What is an AI Pipeline?
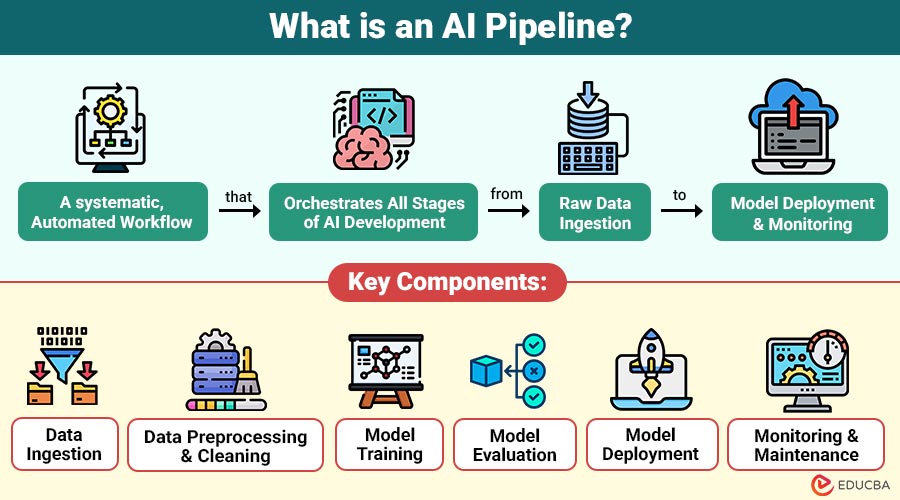
An AI pipeline is a systematic, automated workflow that orchestrates all the stages of AI development—from raw data ingestion to model deployment and monitoring. It ensures that every step in the AI lifecycle is executed efficiently, reproducibly, and reliably.
In simple terms:
- Traditional AI Development: Manual, ad hoc, error-prone, and time-consuming.
- AI Pipeline Approach: Structured, automated, scalable, and trackable.
An AI pipeline typically comprises several key stages: data collection, preprocessing, model training, evaluation, deployment, and ongoing monitoring.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- The AI pipeline transforms fragmented AI tasks into coordinated, automated workflows that support dependable, repeatable production systems.
- Good pipelines connect testing and production, providing structure, rules, and disciplined operations across teams.
- Ongoing monitoring checks models regularly to spot performance drops, data changes, or unusual behavior early, helping keep them accurate and reliable.
- Strategic pipeline adoption reduces long-term technical debt while accelerating innovation, scalability, and enterprise-wide AI maturity.
Importance of AI Pipelines
AI pipelines are critical to modern AI development for several reasons:
1. Automation and Efficiency
By automating repetitive operations like data pretreatment and model training, AI pipelines improve workflow efficiency, lower mistakes, and save time.
2. Scalability
Allows organizations to scale AI solutions across multiple datasets, models, and production environments without reinventing the wheel for each project.
3. Reproducibility
Standardized pipelines ensure that experiments can be repeated with consistent results—a crucial factor for research, compliance, and auditing.
4. Faster Time-to-Market
By streamlining the development process, AI pipelines enable quicker deployment of AI solutions, giving businesses a competitive edge.
5. Collaboration Across Teams
Provides a common framework for data scientists, engineers, and business stakeholders to work together efficiently.
Key Components of an AI Pipeline
It can vary depending on organization and use case, but most pipelines include the following essential components:
1. Data Ingestion
Data ingestion is the process of collecting and importing raw data from multiple sources, ensuring integrity, and preparing it for further processing in AI workflows.
Key Tasks:
- Extracting raw data from diverse sources
- Ensuring data integrity
- Handling real-time or batch ingestion
2. Data Preprocessing and Cleaning
Data preprocessing is the process of cleaning and preparing raw data—filling in missing values, fixing errors, adjusting formats, and creating useful features—so it’s ready for AI models to learn from effectively.
Key Tasks:
- Removing duplicates and inconsistencies
- Handling missing values
- Normalizing and scaling data
- Feature engineering
3. Model Training
Key Tasks:
- Selecting algorithms (e.g., regression, neural networks, decision trees)
- Splitting datasets into training, validation, and test sets
- Adjusting hyperparameters to achieve optimal machine learning performance
4. Model Evaluation
Model evaluation assesses AI model performance using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and cross-validation to ensure reliability and identify areas for improvement.
Key Tasks:
- Measuring accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, or other relevant metrics
- Performing cross-validation
- Conducting error analysis
5. Model Deployment
Model deployment places a validated AI model into production, integrating it with applications or APIs for real-time or batch predictions while ensuring scalability and availability.
