What is Cognitive Computing?
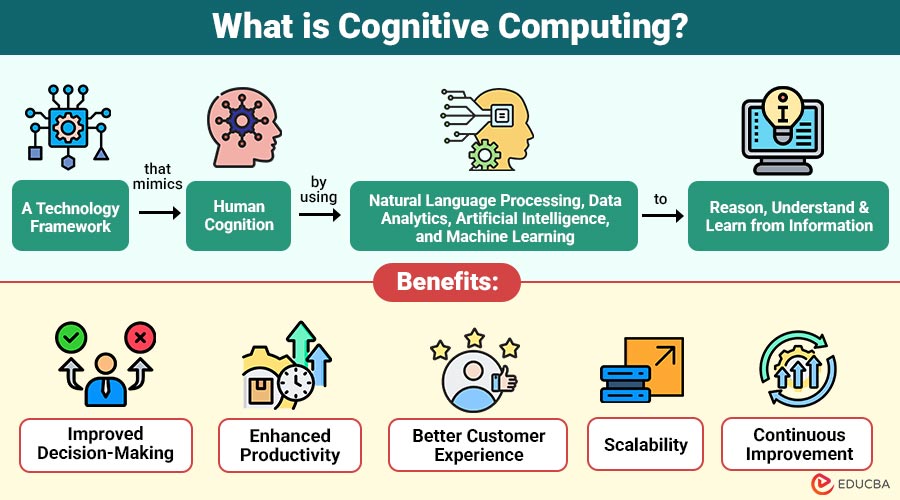
Cognitive computing is a technology framework that mimics human cognition by using natural language processing, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to reason, understand, and learn from information.
These systems are not programmed with fixed answers. Instead, they analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, identify patterns, interpret meaning, and provide probabilistic recommendations rather than absolute conclusions.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Characteristics
- Core Components
- Working
- Use Cases
- Benefits
- Limitations
- Real-World Examples
- Future Trends
Key Takeaways:
- Cognitive computing mimics human reasoning to analyze data, learn continuously, and support smarter decisions effectively.
- It augments humans through context awareness, language understanding, and probabilistic insights rather than fixed answers.
- Successful cognitive systems depend on high-quality data, ethical governance, transparency, and ongoing model improvement efforts.
- Industries use cognitive computing to boost efficiency, personalize services, scale operations, and support better business decisions.
Key Characteristics of Cognitive Computing
Cognitive computing systems differ significantly from conventional software systems due to the following key characteristics:
1. Learning Capability
2. Natural Language Understanding
They understand and process human language, including text and speech, enabling natural, conversational interactions with users.
3. Reasoning and Decision Support
They analyze possibilities, evaluate evidence, and recommend outcomes supported by confidence scores for informed decision-making.
4. Context Awareness
They incorporate user behavior, environmental factors, and historical trends to deliver relevant, context-aware responses effectively.
5. Human–Machine Collaboration
Cognitive systems augment human intelligence by supporting decisions and insights rather than fully replacing human judgment.
Core Components of Cognitive Computing
The following components work together to enable cognitive systems to learn, reason, and interact intelligently:
1. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence provides foundational capabilities that enable machines to perform complex tasks requiring reasoning, perception, and human-like thinking.
2. Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data, identify patterns, learn relationships, and continuously improve predictions and system performance.
3. Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing enables systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language for chatbots, voice assistants, and analysis.
4. Big Data Analytics
Massive amounts of organized and unstructured data from many sources, such as text, photos, videos, and sensors, are processed via big data analytics.
5. Knowledge Representation
Knowledge representation structures information to support reasoning, inference, relationships, and contextual understanding across cognitive computing systems.
How Cognitive Computing Works?
The working can be understood in the following key stages:
1. Data Ingestion
The system gathers data from diverse sources, including databases, documents, emails, images, and social media platforms.
2. Understanding
NLP and computer vision techniques interpret meaning, sentiment, context, and user intent within incoming data streams.
3. Reasoning
The system evaluates alternatives, weighs evidence, applies learned models, and derives informed conclusions with confidence.
4. Learning and Feedback
Continuous learning incorporates human feedback and new data to refine models, accuracy, and recommendations over time.
Use Cases of Cognitive Computing
Here are some key use cases that show how cognitive computing is applied across different industries to solve complex problems and improve decision-making.
1. Healthcare
Helps doctors analyze records, literature, and diagnostics, suggesting treatments, improving accuracy, and detecting diseases earlier.
