What is Data Fabric?
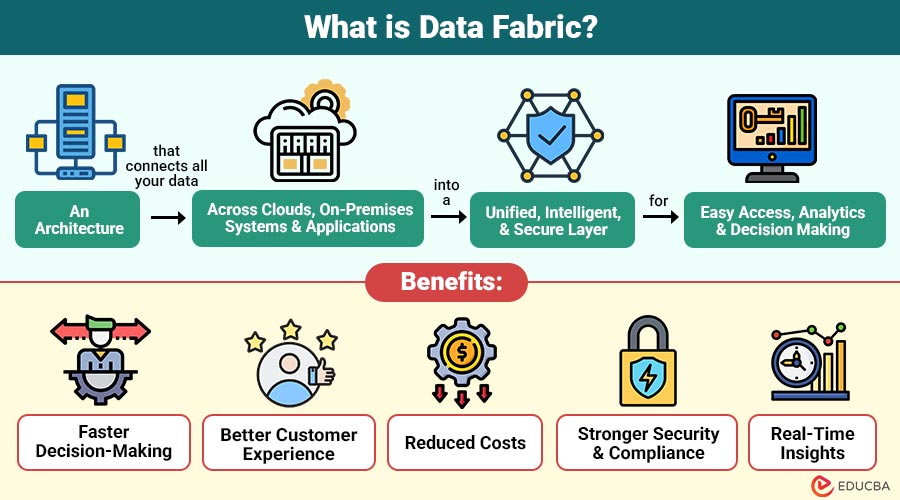
Data Fabric is an architecture that connects all your data—across clouds, on-premises systems, and applications—into a unified, intelligent, and secure layer for easy access, analytics, and decision-making. It uses AI and automation to deliver real-time insights and seamless data experiences across the organization.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why do we Need a Data Fabric?
- Key Features
- Architecture
- Key Components
- Benefits
- Real-World Examples
- Differences
- Challenges
Key Takeaways:
- Data Fabric unifies all organizational data across systems, enabling seamless access, integration, and intelligent real-time insights.
- It uses metadata, automation, and AI to simplify discovery, improve data quality, and enhance governance efficiency.
- It supports hybrid and multi-cloud environments, ensuring scalability, flexibility, and consistent security across platforms.
- Implementing data fabric improves decisions, reduces operational costs, strengthens compliance, and delivers better customer experiences overall.
Why do we Need a Data Fabric?
Here are the key reasons why modern organizations need data fabric:
1. Scattered Data Everywhere
A data fabric unifies scattered data sources, giving organizations a single, connected view across all environments.
2. Difficult Data Discovery
It ensures real-time, accurate data discovery, making it easy to find trustworthy, up-to-date information instantly.
3. Slow Manual Integration
Automated integration pipelines reduce manual effort, saving time, lowering costs, and dramatically speeding up data connectivity.
4. Poor Data Quality
It continuously improves data quality, ensuring reliable, consistent data for analytics and business decision processes.
5. Disconnected Data Tools
It connects diverse data tools seamlessly, improving interoperability and simplifying overall data ecosystem operations efficiently.
Key Features of a Data Fabric
Here are the key features that make data fabric powerful:
1. Unified Data Access
It connects various databases, cloud platforms, APIs, and applications into one unified environment for seamless access.
2. Metadata Intelligence
It uses metadata to understand data location, relationships, usage patterns, and structure, enabling smarter discovery across systems.
3. Automation and AI
AI automates integration, cleansing, classification, governance, and security tasks, reducing manual workloads and significantly increasing operational efficiency.
4. Real-Time Data Sharing
It enables live data delivery for analytics, dashboards, and operational systems, enabling faster decision-making with continuously updated information everywhere.
5. Strong Security
It applies consistent security rules across data sources, ensuring protected access, policy enforcement, and compliance throughout the entire ecosystem.
Architecture of a Data Fabric
A data fabric usually has the following layers:
1. Data Sources Layer
This layer includes all types of raw data sources, such as:
- Cloud storage (AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob)
- Data warehouses
- ERP and CRM systems
- IoT devices and sensors
- Relational and NoSQL databases
- File systems and document repositories
2. Data Integration Layer
This layer connects every source and enables:
- Data ingestion
- Data movement
- Data virtualization
- API-based integration
It ensures data flows smoothly across environments (cloud, on-prem, hybrid).
