What is Enterprise Performance Management (EPM)?
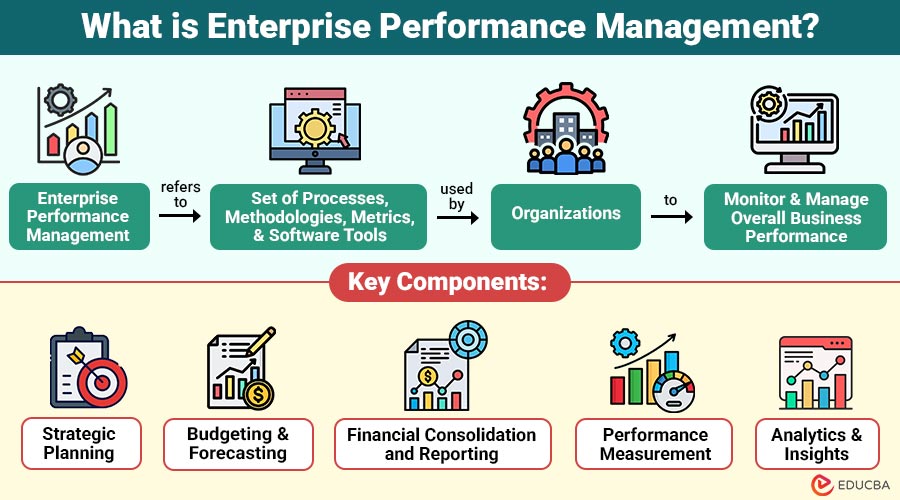
Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) refers to a set of processes, methodologies, metrics, and software tools used by organizations to monitor and manage overall business performance. It focuses on translating strategic goals into measurable outcomes and tracking progress through key performance indicators (KPIs).
EPM combines financial planning, budgeting, forecasting, reporting, and performance analysis into a unified framework. Unlike standalone financial systems, EPM provides a holistic view of organizational performance by connecting financial data with operational and strategic insights.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Enterprise Performance Management aligns organizational strategy with execution by integrating finance, operations, and analytics to deliver measurable performance outcomes.
- Advanced EPM tools enable real-time insights, scenario modeling, and predictive forecasting to support informed business decision-making.
- Using EPM improves financial control and transparency, increases accountability, and helps teams work faster and more efficiently.
- Future EPM trends include AI, cloud solutions, ESG integration, and self-service analytics for sustainable organizational growth.
Key Components of Enterprise Performance Management
Enterprise Performance Management consists of several interconnected components that work together to deliver accurate insights and strategic alignment.
1. Strategic Planning
Strategic planning sets long-term goals and clear targets. EPM helps align these goals with day-to-day operations and financial plans.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting distributes resources to achieve strategic objectives, whereas forecasting projects future financial performance based on historical data and present trends. To improve agility, contemporary EPM systems support rolling forecasts.
3. Financial Consolidation and Reporting
This component focuses on aggregating financial data from multiple departments or subsidiaries to ensure accurate, compliant, and transparent financial statements.
4. Performance Measurement
5. Analytics and Insights
Advanced analytics and dashboards help leaders see trends, risks, and opportunities quickly and make better decisions in real time.
How does Enterprise Performance Management Work?
Enterprise Performance Management integrates data from finance, HR, operations, sales, and other business functions into a unified platform. The process typically follows these steps:
1. Data Collection
Data collection aggregates financial, HR, operational, and sales data from internal systems and external sources accurately, securely, and consistently.
2. Data Standardization
Data standardization aligns formats, definitions, and metrics across departments, ensuring consistency, comparability, accuracy, and reliability for enterprise-wide reporting.
3. Analysis and Modeling
Analysis and modeling evaluate performance using KPIs, trends, scenarios, and predictive models to forecast outcomes effectively for planning.
4. Reporting and Insights
Reporting and insights deliver real-time dashboards, visualizations, and reports that clearly highlight variances, trends, and performance gaps.
5. Decision-Making
Decision-making leverages insights to support strategic and operational decisions, enabling agility, accountability, optimization, and continuous improvement across the organization.
Benefits of Enterprise Performance Management
Implementing enterprise performance management delivers significant benefits across the organization.
1. Improved Strategic Alignment
EPM aligns organizational goals across departments and teams, fostering collaboration, reducing silos, and ensuring every employee works toward unified objectives.
2. Better Decision-Making
Real-time analytics, predictive modeling, and comprehensive insights empower leaders to make informed, data-driven decisions with accuracy, confidence, and efficiency.
