What is Propensity Modeling?
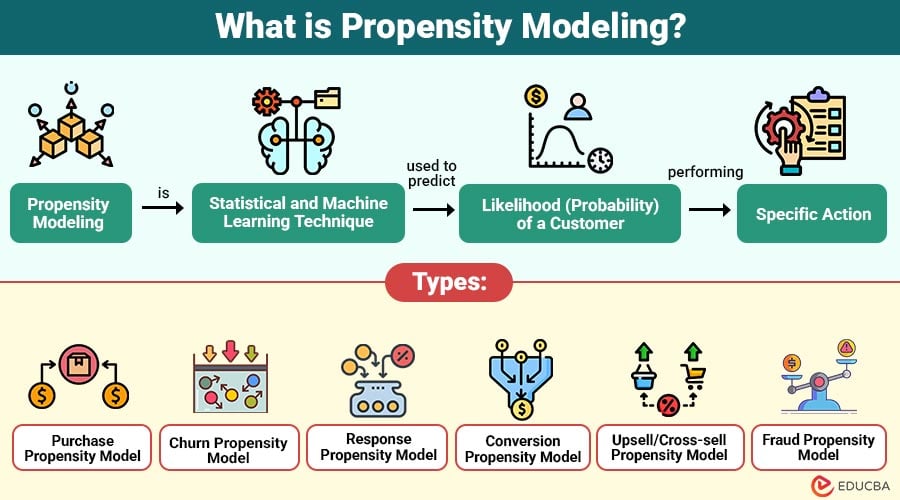
Propensity modeling is a statistical and machine learning technique used to predict the likelihood (probability) of a customer performing a specific action. This action could be anything measurable—such as making a purchase, clicking an ad, subscribing to a product, renewing a service, or even leaving a platform.
By analyzing historical data, the model generates a propensity score (typically between 0 and 1) that represents the probability of the event occurring.
Examples:
- A customer with a 0.85 propensity to purchase is highly likely to buy soon.
- A user with a 0.20 churn risk is unlikely to leave.
- A lead with a 0.92 conversion score is sales-qualified and ready for outreach.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why does Propensity Modeling Matter??
- Working
- Types
- Key Components
- Real-World Use Cases
- Benefits
- Limitations
Key Takeaways:
- Propensity modeling predicts customer actions using statistical and machine-learning techniques to support accurate business decisions.
- It helps businesses target high-likelihood customers, personalize experiences, reduce churn, and maximize marketing efficiency smartly.
- Clean, unbiased, and updated data are essential for building reliable, fair, and high-performing propensity models.
- Regular model monitoring and recalibration ensure predictions remain accurate as customer behavior evolves over time.
Why does Propensity Modeling Matter?
Here are the key reasons why propensity modeling plays a crucial role for modern businesses:
1. Accurate Behavior Prediction
Propensity modeling uses historical patterns and statistical algorithms to forecast future customer actions and intentions accurately.
2. Efficient Budget Allocation
It identifies high-probability audiences, helping businesses prioritize spending on segments most likely to convert.
3. Scalable Personalization
Models reveal customer preferences, enabling tailored messaging and targeted promotions across large audiences with consistent accuracy.
4. Better Retention & Higher CLV
By predicting churn risks and engagement likelihood, companies optimize strategies, boosting loyalty, satisfaction, and long-term revenue growth.
5. Lower Churn & Higher Conversions
Propensity insights highlight at-risk customers and ready-to-convert prospects, enabling timely actions that maximize overall performance.
How does Propensity Modeling Work?
Propensity modeling follows a systematic process using statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms. Below is the simplified workflow:
1. Define the Target Behavior
The first step is to choose the outcome you want to predict, such as:
- Purchase propensity
- Churn propensity
- Upgrade propensity
- Click-through propensity
- Loan default propensity
2. Collect and Prepare Data
Data may include:
- Demographics
- Transaction history
- Website behavior
- Call center interactions
- CRM data
- Email engagement
- Mobile app usage
- Social media signals
Data cleaning, feature engineering, and normalization ensure high-quality input.
3. Select a Modeling Technique
Common statistical and ML methods include:
- Logistic regression
- Decision trees
- Random forests
- Gradient boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM)
- Neural networks
- Survival models
- Support vector machines
The right method depends on:
- Dataset size
- Complexity
- Required interpretability
4. Train the Model
Historical data is used to train the algorithm. The model learns:
- Patterns
- Correlations
- Predictive signals
5. Validate and Fine -Tune
The model is tested using:
- Precision
- Recall
- Accuracy
- AUC-ROC
- Lift curves
Hyperparameter tuning ensures optimal performance.
