What is Augmented Analytics?
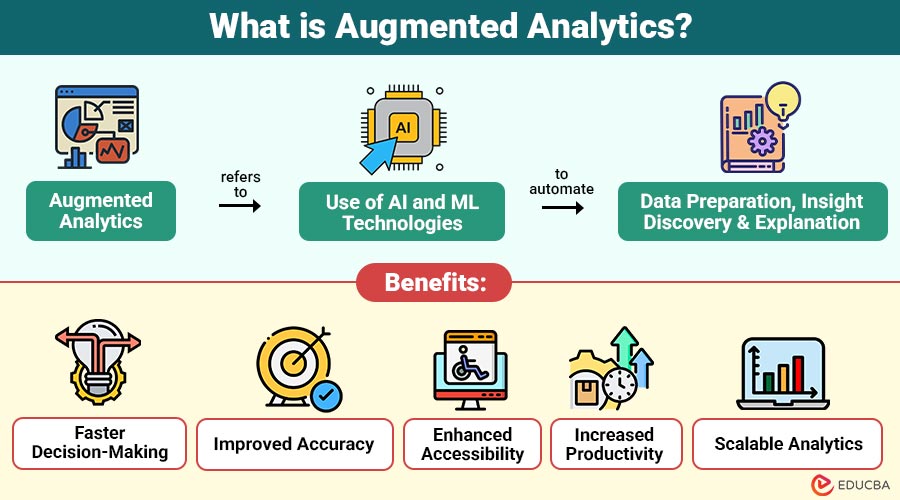
Augmented analytics refers to use of AI and ML technologies to automate data preparation, insight discovery, and explanation. Instead of relying solely on analysts to manually explore datasets, augmented analytics systems proactively identify trends, patterns, anomalies, and correlations.
Key Characteristics:
- Automates complex analytical tasks
- Uses AI-driven recommendations and predictions
- Enables natural language queries and explanations
- Democratizes analytics across the organization
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Augmented analytics automates data preparation and insight discovery using AI, reducing manual analysis and decision delays.
- It democratizes analytics by enabling non-technical users to easily and independently query data through natural language interfaces.
- Machine learning models proactively identify patterns, anomalies, and trends, supporting faster, more accurate business decisions enterprise-wide.
- Successful augmented analytics adoption requires high-quality data, transparent models, and skilled oversight to deliver trusted insights.
How Augmented Analytics Works?
Augmented analytics integrates multiple advanced technologies across the analytics lifecycle:
1. Data Preparation Automation
AI automatically cleans, classifies, enriches, and combines data from multiple sources, reducing manual effort, inconsistencies, and human errors.
2. Machine Learning–Driven Analysis
Machine learning models automatically examine historical and real-time data to uncover hidden patterns, trends, anomalies, and meaningful relationships.
3. Natural Language Processing
Users ask data-related questions in simple language, and the system delivers clear, contextual insights without requiring technical query skills.
4. Automated Insight Generation
The system proactively identifies key changes, trends, and anomalies, delivering actionable insights rather than relying on static dashboards.
5. Visualization and Storytelling
Insights are displayed through intuitive visuals and data narratives, helping users quickly understand findings and make informed decisions.
Key Components of Augmented Analytics
Here are the core components that make augmented analytics powerful and effective:
1. AI & Machine Learning
AI and machine learning automate data analysis, enable accurate forecasting, and detect anomalies without continuous manual intervention.
2. Natural Language Query
Natural language queries make analytics accessible to non-technical people by enabling them to interact with data in common language.
3. Natural Language Generation
Natural language generation transforms complex analytical insights into clear, readable narratives that support faster understanding and decision-making.
4. Automated Data Preparation
Automated preparation of data reduces the time and effort spent on data cleansing, transformation, and integration across many sources.
5. Predictive & Prescriptive Analytics
Predictive and prescriptive analytics forecast future outcomes and recommend optimal actions to improve business performance.
Difference Between Augmented Analytics and Traditional Analytics
Here is a comparison of the two approaches based on key aspects:
| Aspect | Augmented Analytics | Traditional Analytics |
| Data Preparation | Automated using AI | Manual and time-consuming |
| Skill Requirement | Low to moderate | High (analysts, data scientists) |
| Insight Discovery | AI-driven discovery | User-driven exploration |
| Speed | Faster and real-time | Slower |
| Accessibility | Available to all users | Limited to experts |
Use Cases of Augmented Analytics
Here are some key areas where augmented analytics is applied:
1. Business Intelligence & Reporting
Delivers real-time insights automatically, reducing dependence on BI teams and enabling faster, more informed business decisions.