3. Metadata Layer
This layer manages all information about the data, including:
- Schemas
- Usage patterns
- Access history
- Data lineage
- Ownership details
It powers intelligent discovery, automation, and governance.
4. Data Governance Layer
Ensures policy compliance and protection through:
- Security controls
- Access management
- Regulatory compliance
- Data privacy and protection
- Audit trails
5. Data Consumption Layer
This layer provides simplified data access for:
- Analysts
- Data scientists
- Business teams
- Applications
- AI/ML models
Dashboards, analytics, insights, and reports are generated here.
Key Components of Data Fabric
Here are the key components of data fabric:
1. Data Integration Tools
Connect various systems and enable smooth data transfer, synchronization, and unified access across environments.
2. Data Orchestration
Automates data workflows by determining when, how, and where data should efficiently move.
3. Data Catalog
Acts like a searchable library, helping users quickly discover, understand, and access available datasets.
4. Data Governance Framework
Establishes security controls, access permissions, compliance standards, and policies for trustworthy, well-managed organizational data.
5. Knowledge Graph
Maps relationships between data objects, improving contextual understanding, faster search, and smarter data usage.
Benefits of Data Fabric
Here are the key benefits of using it in modern data-driven organizations:
1. Faster Decision-Making
Easy, clean, and reliable data access helps teams make quicker, smarter decisions with greater confidence.
2. Better Customer Experience
Unified customer data from multiple sources enables highly personalized services, improving engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty.
3. Reduced Costs
Reducing manual work, integrations, and data duplication significantly reduces operational and technology expenses.
4. Stronger Security and Compliance
Centralized governance enhances data protection, ensures regulatory compliance, and strengthens overall organizational security practices.
5. Real-Time Insights
Connected systems allow companies to access instant insights, enabling faster responses and improved business performance.
Real-World Examples
Here are the real-world examples of how different organizations use Data Fabric in real scenarios:
1. IBM Data Fabric
IBM Cloud Pak uses Data Fabric capabilities to automate data discovery, governance, and integration for global enterprises.
2. Snowflake + Data Fabric Approach
Many organizations use Snowflake as part of their data fabric to unify cloud data for analytics.
3. T-Mobile
The telecom giant uses a data fabric to combine data from multiple networks and customer touchpoints to deliver a better experience and faster service.
4. Healthcare Providers
Large hospital chains use Data Fabric to consolidate patient data across departments, improving accuracy and reducing errors.
Difference Between Data Fabric and Other Data Architectures
Here is how Data Fabric compares to other popular approaches:
| Aspect | Data Fabric | Data Mesh | Data Warehouse | Data Lake |
| Goal | Unified data access | Decentralized ownership | Structured analytics | Raw data storage |
| Ownership | Centralized with automation | Distributed | Central IT | Central IT |
| Best For | Large, complex environments | Large orgs with many domains | Reporting | Big data analytics |
| Automation | High (AI-driven) | Low | Medium | Low |
Challenges in Implementing Data Fabric
Though powerful, it also comes with challenges:
1. Complex Setup
Implementing it needs strong technical expertise, understanding of systems, and carefully designed data workflows.
2. High Initial Cost
Advanced integration tools, AI capabilities, and infrastructure investments create high upfront costs for organizations.
3. Requires Strong Governance
Weak governance increases security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and inconsistent data usage across multiple systems.
4. Change Management
Teams must adapt through training, mindset shifts, and new processes to fully leverage data fabric capabilities.
Final Thoughts
A data fabric is a powerful architecture that helps organizations unify all their data, break down silos, improve governance, and provide real-time insights. Automation, AI, and metadata intelligence make data management easier, faster, and more secure. Whether you are in finance, healthcare, retail, telecom, or government, adopting a data fabric helps build a smarter, more connected digital ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Does Data Fabric replace Data Lake?
Answer: No. It connects data lakes, warehouses, and other systems.
Q2. Is Data Fabric only for large companies?
Answer: No. Even small businesses can adopt it in a scaled-down form.
Q3. Do I need AI for Data Fabric?
Answer: AI is not mandatory, but greatly improves automation.
Q4. Is Data Fabric expensive?
Answer: Initial investment may be high, but long-term efficiency saves money.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on ” Data Fabric” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