2. Banking and Finance
Banks use cognitive systems for fraud detection, risk assessment, chatbots, and personalized financial recommendations.
3. Customer Service
AI virtual assistants understand customer queries, deliver instant responses, reduce workload, and significantly improve service efficiency.
4. Retail and E-commerce
Retailers use cognitive computing for product recommendations, dynamic pricing, demand forecasting, and enhanced customer experiences.
5. Manufacturing
Cognitive systems predict equipment failures, optimize supply chains, and enhance quality control using intelligent analytics.
Benefits of Cognitive Computing
Below are the key benefits that highlight how cognitive computing enhances intelligence, efficiency, and adaptability across organizations.
1. Improved Decision-Making
Delivers data-driven insights that support complex, high-stakes decisions, enabling more accurate, informed, and confident outcomes.
2. Enhanced Productivity
It automates knowledge-intensive, repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on strategic, creative, and value-added work effectively.
3. Better Customer Experience
Cognitive systems enable personalized, context-aware, seamless interactions across digital channels, improving satisfaction, engagement, and long-term customer loyalty.
4. Scalability
These systems handle increasing data volumes and complexity efficiently, without requiring proportional growth in human resources or effort.
5. Continuous Improvement
Cognitive computing continuously learns from feedback and outcomes, refining models, predictions, and recommendations for greater accuracy over time.
Limitations of Cognitive Computing
Despite its advantages, cognitive computing also faces several limitations:
1. Data Quality Issues
Poor, incomplete, or biased datasets reduce model accuracy, reliability, and fairness, ultimately undermining trustworthy cognitive computing outcomes globally.
2. High Implementation Costs
Building, deploying, and maintaining cognitive systems demands substantial infrastructure, skilled talent, training, integration efforts, and ongoing operational expenses.
3. Interpretability
Complex cognitive models often function as black boxes, limiting transparency, trust, regulatory compliance, and clear explanation of decisions.
4. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Processing sensitive personal data introduces risks around privacy breaches, biased outcomes, consent violations, security failures, and ethical misuse.
Real-World Examples of Cognitive Computing
The following examples demonstrate how cognitive computing is applied in real-world systems to deliver intelligent, context-aware, and data-driven solutions.
1. IBM Watson
Supports healthcare, finance, and customer service by analyzing complex data to deliver intelligent decision support insights.
2. Google Assistant and Alexa
Use cognitive computing to understand speech, context, and user intent and deliver personalized, conversational responses.
3. Fraud Detection Systems
Continuously analyze transaction patterns in real time to detect anomalies, prevent fraud, and reduce financial losses.
4. Enterprise Search Engine
Go beyond keywords by understanding context, intent, and meaning to deliver precise, relevant business answers.
Future Trends in Cognitive Computing
The following trends highlight how cognitive computing is evolving to become more collaborative, transparent, specialized, and responsible in real-world applications.
1. Deeper Human-AI Collaboration
Cognitive systems will function as intelligent co-workers, augmenting human judgment, creativity, productivity, and complex decision-making processes.
2. Explainable Cognitive Models
Future cognitive systems will emphasize transparency, interpretability, trust, and clear reasoning behind automated decisions.
3. Industry-Specific Cognitive Solutions
Customized cognitive platforms will address unique challenges, regulations, workflows, and data needs across specialized industry domains.
4. Integration with IoT and Edge Computing
Cognitive intelligence will analyze data at the edge, delivering faster real-time insights while minimizing delays and response time.
5. Ethical and Responsible AI
Robust governance frameworks will prioritize fairness, privacy protection, accountability, compliance, and responsible deployment of cognitive systems.
Final Thoughts
Cognitive computing marks the next evolution of intelligent systems, blending human-like understanding with advanced machine capabilities. Cognitive computing learns from data, understands context, and makes smart predictions to improve decisions, efficiency, and personalization. As data and AI advance, it will power digital transformation, helping early adopters gain a strong competitive edge in a knowledge-driven global business environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is cognitive computing the same as AI?
Answer: No. Cognitive computing is a specialized approach within AI focused on mimicking human reasoning and supporting decisions.
Q2. Does cognitive computing replace humans?
Answer: No. It is designed to augment human intelligence, not replace it.
Q3. What industries benefit most from cognitive computing?
Answer: Healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and customer service benefit significantly.
Q4. What type of data does cognitive computing use?
Answer: Cognitive computing uses both structured data (databases, spreadsheets) and unstructured data (text, images, audio, videos, and social media content).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cognitive Computing” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