2. Sales and Marketing Optimization
AI-driven analytics analyzes customer behavior, predicts churn, and recommends personalized marketing strategies to improve engagement and conversion rates.
3. Financial Forecasting
Finance teams employ predictive analytics to anticipate income, manage spending, identify financial risks, and support accurate strategic planning.
4. Supply Chain and Operations
Identifies demand changes, supplier risks, and operational inefficiencies early, enabling proactive supply chain decision-making.
5. Human Resources Analytics
HR teams analyze workforce data to predict attrition, evaluate employee performance, and enhance workforce planning and retention strategies.
Benefits of Augmented Analytics
Here are some key benefits organizations gain from using augmented analytics:
1. Faster Decision-Making
Automated insight discovery significantly reduces analysis time, enabling organizations to respond quickly and confidently to changing business conditions.
2. Improved Accuracy
AI-driven analytics minimizes human bias and manual errors, ensuring more consistent, reliable, and data-driven insights across the organization.
3. Enhanced Accessibility
Non-technical users can explore, analyze, and understand data easily using natural language queries and automated explanations.
4. Increased Productivity
Analysts spend less time on data preparation tasks and more time on strategic analysis, innovation, and high-value decision support.
5. Scalable Analytics
Platforms scale efficiently to handle increasing data volumes, users, and analytical complexity without performance degradation.
Challenges of Augmented Analytics
Despite its advantages, it also presents certain challenges:
1. Data Quality Dependency
Depends on high-quality data; inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data can produce misleading and unreliable insights.
2. Model Transparency
Certain AI-generated insights are difficult for people to fully trust because they don’t provide clear explanations.
3. Implementation Complexity
Deploying augmented analytics may require system upgrades, data integration efforts, and organizational change management initiatives.
4. Skill Gaps
Although automation reduces analyst workload, skilled professionals are still required to govern models, interpret results, and ensure accuracy.
Real-World Examples of Augmented Analytics
Here are some industries where augmented analytics is making a real impact:
1. Retail Industry
Retailers use augmented analytics to analyze customer purchasing patterns, optimize inventory levels, and improve demand forecasting.
2. Banking and Financial Services
Banks apply augmented analytics for fraud detection, credit risk assessment, and personalized financial recommendations.
3. Manufacturing
Manufacturers use predictive insights to reduce downtime, improve quality control, and enhance production planning.
Augmented Analytics Tools
Popular platforms offering augmented analytics capabilities include:
1. Microsoft Power BI
Microsoft Power BI uses AI-powered insights, natural language queries, and automated visualizations to support fast, data-driven business decisions.
2. Tableau
Tableau blends easy visual analytics with AI-driven recommendations, enabling users to explore data, find trends, and obtain insights rapidly.
3. Qlik Sense
Qlik Sense delivers associative analytics and AI-powered insight generation, helping users discover hidden relationships across complex datasets.
4. SAP Analytics Cloud
SAP Analytics Cloud integrates BI, predictive analytics, and planning capabilities to deliver intelligent insights across enterprise data environments.
5. IBM Cognos Analytics
IBM Cognos Analytics leverages AI-assisted data exploration and automated storytelling to provide reliable insights for enterprise-level decision-making.
Final Thoughts
Augmented analytics transforms how organizations use data by combining AI, machine learning, and natural language technologies to deliver actionable insights with minimal effort. It enables faster decisions, improves accuracy, and expands analytics access across teams. In today’s data-driven environment, augmented analytics is a strategic necessity, helping organizations anticipate trends, adapt to change, and achieve sustainable long-term growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is augmented analytics the same as business intelligence?
Answer: No. Augmented analytics enhances traditional BI by automating the discovery of insights using AI and ML.
Q2. Do organizations still need data analysts?
Answer: Yes. Analysts play a crucial role in governance, advanced modeling, and validating AI-generated insights.
Q3. Is augmented analytics suitable for small businesses?
Answer: Yes. Cloud-based platforms make augmented analytics accessible and cost-effective for organizations of all sizes.
Q4. What skills are required to use augmented analytics?
Answer: Basic data literacy is sufficient for most users, while advanced skills are required for system configuration and governance.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Augmented Analytics” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

