What is Compliance Management?
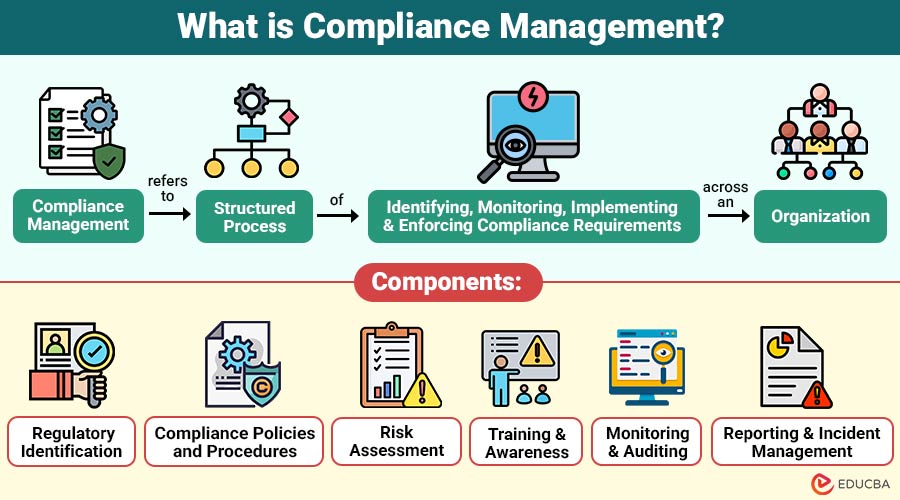
Compliance management refers to the structured process of identifying, monitoring, implementing, and enforcing compliance requirements across an organization. These requirements may originate from regulatory bodies, industry standards, contractual obligations, or internal governance policies.
The goal of compliance management is to ensure that business operations, employees, systems, and processes consistently align with external laws and internal rules while proactively identifying and mitigating compliance risks.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Components
- Process
- Types
- Role of Technology in Compliance Management
- Challenges
- Real-World Use Cases
Key Takeaways:
- Compliance management ensures that organizations consistently follow laws, regulations, standards, and internal policies, thereby significantly reducing legal risks.
- Effective compliance frameworks prevent fraud, misconduct, and ethical violations while promoting accountability across all organizational operations.
- Technology enhances compliance by automating updates, tracking risks, maintaining audit trails, and enabling efficient centralized policy management.
- Proactive compliance builds trust, strengthens reputation, and supports sustainable business growth through transparency and regulatory adherence.
Importance of Compliance Management
Below are key points highlighting its importance:
1. Reduces Legal Penalties
Effective compliance management reduces legal penalties, regulatory fines, and enforcement actions by ensuring adherence to laws.
2. Prevents Fraud and Misconduct
Prevents fraud, misconduct, and ethical violations by establishing controls, monitoring activities, and promoting accountability across organizations.
3. Improves Operational Transparency
Improves operational transparency through clear policies, reporting standards, and consistent oversight of business processes.
4. Enhances Customer and Investor Confidence
Enhances customer and investor confidence by consistently demonstrating integrity, regulatory compliance, and strong governance practices.
5. Supports Sustainable Business Growth
Supports sustainable business growth by reducing risks, strengthening the reputation, and enabling effective long-term strategic planning.
Components of Compliance Management
A robust compliance management framework typically consists of the following components:
1. Regulatory Identification
Identifying applicable laws, regulations, standards, and contractual obligations relevant to the organization’s industry and geography.
2. Compliance Policies and Procedures
Documented rules, guidelines, and standard operating procedures that define compliance expectations.
3. Risk Assessment
Evaluating compliance risks based on likelihood, impact, and business exposure.
4. Training and Awareness
Educating employees and stakeholders on compliance responsibilities and ethical conduct.
5. Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous tracking of compliance adherence through audits, assessments, and control checks.
6. Reporting and Incident Management
Structured mechanisms for reporting violations, managing incidents, and taking corrective actions.
Compliance Management Process
The compliance management lifecycle follows a systematic and repeatable process:
1. Identify Compliance Requirements
Identify applicable laws, regulations, standards, and internal policies relevant to organizational operations and business activities.
2. Assess Compliance Risks
Evaluate potential compliance risks by analyzing regulatory exposure, process gaps, and the likelihood of violations occurring.
