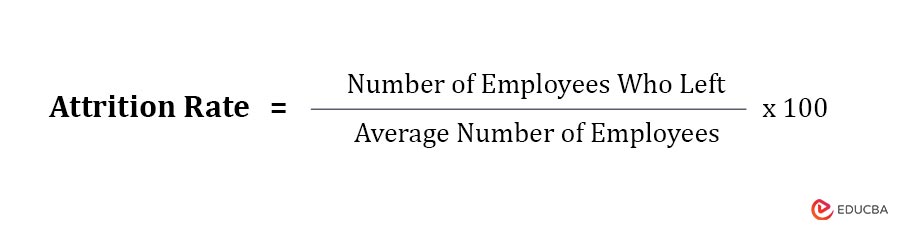
What is Attrition Analysis?
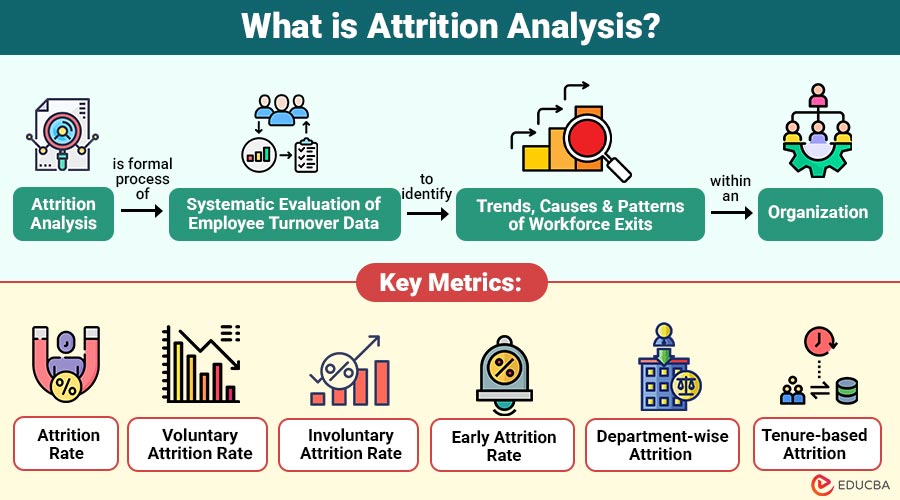
Attrition analysis is the systematic evaluation of employee turnover data to identify trends, causes, and patterns of workforce exits within an organization. It involves analyzing factors such as department, tenure, job role, compensation, performance ratings, engagement scores, and demographic data to determine why employees leave and how attrition impacts the organization.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Attrition analysis helps organizations identify workforce turnover patterns and implement effective employee retention strategies.
- Data-driven attrition insights reduce hiring costs while improving employee engagement and productivity levels.
- Predictive analytics tools empower HR teams to forecast turnover risks and strengthen long-term organizational stability.
- Effective attrition analysis uncovers root causes of employee exits and supports targeted retention initiatives.
Importance of Attrition Analysis
Here are the key reasons why attrition analysis is essential for organizational success and sustainable workforce management:
1. Reduces Hiring Costs
Attrition analysis finds out why employees leave, helping companies save money on hiring, training, and avoid repeated hiring.
2. Improves Employee Engagement
By analyzing exit interviews and feedback, organizations uncover the factors driving dissatisfaction, enabling targeted actions that improve morale, motivation, and overall engagement.
3. Enhances Workforce Planning
Attrition insights support accurate forecasting of staffing needs, ensuring businesses effectively align talent supply with long-term strategic goals.
4. Protects Organizational Knowledge
Reducing attrition keeps experienced employees, so the company retains important knowledge, skills, and expertise needed to succeed.
5. Strengthens Employer Branding
Lower attrition rates enhance company reputation, making organizations more attractive to prospective candidates and improving overall talent acquisition efforts.
Key Metrics in Attrition Analysis
To perform effective attrition analysis, organizations rely on several important HR metrics.
1. Attrition Rate
This metric measures percentage of employees leaving during a specific period.
2. Voluntary Attrition Rate
Voluntary attrition rate tracks employees who resign willingly, helping organizations understand satisfaction levels, career growth concerns, and workplace engagement issues.
3. Involuntary Attrition Rate
4. Early Attrition Rate
Early attrition rate captures employees leaving within the first year, signaling potential hiring mismatches, onboarding gaps, cultural misalignment, or expectations issues.
5. Department-wise Attrition
Department-wise attrition shows which teams have more employees leaving, helping managers spot problems like heavy workloads, low morale, or management issues.
6. Tenure-based Attrition
Tenure-based attrition analysis examines employee exits by service length, revealing retention issues at specific career stages or experience levels.
How Does Attrition Analysis Work?
Attrition analysis follows a structured approach:
Step 1: Data Collection
Collect employee data from HR systems, including demographics, compensation, performance ratings, exit interviews, and engagement surveys for comprehensive workforce insights.
Step 2: Data Cleaning
Step 3: Segmentation
Segment employee data by department, location, tenure, role, and other attributes to identify meaningful turnover patterns and workforce trends.
