What is Geospatial Analytics?
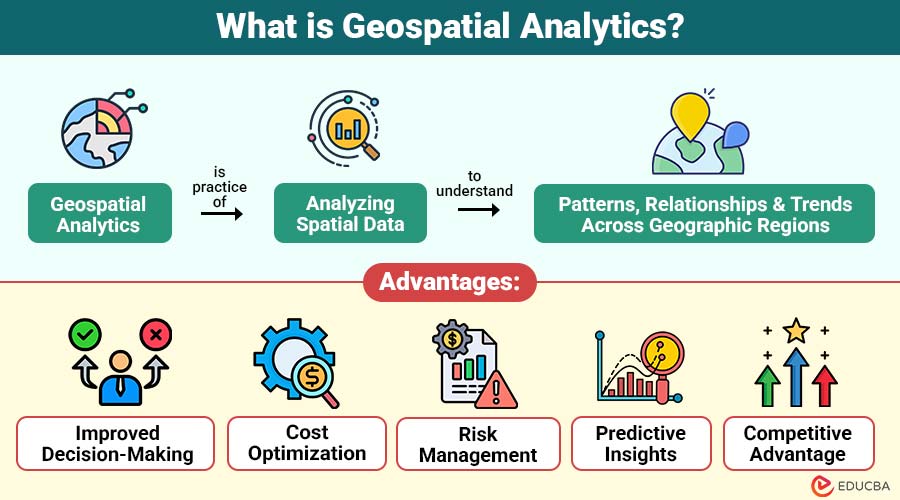
Geospatial analytics is the practice of analyzing spatial data to understand patterns, relationships, and trends across geographic regions. It involves using data linked to specific locations—such as coordinates, postal codes, or satellite imagery—and applying statistical and computational methods to derive actionable insights.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Geospatial analytics reveals hidden geographic patterns, supporting smarter planning, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making across industries.
- Integrating spatial and non-spatial data enhances real-time understanding of environmental, social, and economic dynamics.
- Advanced technologies like AI, cloud computing, and remote sensing enable faster, more accurate location-based insights.
- Businesses and governments gain competitive advantages by leveraging geospatial intelligence for risk management and operational efficiency.
Key Components of Geospatial Analytics
Here are the key components that make up geospatial analytics and drive actionable location-based insights:
1. Spatial Data
Spatial data represents information connected to geographic locations, such as coordinates, polygons, or defined regional boundaries.
2. GIS Platforms
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) platforms such as ArcGIS and QGIS enable mapping, visualization, and advanced analysis of spatial data.
3. Data Processing and Modeling
Algorithms process spatial datasets to detect meaningful patterns, trends, relationships, and anomalies for informed decision-making.
4. Visualization
Spatial data is visualized using heatmaps, contour maps, interactive dashboards, and other tools to provide intuitive geographic insights.
How Geospatial Analytics Works?
Geospatial analytics typically involves the following steps:
1. Data Collection
Data is collected from satellites, drones, IoT devices, GPS systems, sensors, and various public datasets.
2. Data Preprocessing
Raw spatial data is cleaned, standardized, transformed, and formatted to ensure accuracy and usability for analysis.
3. Integration
Spatial data are combined with non-spatial datasets, including demographic, financial, and environmental information, to yield richer insights.
4. Analysis
Spatial clustering, hotspot detection, geostatistics, and predictive modeling techniques are applied to extract patterns and trends.
5. Visualization and Reporting
Insights are shared using easy-to-understand maps, dashboards, and charts, helping people make better and faster decisions.
Key Technologies in Geospatial Analytics
Geospatial analytics relies on a variety of technologies to process and analyze spatial data efficiently:
1. Geographic Information Systems
GIS platforms enable the storage, management, analysis, and visualization of spatial data to enhance geographic understanding.
2. Remote Sensing
Satellites and drones capture imagery and data about Earth’s surface for analysis and mapping purposes.
3. Global Positioning Systems
GPS provides precise location information for mobile devices, vehicles, and physical assets in real time.
