Updated May 8, 2023

Introduction to CAST in PostgreSQL
In the case of handling transactions within multiple databases, data conversion is the basic requirement that is supported by almost all programming paradigms. PostgreSQL provides us with the CAST operator, which we can use to convert one data type to another data type. We can have various cast operations in the PostgreSQL, like converting string to integers, converting string to date and date to a string, casting to Boolean, etc.
Syntax:
CAST (exp AS target_type );Explanation:
- target_type: Define the target data type in which we are converting the value of the exp.
How does the CAST Operator work in PostgreSQL?
The cast operator converts one data type to another, where the table column or an expression’s data type is decided to be. The target data type is the data type to which the expression will get converted. The syntax of the CAST operator’s another version is as follows as well:
Syntax:
Expression::typeConsider the following example to understand the working of the PostgreSQL CAST:
Code:
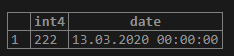
SELECT
'222'::INTEGER,
'13-MAR-2020'::DATE;Output: Illustrate the following snapshot to understand the result of the above statement.
Examples to Implement CAST in PostgreSQL
Now, Let’s look at the following examples, which converts one data type to another.
1. STRING to an Integer CAST
1. Use the following statement to do the conversion:
Code:
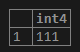
SELECT
CAST ('111' AS INTEGER);Output: Illustrate the following snapshot to understand the result of the above statement:
2. The PostgreSQL CAST operator raises an error if the given value is not convertible to the target data type. Consider the following example for the same,
Code:
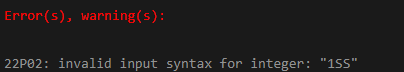
SELECT
CAST ('1SS' AS INTEGER);Output: PostgreSQL will give us the following error after executing the above SQL statement: the value contains a character.
2. STRING to DATE CAST
Convert a STRING constant to DATE type using the following statement:
Code:
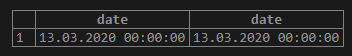
SELECT
CAST ('2020-03-13' AS DATE),
CAST ('13-MAR-2020' AS DATE);Output: Illustrate the following snapshot to understand the result of the above statement:
3. STRING to DOUBLE CAST
1. Now, try to convert a STRING constant to a DOUBLE type using the following statement:
Code:
SELECT
CAST ('22.2' AS DOUBLE);Output: PostgreSQL will give us the following error after executing the above SQL statement: the value contains precision.
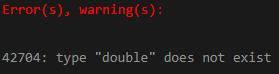
2. To execute the above statement correctly; we have to use the following syntax where instead of DOUBLE, we have to use DOUBLE PRECISION,
Code:
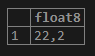
SELECT
CAST ('22.2' AS DOUBLE PRECISION);Output: Illustrate the following snapshot to understand the result of the above statement:
4. STRING to Boolean CAST
Convert a STRING constant to Boolean type using the following statement, where the ‘FALSE’, ‘false’, ‘f’ and ‘F’ gets converted to false, and ‘TRUE’, ‘true’, ‘t’ and ‘T’ gets converted to true as follows:
Code:
SELECT
CAST('FALSE' as BOOLEAN),
CAST('false' as BOOLEAN),
CAST('F' as BOOLEAN),
CAST('f' as BOOLEAN),
CAST('TRUE' AS BOOLEAN),
CAST('true' AS BOOLEAN),
CAST('T' as BOOLEAN),
CAST('t' as BOOLEAN);Output: Illustrate the following snapshots to understand the result of the above statement:

5. STRING to Timestamp CAST
1. Convert a STRING constant to timestamp type using the following statement
Code:
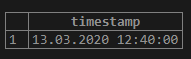
SELECT '2020-03-13 12:40:00'::timestamp;Output: Illustrate the following snapshot to understand the result of the above statement:
6. String to interval CAST
Use the following statement to do the conversion:
Code:
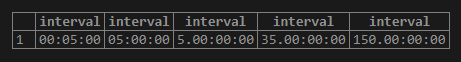
SELECT '5 minute'::interval,
'5 hour'::interval,
'5 day'::interval,
'5 week'::interval,
'5 month'::interval;Output: Illustrate the following snapshot to understand the result of the above statement:
7. CAST with table
1. Now, let’s create a new table of name ‘Grades’, which will have a column named’Grade’ using CREATE TABLE statement as follows:
Code:
CREATE TABLE Grades (
Grade VARCHAR(1)
);2. Now, insert some data into the ‘Grades’ table using the INSERT statement as follows:
Code:
INSERT INTO Grades(Grade)
VALUES
('A'),
('B'),
('C'),
('D');3. Illustrate the Grades table’s content with the help of the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Code:
SELECT
Grade
FROM
Grades;Output:
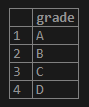
4. Now, suppose the requirement is changed where we have to store the grades in numerical format instead of character, so using the following statement, we can insert numerical values in the Grades table.
Code:
INSERT INTO Grades(Grade)
VALUES
('1'),
('2'),
('3'),
('4');5. The Grades table will store mixed numerical and character types of ratings. Illustrate the content of the Grades table with the help of the following snapshot and SQL statement.
Code:
SELECT
Grade
FROM
Grades;Output:
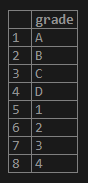
6. So we will convert all values in the Grade column of the Grades table to integer type using the following statement,
Code:
SELECT
CASE
WHEN grade~E'^\\d+$' THEN
CAST (grade AS INTEGER)
ELSE
0
END as grade
FROM
Grades;Output: Illustrate the result of the above statement using the following snapshot

Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you understand how to use the PostgreSQL CAST operator and how the PostgreSQL CAST works to convert one data type to another. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL CAST operators to understand them in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CAST in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

