What is Project Governance?
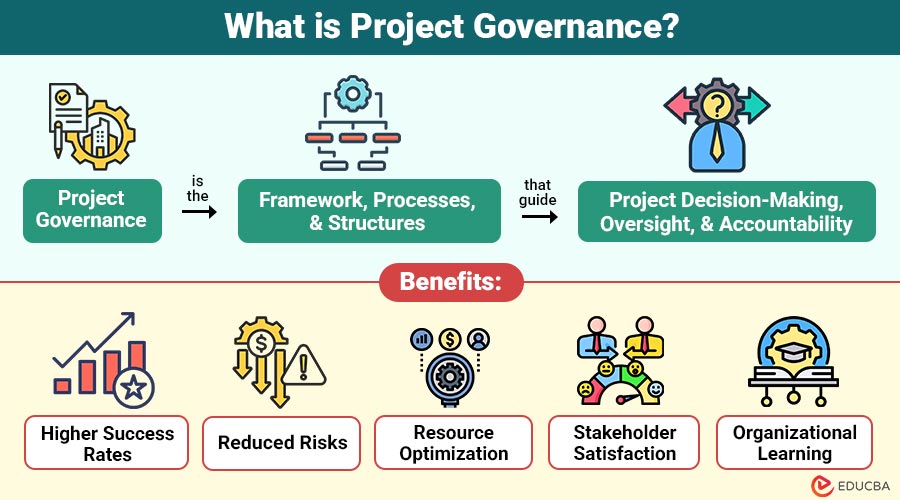
Project governance is the framework, processes, and structures that guide project decision-making, oversight, and accountability. Unlike project management, which focuses on executing project tasks, governance ensures that projects are aligned with organizational strategy, adhere to standards, and achieve desired outcomes.
It specifies who makes decisions, how they are made, and how performance and risks are monitored. Project governance serves as the “compass” for projects, enabling organizations to navigate complexities while staying on course.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Components
- Importance
- Types
- Benefits
- Implementing Effective Governance
- Challenges
- Real-World Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Project governance ensures the alignment of projects with organizational strategy, consistently improving outcomes and value delivery.
- Clear roles, decision frameworks, and policies promote accountability, transparency, and effective stakeholder engagement throughout projects.
- Effective governance identifies and mitigates risks early, thereby enhancing resilience and reducing the likelihood of surprises or project failures.
- Continuous monitoring, reporting, and process improvement strengthen governance, optimizing resources and boosting overall project success.
Key Components of Project Governance
A well-defined project framework typically includes the following components:
1. Governance Structure
Establishes roles and responsibilities for project oversight. This may include a project steering committee, executive sponsors, project managers, and functional leads.
2. Decision-Making Framework
Defines how decisions are made, escalated, and approved. It ensures transparency and accountability in project-related choices.
3. Policies and Procedures
Outlines standardized practices for project planning, risk management, change management, and reporting.
4. Performance Monitoring and Reporting
Sets mechanisms to track project progress, budgets, quality, and risks. Includes dashboards, KPIs, and regular status reports.
5. Risk and Issue Management
Provides guidelines for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Ensures timely escalation and resolution of issues.
6. Stakeholder Engagement
Ensures clear communication with all stakeholders, aligning expectations and fostering collaboration.
Why is Project Governance Important?
Here are the key reasons why it plays a crucial role in organizational success:
1. Strategic Alignment
Governance makes sure projects support the organization’s goals, deliver real value, and avoid wasting resources on tasks that aren’t important.
2. Accountability and Transparency
Clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and processes promote accountability, allowing stakeholders to monitor progress and ensure transparent resource utilization.
3. Risk Reduction
A structured governance framework identifies risks early, enabling timely mitigation strategies, reducing surprises, and increasing overall project resilience.
4. Enhanced Decision-Making
Governance establishes escalation paths and approval structures, ensuring critical decisions are made efficiently, effectively, and with full organizational clarity.
5. Improved Project Outcomes
Strong governance frameworks increase project success rates, enhance stakeholder satisfaction, and optimize resource utilization across all organizational initiatives.
Types of Project Governance
Project governance can vary depending on an organization’s structure, project size, and complexity. Common types include:
1. Corporate Governance-Driven
Organizational policies and executive leadership guide decisions. Common in large enterprises with multiple projects.
2. Project Management Office (PMO)-Driven
The PMO sets standards, processes, and monitoring mechanisms for all projects, ensuring consistency and control.
3. Product or Program Governance
Focused on delivering specific outcomes or products, often applied in technology or R&D projects.