Step 4: Trend Analysis
Study past employee data to find patterns in people leaving the company. This helps identify busy seasons when more employees quit, departments with high turnover, and repeated reasons for leaving that may impact company stability.
Step 5: Root Cause Analysis
Apply statistical methods or predictive models to uncover underlying factors influencing attrition, such as compensation gaps or leadership issues.
Step 6: Strategy Implementation
Develop and implement targeted retention strategies, policies, and engagement initiatives based on insights derived from comprehensive attrition analysis.
Real-World Examples
Here are practical examples demonstrating how attrition analysis helps organizations reduce turnover effectively:
1. IT Company
An IT company noticed a 25% annual attrition rate among junior developers.
After analysis, HR discovered:
- Limited career growth opportunities
- High project workload
- Salary below industry benchmark
The company implemented:
- Structured career progression plans
- Mentorship programs
- Market-aligned salary revisions
Attrition was reduced to 15% within one year.
2. Retail Industry
A retail chain identified high attrition among frontline staff during festive seasons.
Root cause analysis showed excessive working hours and insufficient incentives.
The solution included:
- Flexible scheduling
- Performance bonuses
- Temporary staff support
This significantly improved retention rates.
Benefits of Attrition Analysis
Here are the key benefits that highlight why attrition analysis is crucial for effective workforce management and long-term organizational success:
1. Data-Driven Decisions
Enables HR teams to rely on analytics and insights instead of assumptions when creating workforce planning and retention strategies.
2. Cost Optimization
Reduces hiring, onboarding, and training expenses by identifying causes of turnover early and implementing proactive employee retention measures.
3. Improved Productivity
Keeps the team steady so work stays smooth, people work well together, morale is higher, and frequent employee changes don’t cause problems.
4. Higher Employee Satisfaction
Detects engagement gaps, workplace concerns, and trends in dissatisfaction, allowing organizations to improve culture and the employee experience.
5. Better Talent Retention
Protects important employees by spotting high-performing staff who may leave and helping the company take steps to retain them.
Challenges in Attrition Analysis
Despite its advantages, attrition analysis comes with challenges:
1. Data Quality Issues
Old, incomplete, or inconsistent HR records can cause wrong insights, poor predictions, and weak employee retention plans.
2. Privacy Concerns
Employee data should be handled carefully, following data protection laws and keeping information private to maintain trust within the organization.
3. Complex Causation
Employee attrition usually stems from multiple interconnected factors, making it difficult to accurately isolate specific causes.
4. Resistance to Change
Managers and leadership teams may hesitate to adopt data-driven recommendations, slowing implementation of effective retention initiatives.
Strategies to Reduce Attrition
Based on analysis insights, organizations can implement the following strategies:
1. Competitive Compensation
Make sure pay and benefits are in line with industry norms to draw in talent, keep staff, and lower the risk of turnover.
2. Career Development Programs
Provide continuous training, upskilling opportunities, mentorship, and defined career growth paths to enhance employee commitment.
3. Employee Engagement Initiatives
Conduct regular surveys, gather feedback, address concerns promptly, and create an inclusive workplace culture.
4. Work-Life Balance
Encourage remote work choices, flexible scheduling, and encouraging rules that assist staff in striking a balance between their personal and professional lives.
5. Strong Leadership
Effective managers foster trust, communicate transparently, support team development, and significantly influence employee satisfaction and retention.
Tools Used for Attrition Analysis
Several HR analytics tools help organizations perform attrition analysis effectively:
1. SAP SuccessFactors
A cloud-based HR system that helps companies track employee data, monitor turnover, manage performance, and use insights to keep employees happy and reduce resignations.
2. Workday
Provides real-time HR analytics, workforce planning tools, and dashboards that help organizations monitor turnover trends and employee engagement metrics.
3. Oracle HCM
Delivers comprehensive human capital management capabilities with advanced reporting, predictive analytics, and insights to manage and reduce attrition.
4. Power BI
Microsoft’s business intelligence tool that visualizes HR data, identifies attrition patterns, and supports data-driven workforce decisions.
5. Tableau
A user-friendly data tool that helps HR teams track attrition trends, create dashboards, and find useful insights.
6. Python and R
Programming languages are commonly used to analyze data, create prediction models, and build custom tools to forecast employee attrition.
Final Thoughts
Attrition analysis helps organizations understand employee turnover trends and implement proactive retention strategies. By studying employee data and finding the real reasons why people leave, companies can reduce hiring costs, increase employee happiness, and keep work running smoothly. In today’s data-focused world, businesses that use proper attrition insights instead of guesswork can build stronger teams and achieve long-term stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a good attrition rate?
Answer: A healthy attrition rate typically ranges between 10 and 15%, depending on the industry.
Q2. Is attrition always negative?
Answer: Not necessarily. Some attrition can create opportunities for restructuring and cost optimization.
Q3. How often should attrition analysis be conducted?
Answer: Quarterly or annually, depending on organizational size and workforce dynamics.
Q4. Which departments typically experience higher attrition rates?
Answer: Departments with heavy workloads, limited growth, or repetitive tasks—like sales, support, and IT—often see higher attrition rates.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Attrition Analysis” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.