What is a Data Catalog?
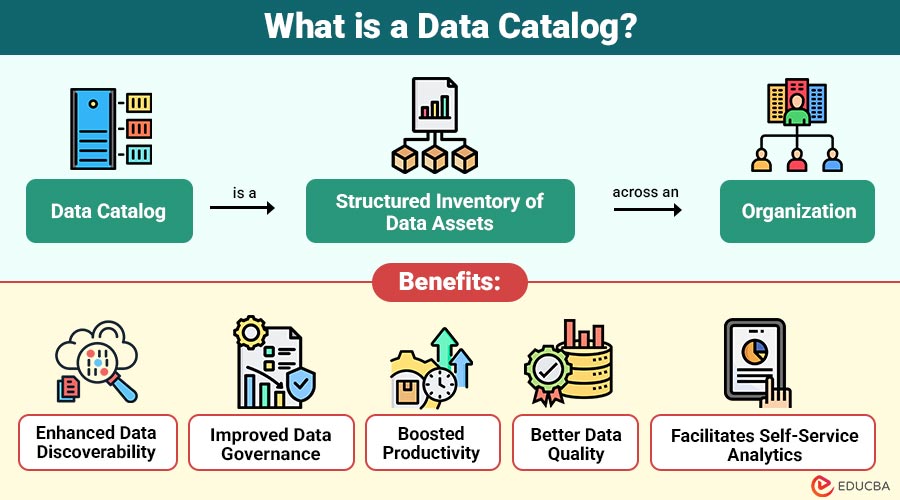
Data Catalog is a structured inventory of data assets across an organization. It includes metadata—data about data—such as data type, source, usage, relationships, and quality. By consolidating metadata into a single location, a data catalog makes it easier for data analysts, scientists, and business users to discover, understand, and trust the data they need.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Data catalogs centralize metadata, simplifying discovery, boosting collaboration, and enabling accurate, informed, and efficient data usage.
- Automated classification and AI-driven tagging in catalogs reduce manual effort while maintaining up-to-date, reliable metadata.
- Implementing a catalog strengthens governance, ensures compliance, tracks lineage, and improves trust in organizational data.
- By promoting self-service analytics, catalogs empower teams to access data and generate actionable insights quickly.
Key Components of a Data Catalog
Here are the main key components that make up a comprehensive data catalog:
- Metadata Repository: Stores information about data assets, including schema, lineage, and usage statistics.
- Data Discovery Tools: Search, filter, and explore datasets based on metadata attributes.
- Data Lineage: Helps consumers understand the data transformation path by tracking its flow from source to destination.
- Data Governance and Stewardship: Includes ownership, compliance rules, and quality metrics to ensure data reliability and security.
- Collaboration Features: Allows users to annotate, tag, and review datasets, promoting shared understanding.
Types of Data Catalogs
It can be classified based on how they manage and organize metadata:
- Business Glossary-Based: Focuses on standardizing business terms across datasets. Useful for ensuring consistent data interpretation across departments.
- Technical Metadata: Capture technical details, including schemas, tables, columns, and relationships. Ideal for IT teams and data engineers.
- Operational: Monitors real-time data pipelines and logs usage patterns to support operational analytics.
- Automated/Intelligent: Uses AI and machine learning to scan, classify automatically, and tag data assets. This reduces manual effort and ensures up-to-date metadata.
How Does a Data Catalog Work?
Here is the key process behind its working:
- Data Crawling: Connects to various data sources, including databases, cloud storage, APIs, and applications. It automatically scans metadata.
- Metadata Extraction: Captures technical, operational, and business metadata, including table structures, column definitions, data types, and ownership.
- Data Classification: Tags datasets with categories like confidential, financial, or marketing data, ensuring proper governance.
- Data Lineage Mapping: Visualizes how data flows from source to destination, providing transparency for auditing and analysis.