Key Tasks:
- Packaging the model (e.g., containerization using Docker)
- Integrating with applications or APIs
- Ensuring scalability and availability
6. Monitoring and Maintenance
Monitoring and maintenance make sure an AI model keeps working properly by checking it, noticing changes, and updating it with new data.
Key Tasks:
- Tracking prediction accuracy over time
- Detecting model drift
- Updating or retraining models as new data becomes available
Types of AI Pipelines
Can be categorized based on workflow, automation, and purpose:
1. Batch Pipeline
2. Real-Time Pipeline
It processes data as it arrives, allowing real-time insights for use cases like fraud detection, recommendations, and IoT systems that need quick responses.
3. Automated Machine Learning Pipeline
Automates feature selection, model training, and hyperparameter tuning, reducing manual effort while accelerating efficient and effective machine learning development.
4. End-to-End Pipeline
Benefits of Implementing AI Pipelines
Implementing AI pipelines offers multiple benefits:
1. Consistency
AI pipelines standardize workflows, ensuring models are built, trained, and deployed uniformly, making processes repeatable.
2. Reduced Errors
Automation reduces human errors in handling data, preparing it, training models, and deploying AI systems effectively.
3. Cost Efficiency
Streamlined pipelines save resources and operational costs, improving AI development and deployment efficiency.
4. Continuous Improvement
Pipelines allow ongoing model training, evaluation, and updates to maintain accurate, relevant AI predictions.
5. Better Compliance
Organized AI workflows make it easy to track, review, and follow company rules and legal requirements.
Challenges in AI Pipeline Implementation
Despite their advantages, they are not without challenges:
1. Complexity in Design
Designing a robust AI pipeline requires deep expertise in data engineering, machine learning algorithms, DevOps practices, and workflow orchestration for reliable outcomes.
2. Data Quality Issues
Bad-quality data can mess up the whole AI process, because wrong, missing, or inconsistent data leads to models that give unreliable or incorrect predictions.
3. Integration Challenges
4. Monitoring and Maintenance Overhead
AI models require continuous monitoring for performance, bias, and drift, which adds operational complexity and ongoing maintenance requirements.
5. Resource Requirements
Big AI pipelines need lots of computing, storage, and infrastructure, raising costs and making resource management harder.
Real-World Applications of AI Pipelines
AI pipelines are used across industries to deliver powerful solutions:
1. Finance
- Fraud Detection
- Algorithmic Trading
- Credit Scoring
2. Retail
- Personalized Recommendations
- Inventory Optimization
- Demand Forecasting
3. Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance
- Quality Control
- Supply Chain Optimization
4. Transportation
- Route Optimization
- Self-Driving Vehicles
- Real-Time Traffic Management
Best Practices for AI Pipeline Development
Below are key best practices for designing scalable, reliable, and efficient AI pipelines from development to production.
1. Start Small, Scale Gradually
Build a minimal AI pipeline first to reduce risk, validate assumptions, and expand complexity as data, requirements, and maturity grow.
2. Automate Where Possible
MLOps tools help AI work automatically by collecting data, teaching the model, testing it, and putting it to use, making AI faster, more reliable, and easier to improve.
3. Focus on Data Quality
Make sure the data is clean, correct, and properly labeled by removing errors, fixing mismatches, and checking data sources so the model works reliably.
4. Incorporate Version Control
Apply version control to code, data, and models for reproducibility, collaboration, experiment tracking, and easy rollback across pipeline stages.
5. Monitor Continuously
Track performance, accuracy, drift, and bias continuously using metrics and alerts to maintain reliable and trustworthy production models.
Final Thoughts
AI pipeline forms the foundation of modern AI development, transforming experimental models into scalable, production-ready solutions. Automating data processing, model training, deployment, and monitoring makes AI systems faster, more reliable, and able to handle more work. It also reduces mistakes, saves time and money, and helps businesses stay competitive as AI use grows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is an AI pipeline different from a traditional ML workflow?
Answer: An AI pipeline is automated, scalable, and integrates all stages from data ingestion to deployment and monitoring. Traditional ML workflows are often ad hoc, manual, and less reproducible.
Q2. What tools are commonly used to build AI pipelines?
Answer: Popular tools include Kubeflow, MLflow, Apache Airflow, TFX (TensorFlow Extended), Prefect, and DataRobot. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud also offer managed AI pipeline services.
Q3. Can AI pipelines handle real-time data?
Answer: Yes, real-time pipelines process streaming data for immediate predictions. Use cases include fraud detection, autonomous vehicles, and real-time recommendation systems.
Q4. Why is monitoring important in AI pipelines?
Answer: Monitoring detects model drift, performance degradation, and errors, ensuring the AI system remains accurate, reliable, and unbiased over time.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “AI Pipeline” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