4. Big Data Analytics
Tools like Apache Spark and Hadoop process, analyze, and manage vast geospatial data efficiently.
5. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
AI and ML models accurately detect patterns and make predictions from complex spatial datasets.
6. Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms provide scalable storage, processing power, and collaboration capabilities for large, dynamic geospatial datasets.
Applications of Geospatial Analytics
Geospatial analytics has far-reaching applications across industries, including business, government, healthcare, transportation, and environmental management.
1. Urban Planning and Smart Cities
City planners use geospatial analytics to optimize land use, improve traffic management, plan public transport routes, and design smart infrastructure.
2. Supply Chain and Logistics
Companies use location analytics to optimize routes, reduce delivery times, manage warehouses, and track fleet movement in real time.
3. Retail and Marketing
Retailers analyze customer locations, competitor distribution, and foot-traffic patterns to identify optimal store locations and target marketing campaigns.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Geospatial data helps monitor deforestation, water pollution, the impacts of climate change, and areas at risk of natural disasters.
5. Defense and Security
Military and intelligence agencies use geospatial analytics for surveillance, threat assessment, and mission planning.
Advantages of Geospatial Analytics
Here are the key advantages organizations gain by leveraging geospatial analytics for location-based decision-making:
1. Improved Decision-Making
Geospatial analytics provides actionable insights based on location data, helping organizations make more informed and effective decisions.
2. Cost Optimization
By analyzing spatial data, businesses can optimize routes, allocate resources efficiently, and streamline logistics, thereby reducing costs.
3. Risk Management
It helps identify potential risks across urban planning, environmental monitoring, and business operations, enabling proactive measures to mitigate them.
4. Predictive Insights
Using spatial modeling and AI, geospatial analytics can anticipate trends and patterns, enabling organizations to plan strategically for the future.
5. Competitive Advantage
Geospatial insights enhance market analysis, customer targeting, and strategic planning, giving businesses a competitive advantage.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable examples of how organizations effectively use geospatial analytics:
1. Uber
Uber employs geospatial analytics to efficiently match drivers with riders and optimize dynamic pricing based on location patterns.
2. Amazon
Amazon leverages location data to place warehouses strategically, optimize delivery routes, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
3. NASA
NASA utilizes remote sensing and spatial analytics to monitor climate change, track disasters, and study Earth’s ecosystems.
4. Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University created COVID-19 dashboards using geospatial data to track infections globally and inform policy decisions.
Challenges in Geospatial Analytics
While geospatial analytics offers tremendous benefits, it also comes with challenges:
1. Data Quality and Accuracy
Inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated location data can lead to misleading insights and poor decision-making.
2. Complexity of Data Integration
Integrating spatial and non-spatial datasets requires specialized technical expertise and advanced data management skills for accuracy.
3. High Computational Requirements
Analyzing large geospatial datasets requires substantial computing power, storage, and optimized infrastructure to enable efficient processing.
4. Privacy Concerns
Collecting and utilizing location data involves ethical, legal, and regulatory considerations to protect individual privacy rights.
Final Thoughts
Geospatial analytics transforms data into actionable location-based insights. By leveraging GIS, AI, big data, and cloud computing, organizations optimize operations, manage risks, and make smarter decisions. Real-time spatial analytics combined with predictive modeling is revolutionizing sectors such as urban planning, healthcare, agriculture, and defense. Beyond maps, it enables a deeper understanding of the world through data, location, and context, driving digital transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What types of data are used in geospatial analytics?
Answer: Data types include vector data (points, lines, and polygons), raster data (satellite imagery), GPS coordinates, IoT sensor data, and demographic or environmental datasets.
Q2. Which industries benefit most from geospatial analytics?
Answer: Urban planning, logistics, retail, healthcare, agriculture, environmental management, defense, and disaster management are major beneficiaries.
Q3. What is the role of AI in geospatial analytics?
Answer: AI helps detect patterns, predict outcomes, classify images, and automate decision-making based on spatial data.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Geospatial Analytics” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.