What is Compensation Management?
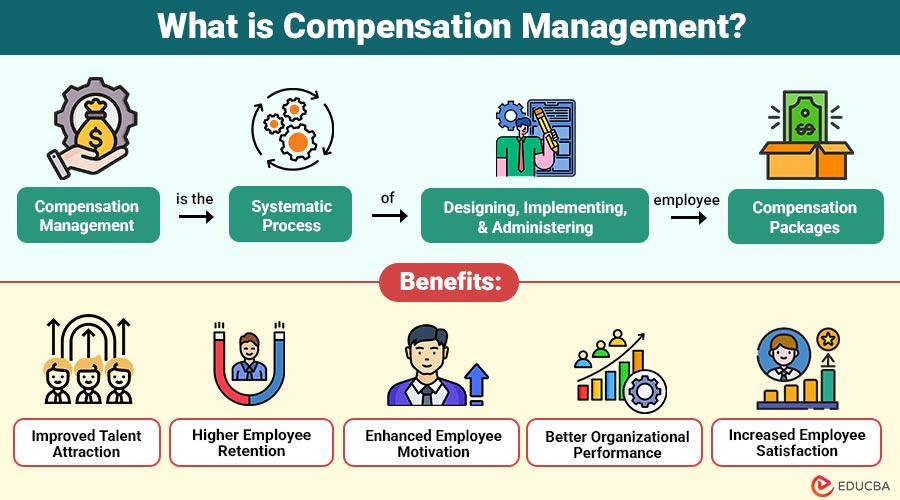
Compensation management is the systematic process of designing, implementing, and administering employee compensation packages. These packages encompass salaries, bonuses, benefits, incentives, and non-monetary rewards offered to employees in exchange for their services.
The main objective is to:
- Reward performance and contributions
- Maintain fairness and internal equity
- Stay competitive in the job market
- Comply with legal and industry standards
- Support long-term employee motivation and retention
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Compensation management strengthens organizational stability by structuring rewards that balance business objectives with employee expectations.
- A strategic pay system enhances employee trust through clear policies, transparent communication, and consistent reward practices
- Appropriate compensation procedures lower regulatory risks, guarantee legal compliance, and shield the company from possible fines.
- Integrated monetary and non-monetary rewards foster long-term engagement, supporting productivity, loyalty, and organizational growth.
Types of Compensation
Compensation is broadly classified into two components: direct and indirect.
1. Direct Compensation
These are monetary benefits paid directly to employees.
- Base Salary (fixed monthly/annual pay)
- Wages (hourly rate)
- Bonuses (performance-based payments)
- Commissions (sales-based earnings)
- Incentives (cash rewards for targets or achievements)
2. Indirect Compensation
These are non-monetary or additional benefits that support employee well-being.
- Health insurance
- Retirement plans
- Paid leaves
- Work-from-home options
- Employee wellness programs
- Travel allowances
- Professional development support
Objectives of Compensation Management
Effective compensation management aims to achieve several goals:
1. Attract High-quality Talent
Compensation management enables organizations to create attractive salary structures and benefits that attract talented, qualified candidates in a competitive job market.
2. Retain Skilled Employees
Providing fair and competitive compensation packages encourages employees to stay longer, reduces turnover, improves stability, and supports consistent organizational performance.
3. Motivate High Performance
Well-designed compensation systems reward strong performance, motivating employees to work harder, achieve their targets, and make positive contributions to the organization’s success.
4. Ensure Fair & Transparent Rewards
Clear, structured compensation policies promote fairness and transparency, enabling employees to understand how pay decisions are made and reducing misunderstandings and conflicts.
5. Maintain Equity & Competitiveness
Compensation management strikes a balance between fair pay within the organization and competitive pay in the industry, ensuring employees feel valued and organizations remain attractive.
6. Align Behaviour with Goals
Strategic compensation encourages employees to focus on organizational goals, aligning their work efforts with company objectives for improved overall performance.
7. Ensure Legal Compliance
Organizations must structure their compensation practices to comply with labor laws, tax rules, and regulatory standards, thereby avoiding penalties and ensuring ethical pay practices.
Key Components of Compensation Management System
To manage compensation effectively, organizations focus on these essential components:
1. Job Evaluation
Job evaluation systematically analyzes roles to determine their relative value, using methods such as ranking, classification, point factor, and factor comparison to inform fair compensation decisions.
2. Salary Structure Design
Salary structure design creates clear pay grades and ranges based on job responsibilities, employee experience, and market rates, ensuring fairness and competitiveness.
3. Performance Management
Performance management links compensation to employee achievements through KPIs, helping reward high performance and support a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
4. Market Benchmarking
Market benchmarking compares internal pay levels with industry standards, ensuring the organization remains competitive in attracting and retaining skilled employees effectively.
5. Benefits Administration
Benefits administration manages health plans, insurance, retirement schemes, and paid leave, ensuring that employees receive supportive and valuable benefits that enhance overall job satisfaction.
