What is Attrition Management?
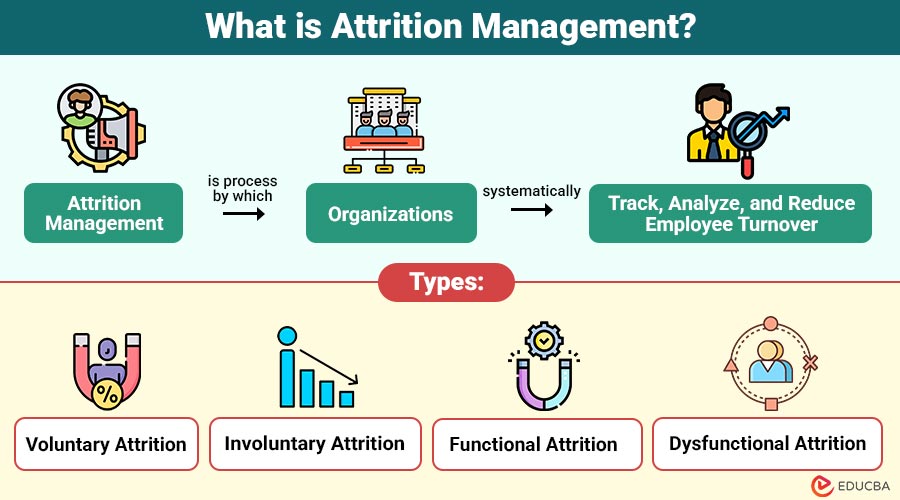
Attrition Management is the process by which organizations systematically track, analyze, and reduce employee turnover.
It involves identifying the reasons employees leave, implementing policies to enhance job satisfaction, and creating a work environment conducive to long-term engagement. Unlike reactive measures that only respond to resignations, attrition management is proactive, aiming to prevent unnecessary talent loss.
Attrition can be classified into different types:
- Voluntary Attrition—When employees leave by choice, often for better opportunities, career growth, or personal reasons.
- Involuntary Attrition—When the organization terminates employment due to performance issues, restructuring, or policy violations.
- Functional Attrition – Occurs when employees leaving the organization have a positive impact on overall performance.
- Dysfunctional Attrition—Occurs when the departure of skilled or high-performing employees negatively affects the organization.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Proactive attrition management reduces turnover costs, preserves knowledge, improves productivity, and strengthens long-term organizational stability and growth.
- Tracking key metrics enables data-driven decisions, early risk identification, and targeted retention strategies across teams organization-wide.
- Employee-centric policies, career development, and engagement initiatives significantly lower voluntary attrition and boost employee loyalty and commitment.
- Sustained leadership involvement and continuous feedback are essential for building trust and effectively maintaining workforce retention.
Importance of Attrition Management
Managing attrition is critical for organizations for several reasons:
1. Cost Savings
Hiring and training new employees involves substantial costs. Attrition management reduces unnecessary recruitment expenditure.
2. Employee Productivity
High turnover disrupts workflows and lowers team efficiency. Retaining employees ensures continuity and stability.
3. Knowledge Retention
Experienced employees carry institutional knowledge that is difficult to replace. Reducing attrition ensures valuable expertise remains within the organization.
4. Improved Employee Engagement
A focus on employee satisfaction and retention increases motivation, engagement, and loyalty.
5. Enhanced Employer Brand
Companies with low attrition rates are viewed as desirable workplaces that attract top talent.
Key Metrics in Attrition Management
Effective attrition management requires monitoring and analyzing relevant metrics. Key metrics include:
1. Attrition Rate
Calculates the proportion of workers who leave the company over a given time frame.
2. Retention Rate
Shows the proportion of workers who stay with the company for a predetermined amount of time, indicating workforce stability.
3. Average Tenure
Represents the average length of time employees stay with the organization, highlighting employee loyalty and career progression effectiveness.
4. Voluntary vs. Involuntary Attrition
Differentiates between employee-initiated exits (resignations) and organization-initiated exits (terminations, layoffs), thereby helping identify the root causes of turnover.
5. Exit Interview Insights
Provides qualitative data on employee departure reasons, such as compensation, leadership, workload, or career growth, enabling targeted retention strategies.
Common Causes of Employee Attrition
Understanding why employees leave is the first step in attrition management. Common reasons include:
1. Lack of Career Growth
Employees leave organizations that fail to provide clear career paths, opportunities for promotion, and ongoing professional development.
