What is Model Drift?
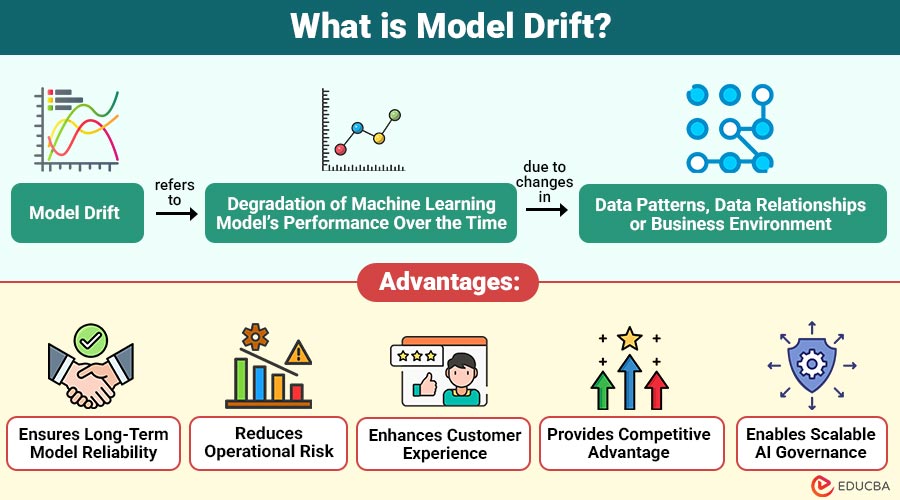
Model drift refers to degradation of machine learning model’s performance over the time due to changes in data patterns, data relationships, or the business environment. Even a perfectly trained model becomes outdated when the real world shifts away from the original training conditions.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Types
- Causes
- How to Detect Model Drift?
- How to Prevent Model Drift?
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Model drift reduces prediction accuracy over time, making continuous monitoring and retraining essential for reliability.
- Detecting drift early prevents operational failures and mitigates risks in dynamic business and technical environments.
- Proactive drift management ensures AI models adapt to changing data patterns, maintaining long-term effectiveness.
- Combining automated monitoring, robust pipelines, and domain expertise strengthens model resilience against evolving real-world conditions.
Why is Model Drift Important?
Here are key reasons that highlight the importance of monitoring and managing in production systems:
1. Accuracy
It helps maintain stable prediction quality by monitoring performance changes and identifying deviations caused by evolving data patterns.
2. Risk Reduction
Detection minimizes losses by preventing flawed predictions from impacting business decisions, operations, and sensitive security-related systems.
3. Trust
Regular drift monitoring ensures predictions remain reliable, promoting user confidence and supporting the adoption of AI-driven decision-making processes.
4. Governance
Detecting drift helps ensure regulatory compliance, supports transparent documentation, supports audit readiness, and enables proper lifecycle management for deployed models.
5. Retraining
Identifying drift early signals the need for updates, ensuring models are retrained on current data to maintain effectiveness.
Types of Model Drift
It can occur in multiple forms. The three major types include
1. Data Drift
When the distribution of input data shifts while the predicted output stays constant, this is known as data drift.
2. Concept Drift
When the relationship between inputs and outputs shifts, concept drift happens. To put it simply, the meaning of the target variable evolves.
3. Label Drift
Occurs when the distribution of target classes changes, affecting model predictions over time.
Causes of Model Drift
It results from internal and external factors that gradually degrade a model’s predictive performance.
1. Seasonal or Temporal Changes
Holidays, weather variations, and seasonal habits regularly change user behavior, significantly impacting model predictions over time.
2. Market and Economic Shifts
Inflation, recessions, regulatory changes, pandemics, and global events continuously modify user patterns, causing model performance to drift.
3. Evolving User Preferences
Customer interests, needs, and consumption habits constantly evolve, resulting in outdated models that fail to reflect them accurately.
4. Technological Upgrades
The introduction of new devices, sensors, or platforms can change data formats, affecting models trained on previous datasets.
5. Data Quality Issues
Missing data, noisy signals, or hardware failures introduce inconsistencies, leading models to produce inaccurate or unreliable predictions.
How to Detect Model Drift?
Detecting drift early is essential for maintaining model health. Some of the key methods include:
1. Performance Monitoring
Track metrics such as accuracy, F1 score, or RMSE continuously; consistent declines over time indicate potential model drift.
