What are Autonomous Agents?
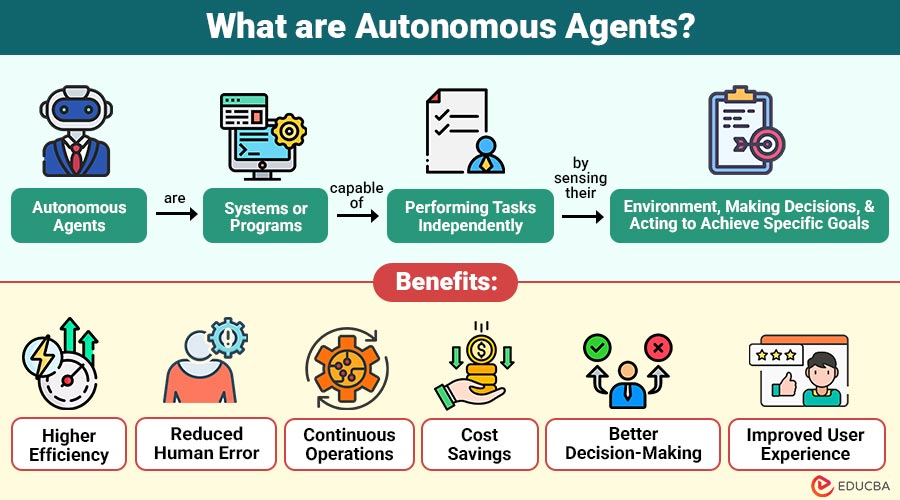
Autonomous agents are systems or programs capable of performing tasks independently by sensing their environment, making decisions, and acting to achieve specific goals. They combine artificial intelligence, decision-making logic, and automation to perform complex tasks with minimal human interference.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Autonomous agents independently perceive, decide, and act, enabling intelligent automation across diverse industries and applications.
- Their effectiveness relies on key characteristics like autonomy, learning, adaptability, and goal-oriented decision-making.
- Different agent types support a range of use cases, from simple reactive systems to complex multi-agent environments.
- Successful adoption requires balancing efficiency gains with ethical, security, data quality, and implementation challenges.
Characteristics of Autonomous Agents
It exhibits several characteristics:
1. Autonomy
Perform tasks independently, making decisions and acting without needing step-by-step human instructions.
2. Reactivity
Agents can detect changes in their environment and respond quickly to unforeseen events or real-time inputs
3. Proactiveness
They anticipate future situations and take preemptive actions rather than only reacting to current circumstances.
4. Social Ability
Some agents can communicate, collaborate, or coordinate effectively with humans, other agents, or external systems.
5. Goal-Oriented Behavior
Agents are programmed to achieve specific objectives through autonomous, self-directed actions and decision-making.
6. Learning Capability
Advanced agents leverage machine learning techniques to autonomously improve decisions, behaviors, and performance over time.
7. Adaptability
Agents dynamically adjust strategies and behaviors in response to new information, environmental changes, or operational constraints.
How Autonomous Agents Work?
The architecture of an autonomous agent generally includes the following components:
1. Perception Layer
Collects data from sensors, APIs, logs, or streams, understanding the environment for informed agent decisions.
2. Reasoning and Decision-Making Layer
Analyzes goals, constraints, and potential actions using AI models, rules, and heuristics to select optimal solutions autonomously.
3. Planning Module
Creates action sequences to achieve long-term objectives, applied to robotics, navigation, and complex, critical tasks.
4. Action Layer
Carries out selected actions, such as robotic movement, API commands, or software dashboard updates, effectively.
5. Learning Module
Applies machine learning or reinforcement learning to improve strategies, decisions, efficiency, and accuracy over time.
6. Communication Interface
Facilitates interaction with humans, other agents, or software systems, ensuring smooth collaboration and information exchange.
