final Thoughts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the primary purpose of data lineage?
Answer: To track the flow and transformation of data from its source to its final destination.
Q2. Is data lineage required for regulatory compliance?
Answer: Yes. Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX require data traceability.
Q3. Can data lineage be automated?
Answer: Yes. Modern tools, such as Purview, Collibra, and Atlas, provide automated lineage extraction.
Q4. Why is column-level lineage important?
Answer: It helps troubleshoot errors and understand precise transformation logic.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Lineage” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

