What is the Business Life Cycle?
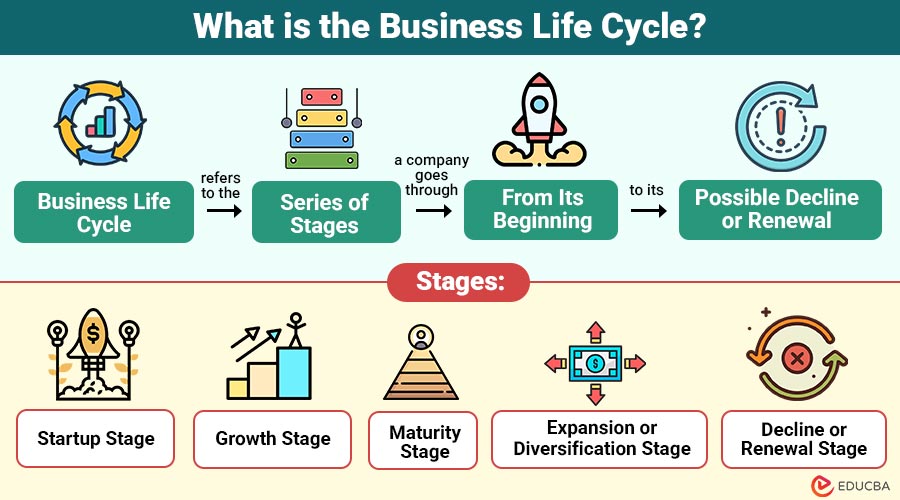
The Business Life Cycle refers to the series of stages a company goes through from its beginning to its possible decline or renewal. It includes phases such as startup, growth, maturity, expansion, and decline. Each phase brings its own set of challenges and opportunities that shape a company’s operations and growth.
In simple terms, the business life cycle is like the journey of a business — starting from an idea, developing into a successful enterprise, reaching stability, and then either evolving to stay competitive or facing decline. Understanding this cycle helps entrepreneurs make smart decisions at every stage.
Table of Contents:
- What is the Business Life Cycle?
- 5 Core Stages
- Key factors
- How to Identify Which Stage Your Business Is In?
- Strategies to Sustain Long-Term Growth
- Case Studies
Key Takeaways
- The business life cycle consists of five key stages—startup, growth, maturity, expansion, and decline or renewal—each requiring unique strategies for success.
- Knowing which stage your business is in enables leaders to make smarter decisions and create strategies that support long-term, sustainable growth.
- Factors like innovation, financial management, leadership, and adaptability play a vital role in moving smoothly through each phase.
- Long-term success depends on continuous improvement, customer focus, and readiness to evolve with changing market trends and technologies.
The 5 Core Stages of the Business Life Cycle
1. Startup Stage
The startup stage marks the birth of a business idea and its transformation into reality. Entrepreneurs focus on developing a unique concept, testing its market potential, and attracting early customers. This phase often faces challenges like limited funding, low brand awareness, and high uncertainty. Success depends on maintaining lean operations, experimenting with innovative solutions, and adapting quickly to market feedback. Agility and persistence are key to moving forward.
2. Growth Stage
During the growth stage, the business experiences rapid increases in customer base and revenue. This is when companies expand their market presence, hire more employees, and strengthen their operations. However, scaling too fast can lead to quality issues or inefficiencies. To sustain growth, businesses must balance expansion with consistent product or service quality and smart competition management.
3. Maturity Stage
At this point, the business enjoys stability, strong brand recognition, and steady profits. The focus shifts toward improving efficiency, refining processes, and exploring innovation to maintain relevance. Market diversification and product upgrades become essential. The biggest risk is complacency—businesses must continue innovating to avoid stagnation or decline.
4. Expansion or Diversification Stage
This stage involves exploring new opportunities beyond the core business—such as launching new products, entering global markets, or merging with other firms. Effective resource management becomes vital to ensure sustainable growth. Businesses embracing digital transformation and globalization can unlock long-term competitiveness and resilience in changing markets.
5. Decline or Renewal Stage
If market conditions shift or innovation slows, a business may face decline. Recognizing early warning signs—such as declining sales or reduced demand—is crucial. Companies can respond through rebranding, restructuring, or launching fresh product lines to regain momentum. Businesses that adapt creatively often turn decline into renewal, while others may choose to exit strategically.
Key Factors Influencing Each Stage
- Market Trends and Customer Behavior: Changing consumer preferences and industry trends can either drive growth or create challenges. Staying updated helps businesses adapt quickly.