2. Statistical Drift Detection
Use tests such as the KS Test, PSI, Chi-Square Test, or Jensen–Shannon Divergence to compare distributions of datasets.
3. Concept Drift Detectors
Algorithms such as ADWIN, DDM, and EDDM identify changes in the relationships between features and targets over time.
4. Monitoring Feature Importance
Observe sudden changes in feature contributions; shifts often indicate evolving user behavior that affects model predictions.
5. Shadow Deployment
Deploy the new model alongside the production version; compare outputs to detect performance differences or unexpected deviations.
How to Prevent Model Drift?
It can be mitigated through proactive monitoring and maintenance.
1. Scheduled Model Retraining
Retrain models periodically—weekly, monthly, or quarterly—based on industry requirements to maintain prediction accuracy over time.
2. Continuous Learning Pipelines
Automate data ingestion, training, validation, and deployment using MLOps tools like MLflow, Kubeflow, SageMaker, and Vertex AI.
3. Incremental Learning
Allow models to learn incrementally from new data, reducing the need for full retraining while maintaining accuracy.
4. Ensemble Modeling
Combine multiple models’ predictions to reduce sensitivity to drift and consistently improve overall prediction robustness.
5. Data Quality Monitoring
Continuously track missing values, schema changes, and outliers to prevent inconsistencies affecting model performance and reliability.
Advantages of Managing Model Drift
Here are the key advantages:
1. Ensures Long-Term Model Reliability
Proactive drift management maintains consistent model performance over time, ensuring reliable predictions across evolving data patterns.
2. Reduces Operational Risk
Detecting and handling drift early minimizes errors, preventing costly operational failures and incorrect business decisions effectively.
3. Enhances Customer Experience
Accurate, up-to-date models deliver personalized, relevant experiences that consistently improve customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
4. Provides Competitive Advantage
Superior forecasting powers, swift change adaptation, and competitive advantage are all maintained by organizations that manage.
5. Enables Scalable AI Governance
Drift management supports compliance, monitoring, and standardized model maintenance, allowing AI systems to scale safely across environments.
Disadvantages in Handling Model Drift
Here are the main disadvantages:
1. Requires Continuous Monitoring
Maintaining model performance necessitates constant monitoring to detect drift and ensure predictions remain reliable over time.
2. Needs High-Quality Data Pipelines
Effective drift management relies on robust, clean, and well-structured data pipelines to prevent errors.
3. Can Be Computationally Expensive
Detecting and correcting model drift often requires significant computational resources, substantially increasing operational costs.
4. Hard to Diagnose Root Causes
Identifying the exact cause of model drift can be complex and require in-depth analysis.
5. Demands Domain Expertise
Understanding and addressing requires domain knowledge to interpret data and model behavior accurately.
Examples of Model Drift in Real Life
The table below illustrates how different types commonly occur across real-world industries and applications.
| Industry | Example Scenario | Type of Drift |
| E-commerce | Customer buying behavior changes during festive seasons | Data Drift |
| Banking | Fraudsters adopt new tactics | Concept Drift |
| Healthcare | Disease prevalence changes over time | Label Drift |
| Manufacturing | Sensor calibration deteriorates | Data Drift |
| Social Media | Trend topics evolve daily | Concept Drift |
Final Thoughts
Model Drift is inevitable in any production machine learning system. As environments evolve, models lose relevance and accuracy, making drift detection and prevention essential. With the right monitoring mechanisms, retraining workflows, and MLOps practices, organizations can ensure their models remain robust, reliable, and aligned with real-world behavior. Businesses that invest in drift management achieve greater efficiency, improved decision-making, and long-term AI success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How can businesses minimize the impact of model drift?
Answer: Businesses can reduce model drift through monitoring, retraining, incremental learning, robust pipelines, ensembles, and MLOps practices.
Q2. How often should models be retrained?
Answer: The frequency depends on industry dynamics—daily for fraud detection, monthly for retail, and quarterly for manufacturing.
Q3. What tools can help monitor drift?
Answer: Evidently AI, MLflow, Fiddler AI, Sagemaker Model Monitor, and WhyLabs.
Q4. Can deep learning models reduce drift automatically?
Answer: No. They still require monitoring, although they may adapt better with more data.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Model Drift” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.