- Search and Discovery: Users can easily find datasets by searching with keywords, tags, or filters, making data easier to access and use on their own.
- Collaboration and Governance: Teams can annotate datasets, provide usage recommendations, and ensure compliance with data policies.
Benefits of Using Data Catalog
Implementing offers multiple strategic, operational, and technical benefits:
- Enhanced Data Discoverability: Users can quickly locate relevant datasets without wasting time searching multiple systems.
- Improved Data Governance: A catalog enforces data policies, tracks lineage, and maintains data ownership for regulatory compliance.
- Boosted Productivity: Data analysts and scientists spend less time searching for data and more time extracting insights.
- Better Data Quality: By including quality metrics and lineage information, organizations can identify and fix inaccurate or outdated data.
- Facilitates Self-Service Analytics: Empowers business users to find and use data independently without relying heavily on IT teams.
Real-World Use Cases
Here are some practical use cases of how organizations leverage data catalogs across industries:
- Retail Sector: Retailers integrate sales, inventory, and customer data across channels. It helps analysts identify product trends and optimize stock management.
- Financial Services: Banks maintain millions of transaction records. It supports risk management, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance by organizing sensitive financial data.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and research centers use catalogs to discover patient records, lab results, and research data, ensuring accurate reporting and compliance with health regulations.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers leverage catalogs to combine production, supply chain, and sensor data for predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
- Marketing and Advertising: Marketers use data catalogs to unify customer engagement data, enabling precise targeting and personalized campaigns.
Challenges of Using Data Catalogs
While beneficial, organizations may face challenges when implementing:
- Data Silos: Integrating diverse, disconnected data sources is difficult and often requires significant technical and organizational effort
- Metadata Accuracy: Manual metadata entry causes inconsistencies; automated metadata collection greatly improves reliability and reduces human errors.
- Change Management: Driving user adoption requires cultural alignment, training efforts, and strong leadership support across different teams.
- Scalability: Enterprises need robust catalogs capable of efficiently managing rapidly growing data volume and increasing complexity.
Popular Data Catalog Tools
Here are some of the leading tools organizations use to organize, manage, and govern their data:
- Collibra: A comprehensive governance and data catalog solution.
- Alation: AI-powered catalog with strong collaboration features.
- Informatica Enterprise Data Catalog: Enterprise-grade solution with automated metadata scanning.
- Microsoft Purview: Cloud-native catalog for Azure and hybrid environments.
- Google Cloud Data Catalog: Metadata management and discovery for GCP assets.
Future Trends in Data Cataloging
Here are some emerging trends shaping the future:
- AI-Driven Metadata Management: AI will automate metadata tagging, classification, and recommendations, improving accuracy, consistency, and overall efficiency.
- Integration with Data Mesh: Catalogs will work with decentralized data models, making it easier to find, trust, and manage data across different teams.
- Enhanced Data Lineage Visualization: Interactive, real-time lineage mapping will help analytics teams track data flows and dependencies more effectively.
- Focus on Data Privacy: Stronger privacy controls will support compliance with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and emerging data protection regulations.
Final Thoughts
A data catalog is essential for modern, data-driven organizations. It centralizes and manages data, making it easy for users to find and use information independently. This boosts efficiency and supports timely, accurate decisions. With strong governance and adoption, it turns scattered data into a valuable strategic asset, helping teams unlock the full power of organizational data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a data catalog and a data warehouse?
Answer: A data warehouse stores structured data for analysis, while a data catalog indexes and organizes metadata for discoverability and governance.
Q2. Can small businesses benefit from data catalogs?
Answer: Yes, even small organizations can improve data discoverability and governance, though simpler solutions may suffice.
Q3. How is AI used in data catalogs?
Answer: AI automatically classifies, tags, and recommends datasets, reducing manual metadata management.
Q4. Do data catalogs support real-time data?
Answer: Yes, many modern catalogs support operational and streaming data for real-time analytics.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Catalog” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.