3. Enhanced Financial Control
Centralized budgeting, forecasting, and reporting improve financial accuracy, minimize errors, strengthen compliance, and enable better governance throughout the organization.
4. Increased Organizational Agility
Rolling forecasts, scenario analysis, and adaptive planning enable businesses to respond quickly to market shifts, opportunities, and emerging risks.
5. Transparency and Accountability
Clearly defined KPIs, dashboards, and performance metrics improve visibility, accountability, and ownership across all levels of the organization.
Use Cases of Enterprise Performance Management
Enterprise performance management is widely used across industries and business functions.
1. Financial Planning and Analysis
Finance teams leverage EPM to consistently and efficiently manage budgets, forecasts, financial reporting, and performance tracking across all organizational units.
2. Corporate Strategy Management
Executives use EPM to monitor strategic initiatives, measure progress against long-term objectives, and ensure organizational goals remain aligned effectively.
3. Operational Performance Tracking
Operations teams continuously and systematically utilize EPM metrics to optimize productivity, resource allocation, supply chain efficiency, and overall process performance.
4. Risk and Compliance Management
EPM ensures regulatory compliance by providing accurate reporting, audit readiness, risk monitoring, and reliable transparency throughout the organization.
Popular Enterprise Performance Management Tools
Several software vendors offer comprehensive Enterprise Performance Management solutions:
1. Oracle EPM Cloud
Provides sophisticated financial planning, reporting, analytics, and consolidation to help businesses make better decisions and streamline operations.
2. SAP Analytics Cloud
It helps businesses plan better, understand their data, predict future results, and improve how they work—all in one system.
3. IBM Planning Analytics
AI-driven forecasting, modeling, and scenario analysis help organizations predict trends, improve planning accuracy, and enhance overall business performance.
4. Workday Adaptive Planning
Cloud-based solution for planning, budgeting, and financial modeling, empowering businesses with scalable, flexible, real-time performance management capabilities.
5. Anaplan
It helps finance, sales, operations, and HR plan together, work as a team, align goals, and make better decisions using data.
Challenges in Implementing Enterprise Performance Management
Despite its benefits, EPM implementation can present challenges:
1. Data Integration Complexity
Combining data from different systems needs proper planning and checking to keep information accurate and consistent across the organization.
2. Change Management
Employees may resist adopting new processes, tools, and workflows, requiring training, communication, and leadership support for successful EPM implementation.
3. Cost and Resource Requirements
Implementing EPM solutions demands significant investment in software, infrastructure, skilled personnel, and ongoing maintenance across the organization.
4. Data Quality Issues
Inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data can undermine performance insights, leading to flawed decisions, reduced trust, and ineffective EPM results.
Future Trends in Enterprise Performance Management
The future of enterprise performance management is shaped by emerging technologies and evolving business needs.
1. AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Forecasting
AI and machine learning help organizations predict future trends more accurately, understand data better, and make early, smarter decisions.
2. Real-Time Performance Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of KPIs and metrics allows organizations to detect issues, optimize processes, and respond quickly to changes.
3. Integrated ESG and Sustainability Reporting
EPM now includes environmental, social, and governance measures, helping businesses operate responsibly, transparently, and sustainably worldwide.
4. Cloud-Based and Mobile EPM Solutions
Cloud and mobile EPM tools let teams work from anywhere, scale easily, share data, and collaborate better across locations.
5. Self-Service Analytics for Business Users
Without relying on IT departments, self-service analytics enables business users to analyze data, generate insights, and make defensible decisions.
Final Thoughts
Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) is essential for organizations pursuing sustainable growth and competitive advantage. By integrating strategy, finance, and analytics, EPM provides a comprehensive framework for managing performance effectively. Organizations that implement EPM achieve greater visibility, stronger financial control, and data-driven decision-making. Amid uncertainty and complexity, EPM remains vital for strategic success and operational excellence across all business functions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the primary purpose of EPM?
Answer: The primary purpose of EPM is to align strategy with execution by planning, measuring, and optimizing organizational performance.
Q2. Is EPM only for large enterprises?
Answer: While commonly used by large organizations, modern cloud-based EPM solutions are suitable for mid-sized and growing businesses as well.
Q3. How does EPM support decision-making?
Answer: EPM provides real-time insights, forecasts, and scenario analysis that enable informed, data-driven decisions.
Q4. What departments use EPM?
Answer: Finance, strategy, operations, HR, and executive leadership commonly use EPM systems.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Enterprise Performance Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