6. Generate Propensity Scores
Each customer receives a probability score, such as:
- 0.95 purchase likelihood
- 0.72 churn likelihood
- 0.40 upsell likelihood
7. Deploy and Take Action
Businesses use these scores to:
- Prioritize leads
- Personalize offers
- Prevent churn
- Enhance retention
- Design marketing journeys
Types of Propensity Models
Here are the major types of businesses commonly use:
1. Purchase Propensity Model
Estimates how likely a customer is to purchase a specific product or service based on behavior.
2. Churn Propensity Model
Uses behavioral indications, engagement patterns, and discontent indicators to identify consumers who are at risk of leaving.
3. Response Propensity Model
Predicts how likely individuals are to respond to marketing messages using interaction history and demographic insights.
4. Conversion Propensity Model
Measures the likelihood of leads converting within funnels by assessing intent signals and behavioral engagement patterns.
5. Upsell/Cross-sell Propensity Model
Forecasts additional products customers might purchase by evaluating prior buying habits and related preference indicators.
6. Fraud Propensity Model
Detects potentially fraudulent activities by assessing anomalous behavior patterns and scoring transactions for higher risk.
Key Components of Propensity Modeling
Here are the essential key components that make up an effective propensity modeling framework:
1. Target Variable
Represents the specific customer action or outcome you aim to predict, such as purchase or churn.
2. Predictor Variables
Consists of behavioral, transactional, demographic, and external data used to explain customer actions and outcomes.
3. Modeling Algorithm
Uses statistical or machine learning techniques to compute probability estimates for targeted customer behaviors.
4. Propensity Score
Provides a numerical probability indicating the likelihood that a customer will perform the predicted action.
5. Action Framework
Applies business rules to determine appropriate marketing, retention, or sales actions based on calculated scores.
Real-World Use Cases of Propensity Modeling
Here are the most common and impactful ways organizations apply propensity modeling:
1. Marketing and Personalization
- Predict who will respond to an email campaign
- Deliver personalized product recommendations
- Optimize ad spend on high-likelihood customers
2. Sales Optimization
- Lead scoring
- Opportunity prioritization
- Sales forecasting
3. Customer Retention
- Predict churn before it happens
- Trigger personalized retention messages
- Offer incentives to high-risk customers
4. E-Commerce
- Target high-propensity buyers with discounts
- Recommend next-best offers
- Reduce cart abandonment
Benefits of Propensity Modeling
Here are the benefits businesses gain by applying propensity modeling:
1. Higher Conversion Rates
Targeting high-likelihood customers increases engagement, improves campaign performance, and significantly boosts overall sales outcomes.
2. Reduced Marketing Costs
Eliminates unnecessary spending by focusing resources only on customers most likely to act positively.
3. Better Customer Experience
Enables tailored, relevant communication that enhances satisfaction by effectively addressing individual preferences and customer needs.
4. Improved Retention
Predictive insights support proactive measures that reduce churn and strengthen long-term customer loyalty and satisfaction.
5. Increased ROI
Optimized targeting ensures every marketing investment generates greater impact, improving profitability and overall business performance.
Limitations of Propensity Modeling
While powerful, propensity modeling has certain limitations:
1. Data Quality Issues
Poor or incomplete data significantly reduces predictive accuracy and limits the overall effectiveness of propensity models.
2. Bias in Data
Historical biases within datasets can unintentionally distort predictions and produce unfair, inaccurate, or misleading model outcomes.
3. Complexity of ML Models
Advanced machine learning techniques often require specialized skills, robust infrastructure, and substantial computational resources for deployment.
4. Changing Customer Behavior
Rapidly changing customer behaviors require continuous model updates to maintain prediction reliability and overall operational effectiveness.
5. Privacy Concerns
Organizations must ensure strict compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and related regulations to protect customer data privacy.
Final Thoughts
Propensity modeling is a powerful predictive technique that enables organizations to understand customer behavior with precision. By calculating the probability of future actions—such as buying, churning, upgrading, responding, or defaulting—businesses can design highly targeted campaigns, reduce costs, improve customer experiences, and maximize ROI. In an era where personalization and proactive decision-making are critical, propensity modeling is no longer optional—it is an essential strategy for any modern business seeking sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Which industries use propensity modeling?
Answer: Retail, e-commerce, banking, insurance, telecom, healthcare, travel, and more.
Q2. Is machine learning necessary for propensity modeling?
Answer: Machine learning isn’t always required; statistical methods like logistic regression often suffice.
Q3. How often should models be updated?
Answer: Every 30–90 days, depending on changes in customer behavior.
Q4. What tools are commonly used?
Answer: Python, R, SAS, SPSS, AWS SageMaker, Azure ML, H2O.ai, and Google Vertex AI.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Propensity Modeling” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