2. Inadequate Compensation
Non-competitive salaries and benefits reduce motivation, encouraging employees to seek better-paying opportunities elsewhere.
3. Poor Work-Life Balance
Excessive workloads and long hours lead to burnout, stress, and dissatisfaction, thereby increasing employee turnover.
4. Weak Organizational Culture
Poor leadership, limited recognition, and low engagement create dissatisfaction, reducing employee commitment and retention.
5. Better Opportunities
Competitive job markets attract skilled employees with higher pay, growth prospects, and flexible working conditions.
6. Lack of Training and Development
Limited learning opportunities hinder skill development, leading to disengagement and an increased likelihood of employee turnover.
Strategies for Effective Attrition Management
To manage attrition proactively, organizations can implement the following strategies:
1. Recruitment and Onboarding
Effective recruitment and structured onboarding ensure cultural fit, role clarity, and a smoother employee integration process.
2. Competitive Compensation and Benefits
Competitive compensation, incentives, and benefits improve satisfaction, motivation, loyalty, and long-term employee retention across all roles.
3. Career Development and Training
Clear career paths, continuous learning, mentoring, and skill development increase engagement and reduce voluntary attrition rates.
4. Employee Engagement
Regular feedback, recognition, teamwork, and open communication strengthen engagement, trust, and organizational commitment among all employees.
5. Work-Life Balance Initiatives
Flexible schedules, remote work, and wellness initiatives prevent burnout, improve morale, and support employee well-being consistently.
6. Performance Management
Transparent performance management, including feedback, recognition, and rewards, drives motivation, accountability, and retention across all teams.
7. Exit Analysis and Feedback
Exit interviews and feedback analysis reveal the causes of attrition, informing policy improvements and retention strategies for organizations.
Challenges in Attrition Management
While implementing attrition management strategies, organizations may face challenges such as:
1. Measuring Engagement and Satisfaction
Quantifying employee engagement and satisfaction is difficult because happiness, motivation, and perceptions vary widely across individuals.
2. Identifying True Causes
Employees may withhold honest feedback, making it difficult to identify the genuine reasons for voluntary attrition.
3. Changing Organizational Culture
Transforming organizational culture requires sustained leadership commitment, consistent behaviors, and long-term alignment across all levels of the organization.
4. Cost Constraints
Retention initiatives require significant long-term financial investment in training, rewards, technology, and employee well-being programs.
Real-World Examples
Here are some leading organizations that demonstrate effective attrition management practices in real-world scenarios:
1. Google
Offers career development programs, mentorship, flexible work options, and extensive benefits, resulting in high retention rates.
2. Microsoft
Uses employee engagement surveys and performance-based incentives to reduce voluntary attrition.
3. Salesforce
Focuses on employee wellness, diversity, and inclusion to enhance retention and workplace satisfaction.
Best Practices for Attrition Management
Here are proven best practices organizations can adopt to manage and reduce employee attrition effectively:
1. Proactive Monitoring
Continuously monitor attrition metrics and workforce trends to identify risks before issues escalate proactively.
2. Employee-Centric Policies
Develop employee-centric policies that address career growth, recognition, well-being, flexibility, and work-life balance expectations.
3. Transparent Communication
Maintain transparent communication about goals, expectations, career paths, and feedback channels to build trust.
4. Leadership Involvement
Encourage leaders and managers to engage regularly with teams and identify early signs of dissatisfaction.
5. Data-Driven Decisions
Leverage data analytics to identify attrition patterns and evaluate the effectiveness of retention initiatives.
Final Thoughts
Attrition management is critical for organizational stability, sustainable growth, and employee satisfaction. Understanding turnover drivers and implementing structured retention strategies helps organizations retain talent, reduce hiring costs, and enhance productivity. Proactive attrition management ensures employees feel valued, engaged, and motivated. Increasing loyalty and long-term excellence is an ongoing process that requires frequent monitoring, analysis, leadership commitment, and policy changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How can technology help in attrition management?
Answer: HR analytics, AI-based engagement tools, and performance monitoring software help track attrition trends and predict potential resignations.
Q2. What role does leadership play in reducing attrition?
Answer: Strong leadership ensures employee engagement, effective communication, recognition, and career growth, reducing voluntary attrition.
Q3. Is some attrition acceptable for organizations?
Answer: Yes, functional attrition allows underperforming employees to leave, thereby creating space for higher-performing talent.
Q4. How often should organizations review attrition rates?
Answer: Organizations should monitor attrition monthly or quarterly to address potential issues and refine retention strategies proactively.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Attrition Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