- Financial Management: Proper budgeting, cost control, and reinvestment are crucial at every stage. Strong financial planning ensures survival during slow phases and supports expansion during growth.
- Leadership and Vision: Effective leadership shapes company direction, motivates teams, and makes strategic decisions that influence long-term success.
- Innovation and Technology: Adopting new technologies and creative ideas enables businesses to stay competitive, boost efficiency, and adapt to changing market demands.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes, skilled employees, and strong internal systems ensure smooth operations and sustainable growth.
- Brand Reputation and Customer Relations: Building trust and maintaining a positive image attracts loyal customers and long-term success.
- Adaptability: The ability to adjust to market shifts, competition, and challenges determines how well a business moves through each stage.
How to Identify Which Stage Your Business Is In?
- Revenue and Profit Trends: Analyze your sales and profit growth. Rapid increases often indicate the growth stage, while steady or declining figures may suggest maturity or decline.
- Customer Base and Market Reach: A growing number of loyal customers signals expansion, whereas stagnant or shrinking demand could indicate a mature or declining phase.
- Operational Structure: Startups usually have flexible, small teams, while mature businesses have established systems, departments, and clear hierarchies.
- Cash Flow Patterns: Frequent cash shortages are common in the startup phase, while consistent positive cash flow reflects maturity or expansion.
- Product Portfolio: Businesses in growth or expansion stages tend to introduce new products or diversify their offerings.
- Competitive Position: If your brand leads the market, you may be in the maturity stage; if you’re struggling to stand out, it might be the startup or decline phase.
- Business Goals: Short-term survival goals signal early stages, while long-term sustainability goals reflect maturity or renewal.
Strategies to Sustain Long-Term Growth
- Continuous Innovation: Keep evolving your products, services, and processes to stay relevant and meet changing customer needs. Innovation keeps your business competitive and future-ready.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Concentrate on providing outstanding value and fostering lasting relationships. Loyal customers are key drivers of consistent growth.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use data to understand market trends, customer behavior, and how your business is performing. Smart data insights lead to informed and effective strategies.
- Employee Development: Invest in training, leadership programs, and a positive work culture to build a motivated and skilled workforce.
- Diversification: Grow your business by entering new markets or offering related products to lower risks and create more income sources.
- Efficient Resource Management: Optimize operations, control costs, and reinvest profits strategically for steady growth.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Building an ethical and eco-friendly brand not only enhances reputation but also attracts conscious consumers and investors.
Case Studies: Successful Business Life Cycle Management
- Apple Inc. – From Decline to Global Dominance: In the late 1990s, Apple faced a severe decline, with market share dropping below 4%. After Steve Jobs’ return and the launch of the iMac, iPod, and iPhone, Apple reinvented itself. By 2024, its market valuation had increased by more than $3 trillion, showcasing the power of innovation and renewal.
- Netflix – Adapting Through Transformation: Originally a DVD rental company in 1997, Netflix shifted to streaming in 2007 and later to content production in 2013. This adaptability led to over 300 million subscribers globally by 2024, proving the importance of evolution through different business stages.
- Coca-Cola – Sustaining Growth Over a Century: Established in 1886, Coca-Cola’s continuous brand innovation and diversification into 500+ beverage products have kept it profitable, with annual revenues exceeding $47 billion. Its success highlights effective long-term growth and global expansion strategies.
Conclusion
The business life cycle is a continuous journey of evolution, learning, and adaptation. Each stage—startup, growth, maturity, expansion, and renewal—comes with unique challenges and opportunities that shape a company’s future. Long-term success depends on how effectively a business innovates, manages change, and responds to market dynamics. By understanding where they stand in the cycle, entrepreneurs can make smarter decisions, sustain growth, and build a resilient foundation for lasting success in a competitive business world.
FAQs
1. How long does each stage of the business life cycle last?
Answer: The duration varies depending on the industry, market conditions, and business strategy—ranging from months to several years.
2. Can a business experience multiple stages at once?
Answer: Yes, some parts of a company may be growing while others mature or decline simultaneously.
3. Is it possible to skip a stage in the business life cycle?
Answer: No, each stage naturally evolves from the previous one, though some may progress faster than others.
4. What role does technology play in the business life cycle?
Answer: Technology accelerates growth, improves efficiency, and helps businesses stay competitive at every stage.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on the Business Life Cycle helped you understand company growth stages. For more insights, explore these related articles below:

