What is Arbitrage Trading?
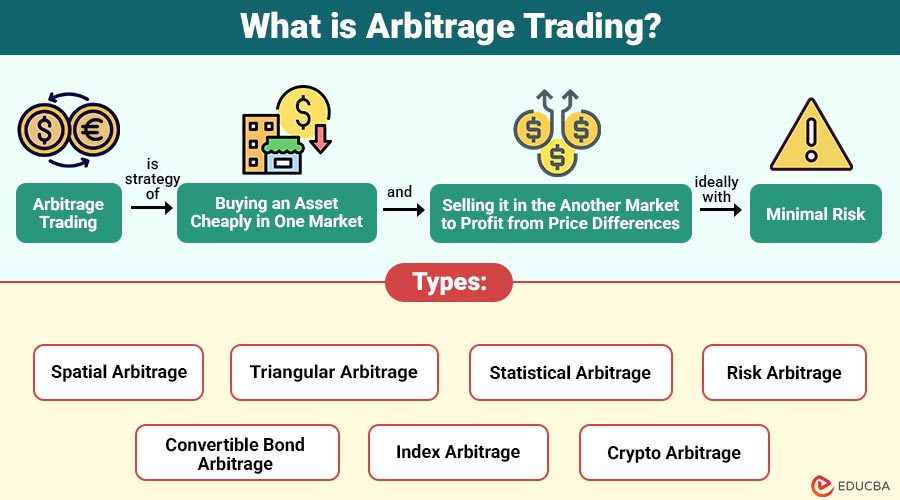
Arbitrage trading is the strategy of buying an asset cheaply in one market and selling it in the another market to profit from price differences, ideally with minimal risk. The trades are simultaneous to eliminate the possibility of price movements during execution.
For example, if Bitcoin is trading at ₹30,00,000 on Exchange A and ₹30,20,000 on Exchange B, a trader can buy on A and sell on B to lock in a ₹20,000 profit.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Working
- Why does Arbitrage Happen?
- Types
- Benefits
- Challenges
- How to Get Started with Arbitrage Trading?
- Real-World Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Arbitrage exploits temporary price differences across markets, enabling traders to lock in low-risk profits immediately.
- Automated trading systems are essential because arbitrage opportunities vanish within seconds due to rapid market equalization.
- Transaction costs, liquidity issues, and execution delays can significantly reduce or eliminate potential arbitrage profits.
- Arbitrage enhances market efficiency by narrowing price gaps, improving liquidity, and stabilizing overall financial ecosystems.
How does Arbitrage Trading Work?
Here are the key steps that explain how an arbitrage opportunity is identified and executed:
1. Price Discrepancy
Prices differ for the same asset across exchanges due to liquidity, volume, fees, or demand-supply imbalances.
2. Speed
Arbitrage opportunities exist for seconds or less. Traders use automated trading systems to execute simultaneously.
3. Equalization
Once traders start exploiting the price gap, the prices converge, eliminating the arbitrage opportunity.
Why does Arbitrage Happen?
Here are the major factors that create temporary price differences across markets, enabling arbitrage opportunities.
1. Latency in Data Transfer
Delays in transmitting price information create temporary price gaps that traders exploit for quick arbitrage profits.
2. Differences in Trading Volumes
Unequal buy-sell activity across markets leads to price discrepancies that arbitrageurs can exploit.
3. Currency Conversion Fluctuations
Rapid changes in exchange rates create mispriced assets across currencies, enabling profitable arbitrage opportunities to materialize instantly.
4. Varying Liquidity Levels
Markets with different liquidity conditions exhibit inconsistent prices, allowing traders to exploit gaps before they normalize.
5. Market Manipulation
Unexpected announcements or intentional price moves temporarily distort asset values, creating short-lived arbitrage chances.
Types of Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage comes in multiple forms. Here are the most common and powerful types:
1. Spatial Arbitrage (Exchange Arbitrage)
Purchasing a product at a discount on one exchange and profiting from its simultaneous sale on another.
2. Triangular Arbitrage
Exploiting mismatched exchange rates between three currency pairs to end with more of the original currency profitably.
3. Statistical Arbitrage
Using quantitative models and algorithms to detect temporary pricing deviations and execute rapid trades for consistent low-risk profits.