3. Define Controls and Policies
Develop clear controls and policies to address identified risks and ensure consistent regulatory compliance across the organization.
4. Implement Compliance Measures
Implement compliance measures through training, system controls, procedures, and accountability mechanisms across the organization.
5. Monitor and Audit Compliance
Continuously monitor and audit compliance performance to detect violations, control failures, and improvement opportunities.
6. Report and Remediate Issues
The report identified compliance issues promptly and remediated gaps through corrective actions, documentation, and follow-up processes.
Types of Compliance Management
Here are the main types of compliance management:
1. Regulatory Compliance
Ensures adherence to applicable government laws, regulations, and statutory requirements governing industry operations and business activities.
2. Corporate Compliance
Focuses on internal governance, ethical standards, corporate policies, and adherence to codes of conduct organization-wide.
3. Financial Compliance
Covers accounting standards, financial reporting, audits, taxation rules, and transparency in financial management practices.
4. Data and Privacy Compliance
Ensures the protection of personal and sensitive data in accordance with laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection regulations.
5. IT and Cybersecurity Compliance
Protects systems and digital assets by adhering to information security standards, including ISO 27001, SOC, and PCI DSS.
6. Environmental Compliance
Ensures adherence to environmental laws, sustainability standards, emissions controls, and responsible resource management practices.
Role of Technology in Compliance Management
Technology plays an important role in scaling and automating compliance efforts.
1. Centralized Policy Management
Technology enables centralized management of policies, ensuring consistent access, updates, and communication across the entire organization.
2. Automated Regulatory Updates
Automates tracking of regulatory changes, providing timely updates and reducing manual monitoring efforts for compliance teams.
3. Risk Assessment Dashboards
Provides dashboards to visualize, analyze, and prioritize compliance risks, supporting informed decision-making and mitigation strategies.
4. Audit Trails and Reporting
Maintains detailed audit trails and generates reports, ensuring accountability, transparency, and easier regulatory inspections or reviews.
5. Incident and Case Management
Facilitates the efficient tracking, investigation, and resolution of compliance incidents or cases within the organization.
6. Role-Based Access Controls
Ensures that confidential compliance data is secure and accessible only to authorized users by implementing role-based access controls.
Challenges in Compliance Management
Despite its importance, organizations face several compliance challenges:
1. Changing Regulations
Businesses find it difficult to keep up with the ever-changing laws, rules, and regulations that apply across industries.
2. Global Compliance Complexity
Managing compliance across multiple countries involves understanding diverse regulations, languages, and jurisdictional requirements simultaneously..
3. Employee Awareness Gaps
Employees may be unaware of policies, regulations, and responsibilities, increasing the risk of violations and operational non-compliance.
4. Data Privacy Risks
Protecting sensitive data and digital assets from breaches is challenging amid stringent privacy regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Real-World Use Cases
Here are practical use cases across different industries:
1. Banking & Financial Services
Ensures adherence to AML, KYC, SOX, and financial reporting regulations, reducing risk and legal exposure.
2. Healthcare
Manages patient data privacy, clinical standards, and regulatory audits to ensure safety and legal compliance.
3. IT & SaaS Companies
Complies with data protection laws, cybersecurity frameworks, and service certifications to protect systems and customer information.
4. Manufacturing
Meets environmental, safety, and quality compliance requirements, ensuring regulatory adherence and operational efficiency across production processes.
5. Retail & E-Commerce
Ensures consumer protection, tax compliance, and data security while maintaining trust and legal adherence.
Final Thoughts
Compliance management is no longer just about meeting regulatory requirements—it is about building resilient, ethical, and trustworthy organizations. By implementing structured compliance frameworks, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of accountability, organizations can transform compliance from cost center into a competitive advantage. As regulations continue to evolve, proactive and technology-driven compliance management will remain essential for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main objective of compliance management?
Answer: The main objective is to ensure adherence to laws, regulations, standards, and internal policies while minimizing legal and operational risks.
Q2. Is compliance management mandatory?
Answer: Yes, compliance management is mandatory in regulated industries and essential for all organizations to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Q3. How does compliance management differ from governance?
Answer: Governance defines decision-making structures, while compliance ensures adherence to rules and regulations.
Q4. Can small businesses implement compliance management?
Answer: Yes, compliance management can be scaled based on organizational size and complexity.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Compliance Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.