Types of Autonomous Agents
It can be broadly classified into several types:
1. Reactive Agents
- Respond immediately to environmental inputs without complex reasoning
- Do not maintain memory or internal world models
- Commonly used in simple automation and basic navigation systems
2. Deliberative Agents
- Use internal models to reason about the environment
- Perform planning and strategic decision-making
- Suitable for complex systems like robotics and autonomous vehicles
3. Hybrid Agents
- Combine fast reactive responses with deliberate planning capabilities
- Balance short-term reactions and long-term goals
- Used in real-world systems requiring flexibility and efficiency
4. Learning Agents
- Improve performance through experience and feedback
- Apply machine learning or reinforcement learning techniques
- Widely used in recommendation engines, chatbots, and fraud detection
5. Multi-Agent Systems
- Consists of multiple autonomous agents interacting with each other
- Enable cooperation, coordination, or competition among agents
- Applied in swarm robotics, smart grids, and distributed simulations
6. Autonomous Robotic Agents
- Physical agents capable of sensing, movement, and decision-making
- Operate independently in real-world environments
- Used across manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and exploration
Examples of Autonomous Agents in Real World
Autonomous agents are already transforming industries. Some widely used examples include:
1. Self-Driving Cars (e.g., Tesla Autopilot, Waymo)
- Sense environment
- Predict obstacles
- Navigate routes autonomously.
2. Virtual Personal Assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa)
- Understand voice commands
- Respond intelligently
- Automate user tasks.
3. AI Chatbots
- Handle customer queries
- Learn user patterns
- Improve service quality.
4. Trading Bots in Finance
- Analyze markets
- Execute high-frequency trades
- Optimize investment strategies.
5. Warehouse Robots (e.g., Amazon Kiva Robots)
- Navigate warehouses
- Transport inventory autonomously.
Benefits of Autonomous Agents
It offers multiple benefits that enhance efficiency, accuracy, scalability, and overall business performance across industries.
1. Higher Efficiency
Agents automate repetitive and complex tasks faster than humans, significantly improving productivity and operational speed.
2. Reduced Human Error
Eliminates mistakes caused by fatigue, inconsistency, oversight, and manual errors in process operations.
3. Continuous Operations
Operates continuously, 24/7, with no breaks, downtime, or performance degradation across systems and services.
4. Cost Savings
Automation reduces labor costs, operational expenses, resource wastage, and long-term business overheads.
5. Better Decision-Making
AI-driven autonomous agents analyze data, apply logic, predict outcomes, and deliver faster, accurate decisions consistently.
6. Improved User Experience
Autonomous agents, such as chatbots, deliver faster responses, personalized interactions, and consistent support experiences across channels.
Challenges of Autonomous Agents
Although powerful, it comes with certain challenges:
1. Ethical Concerns
2. Data Privacy Risks
Rely heavily on data, increasing risks of misuse, breaches, and privacy violations.
3. Technical Complexity
Designing autonomous agents that understand context, adapt dynamically, and learn effectively remains technically challenging.
4. Dependency on High-Quality Data
Biased, incomplete, or poor-quality data can lead autonomous agents to make incorrect decisions.
5. High Implementation Costs
Building, deploying, and maintaining large-scale autonomous systems requires significant financial and technical resources.
6. Security Threats
It may be vulnerable to hacking, manipulation, and adversarial attacks.
Final Thoughts
Autonomous agents are transforming intelligent automation by independently sensing, learning, planning, and acting across industries. As AI advances, it will evolve into a complex problem solver, driving innovation, efficiency, and scalability. Organizations adopting autonomous agents can boost productivity, reduce errors, and enhance customer experiences, enabling smarter businesses, cities, and data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Do autonomous agents replace human jobs?
Answer: They automate repetitive tasks but also create roles in supervision, AI training, and system management.
Q2. Can autonomous agents work together in complex environments?
Answer: Yes, through multi-agent systems, autonomous agents collaborate, coordinate, or compete to solve complex, distributed problems efficiently.
Q3. What skills are needed to build autonomous agents?
Answer: AI, machine learning, programming (Python), robotics, data science, and systems engineering.
Q4. Are autonomous agents safe?
Answer: With proper design, testing, and regulation, they are safe—but cybersecurity and ethics must be addressed.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Autonomous Agents” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