4. Risk Arbitrage (Merger Arbitrage)
Profiting from price differences that occur during mergers and acquisitions by betting on expected deal completion outcomes.
5. Convertible Bond Arbitrage
Buying discounted convertible bonds while short-selling the issuer’s stock to profit from mispricing between debt and equity components.
6. Index Arbitrage
Taking advantage when an index futures price diverges from the value of its underlying stocks, locking arbitrage profits.
7. Crypto Arbitrage
Capturing price differences across various crypto exchanges, markets, or funding mechanisms in highly fragmented digital asset environments.
Benefits of Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage offers compelling benefits:
1. Low-Risk Profit
Arbitrage provides low-risk profit opportunities by allowing traders to simultaneously enter offsetting positions, thereby minimizing exposure to market fluctuations.
2. Instant Gains
It delivers immediate profits because price discrepancies are captured instantly, unlike traditional investments, which require extended holding periods.
3. Enhances Market Efficiency
Improves overall market efficiency by reducing pricing gaps, boosting liquidity, and promoting more stable, well-functioning financial markets.
4. Works in Volatile Markets
Volatile markets create frequent price imbalances, allowing arbitrage traders to exploit temporary discrepancies for steady, consistent gains.
Challenges of Arbitrage Trading
Here are some common challenges that traders face while attempting arbitrage strategies:
1. High Speed and Competition
High-frequency traders execute trades at extremely high speeds, making it difficult for manual arbitrage traders to compete effectively today.
2. Transaction Fees
Various fees, including brokerage fees, taxes, withdrawal fees, and slippage, can significantly reduce or eliminate arbitrage profits.
3. Execution Risk
If trades fail to execute simultaneously, unexpected price movements can quickly eliminate potential arbitrage profits.
4. Liquidity Risk
Insufficient liquidity can block completing both trade legs, creating slippage risks and reducing expected arbitrage profits
5. Regulatory Restrictions
Regulations like withdrawal limits, capital controls, and mismatched trading hours can severely restrict profitable arbitrage opportunities.
How to Get Started with Arbitrage Trading?
Here are the essential steps to execute arbitrage strategies effectively.
1. Pick a Market
Select a specific market, such as stocks, crypto, forex, or commodities, to focus your arbitrage strategy effectively.
2. Use Price Monitoring Tools
Utilize real-time tracking tools such as TradingView, CoinMarketCap, and algorithmic scanners to identify profitable discrepancies.
3. Automate Trading
Automation ensures faster execution and reduced human error, making arbitrage trades far more accurate and consistently profitable.
4. Track Transaction Costs
Carefully calculate all fees involved and only execute arbitrage trades when expected profits exceed total costs.
5. Practice with Demo Accounts
Use demo accounts to simulate arbitrage strategies, understand execution challenges, and build confidence before risking capital.
Real-World Examples
Here are practical examples of how arbitrage opportunities arise across different financial markets.
1. Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
Bitcoin:
- Binance – $41,200
- Coinbase – $41,350
Profit = $150 per BTC.
2. Forex Triangular Arbitrage
Assume:
- 1 USD = 0.91 EUR
- 1 EUR = 0.86 GBP
- 1 GBP = 1.30 USD
Start with 1 USD → 0.91 EUR → 0.7826 GBP → 1.01738 USD.
Profit = 1.74% per cycle.
Final Thoughts
Arbitrage trading is a low-risk strategy that profits from market inefficiencies across stocks, forex, and crypto markets. Success depends on fast execution, precise price analysis, and effective use of technology. Though it may seem simple, traders must carefully manage fees, liquidity, and execution risks. When executed properly, arbitrage delivers consistent, predictable returns, making it a valuable strategy for both individual traders and institutional investors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is arbitrage trading safe?
Answer: Arbitrage is low-risk but not completely risk-free due to execution and liquidity risks.
Q2. Can beginners practice arbitrage?
Answer: Yes, but start small and learn automated tools.
Q3. How much money do you need to start?
Answer: Crypto arbitrage can start with small capital; stock index arbitrage may require higher funds.
Q4. Does arbitrage still exist today?
Answer: Yes, but opportunities close quickly due to competition from HFT systems.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Arbitrage Trading” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