6. Incentive and Reward Programs
Incentive and reward programs encompass cash bonuses and non-monetary rewards, designed to motivate employees, enhance productivity, and reinforce desired performance behaviors.
7. Payroll Management
Payroll management ensures accurate and timely salary payments, compliance with deductions, and proper record-keeping, thereby supporting employee trust and facilitating smooth financial operations.
8. Legal Compliance
Legal compliance ensures that compensation practices adhere to labor laws, minimum wage rules, tax regulations, and equal pay standards, thereby protecting organizations from penalties and disputes.
Compensation Management Strategies
To build an effective compensation system, organizations use the following strategies:
1. Pay-for-Performance Strategy
Rewards employees based on measurable performance results, encouraging higher productivity and aligning individual contributions effectively with organizational goals.
2. Skill-Based Pay
Increases compensation when employees acquire new skills or competencies, promoting continuous learning and enhancing workforce flexibility and capability
3. Market-Based Pay Strategy
Sets compensation according to current market trends and industry benchmarks to maintain competitiveness and attract highly skilled employees.
4. Total Rewards Approach
Combines monetary pay, benefits, recognition, and career growth opportunities to enhance employee satisfaction, engagement, and long-term organizational loyalty.
5. Variable Pay Strategy
Provides flexible incentives and bonuses tied to both short-term and long-term objectives, rewarding performance outcomes that exceed fixed salaries.
6. Equity-Based Compensation
Offers stock options, ESOPs, or RSUs, enabling employees to share in the company’s organizational ownership and benefit from its long-term performance.
Benefits of Compensation Management
A strong compensation management system leads to major organizational benefits:
1. Improved Talent Attraction
Competitive and well-structured compensation packages attract highly skilled candidates, thereby strengthening the organization’s recruitment success.
2. Higher Employee Retention
Fair and consistent compensation reduces employee turnover, increases loyalty, and fosters long-term organizational stability.
3. Enhanced Employee Motivation
Employees feel valued and motivated, resulting in a stronger commitment and increased effort toward achieving organizational goals.
4. Better Organizational Performance
Motivated employees consistently deliver higher productivity, improved quality, and stronger overall organizational performance.
5. Increased Employee Satisfaction
Transparent and fair reward systems create a positive work environment and significantly improve employee satisfaction levels.
Challenges in Compensation Management
Despite its importance, companies often face these challenges:
1. Budget Constraints
Limited financial resources restrict organizations from offering competitive salaries, bonuses, and benefits, making it challenging for them to attract and retain employees.
2. Pay Inequity Issues
Unclear or unfair pay structures create dissatisfaction, reduce morale, and may increase employee turnover across the organization.
3. Market Fluctuations
Constant changes in job market trends require frequent compensation adjustments to maintain competitiveness and retain skilled talent.
4. Performance Measurement Difficulties
Inaccurate or biased performance evaluation methods negatively impact reward decisions, reducing fairness and employee motivation.
5. Compliance Complexity
Evolving labor laws, tax regulations, and industry standards necessitate ongoing monitoring to ensure that compensation practices remain compliant with these regulations.
Compensation Management Process (Step-by-Step)
Here are the key steps involved in an effective compensation management process:
1. Conduct Job Analysis
Identify job duties, required skills, and competencies to understand each role’s organizational contribution and responsibilities clearly.
2. Evaluate Jobs
Rank or classify jobs based on value, complexity, and responsibilities to ensure fair internal compensation structures.
3. Define Compensation Objectives
Set clear goals, such as fairness, competitiveness, motivation, and performance alignment, to guide your compensation strategy effectively.
4. Design Salary Structure
Create pay grades, salary ranges, and progression paths that support equitable compensation and long-term career growth.
5. Develop Incentive Plans
Design bonuses, profit-sharing, and recognition programs that motivate employees and improve organizational performance outcomes.
6. Implement Benefits Programs
Provide health insurance, retirement plans, and leave policies to enhance employee satisfaction, security, and overall well-being.
7. Communicate Policies
Ensure employees understand compensation policies, structures, and decision-making processes to maintain trust and transparency.
8. Monitor & Review Regularly
Continuously assess pay structures and incentives, adjusting them based on market changes and organizational needs.
Final Thoughts
Compensation management is essential for building a motivated, loyal, and high-performing workforce. When designed strategically, it helps organizations attract the right talent, reward performance fairly, and maintain internal and external equity. With the evolving workplace, modern organizations must strike a balance between competitive pay, flexible benefits, and meaningful recognition to sustain long-term employee satisfaction and business success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why is compensation management important?
Answer: It helps attract talent, improve retention, motivate employees, and ensure fairness.
Q2. What factors influence compensation?
Answer: Experience, skills, job role complexity, company budget, and market demand.
Q3. What is a total rewards strategy?
Answer: It includes salary, benefits, recognition, career development, and workplace culture.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Compensation Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