4. Agile Governance
In agile projects, governance emphasizes flexibility, iterative decision-making, and continuous stakeholder engagement.
Benefits of Strong Project Governance
Here are the key benefits organizations gain from implementing robust project governance:
1. Higher Success Rates
Strong project governance ensures that projects are completed on time, within budget, meet their objectives, and consistently achieve organizational goals.
2. Reduced Risks
Early risk identification and proactive mitigation strategies prevent unexpected issues, minimizing project disruptions and avoiding costly delays or failures.
3. Resource Optimization
Governance enables efficient allocation and utilization of time, budget, and human resources, maximizing productivity and overall project effectiveness.
4. Stakeholder Satisfaction
Transparent communication, predictable project outcomes, and clear accountability build trust, strengthen relationships, and improve overall stakeholder confidence.
5. Organizational Learning
Capturing lessons learned through governance supports continuous improvement, knowledge sharing, and enhanced performance across future projects.
Implementing Effective Project Governance
Establishing project governance requires careful planning and execution. Here is a step-by-step approach:
1. Define Governance Objectives
Clearly articulate what governance should achieve—strategic alignment, risk management, quality assurance, or all of the above.
2. Identify Roles and Responsibilities
Establish a governance structure with defined roles, including:
- Executive Sponsor: Provides strategic direction and approvals.
- Project Steering Committee: Oversees project progress, risks, and issues.
- Project Manager: Manages day-to-day execution.
- Functional Leads: Ensure departmental contributions and compliance.
3. Develop Policies and Standards
Standardize procedures for project planning, change management, reporting, and risk assessment. This creates consistency and transparency across projects.
4. Implement Monitoring and Reporting Mechanisms
Monitor project progress using KPIs, dashboards, and regular status reports. Track numbers like budget and timeline, as well as feedback-based measures like stakeholder satisfaction.
5. Establish Risk and Issue Management
Establish procedures to proactively identify, evaluate, prioritize, and mitigate project risks to ensure smooth execution.
6. Engage Stakeholders
To guarantee that stakeholders are informed, consulted, and in agreement throughout the project lifetime, create a communication plan.
7. Continuous Improvement
Regularly review governance effectiveness and adapt processes based on lessons learned and evolving business needs.
Challenges in Project Governance
While governance is critical, implementing it effectively can be challenging:
1. Resistance to Oversight
Project teams may see governance as too controlling or full of unnecessary rules. Because of this, they might resist being monitored, which can lead to poor compliance and make the processes less effective.
2. Lack of Clear Roles
When roles and responsibilities are unclear, decisions get delayed, accountability is lost, and people become confused. This hurts project efficiency and reduces stakeholder trust.
3. Complex Reporting Requirements
Excessive reporting demands can overwhelm teams, consuming time and resources, reducing productivity, and diverting focus from core project activities.
4. Dynamic Business Environment
Rapid changes in strategy, technology, or market conditions can render governance processes outdated, requiring constant updates and adaptability to remain effective.
5. Balancing Control and Flexibility
Overly rigid governance stifles innovation, while excessive flexibility risks project drift; therefore, striking a balance is crucial for success.
Real-World Examples
Here are some practical scenarios where project governance plays a crucial role:
1. IT System Implementations
Big ERP projects often fail if there is no proper governance. Having a steering committee that checks key milestones, budgets, and risks makes the project much more likely to succeed.
2. Construction Projects
Mega infrastructure projects, like highways or airports, employ project governance to coordinate multiple contractors, manage risks, and ensure compliance with regulations.
3. Agile Software Development
Even in agile environments, governance ensures that sprints align with strategic objectives, budgets, and quality standards.
Final Thoughts
Project governance is a strategic necessity, ensuring projects deliver measurable value aligned with organizational goals. Defining roles, setting clear ways to make decisions, checking progress regularly, and handling risks help projects succeed, reduce mistakes, and build trust among everyone involved. In every industry, strong governance helps organizations move from fixing problems at the last minute to planning ahead and managing projects smartly. This leads to long-term success, even in a challenging business world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is project governance different from project management?
Answer: Project governance focuses on oversight, accountability, and strategic alignment, while project management handles day-to-day execution of project tasks.
Q2. Who is responsible for project governance?
Answer: Typically, executive sponsors, steering committees, and PMOs are responsible for governance, while project managers execute within the framework.
Q3. Can agile projects have governance?
Answer: Yes, agile projects implement governance flexibly and iteratively, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and mitigating risk.
Q4. How often should governance processes be reviewed?
Answer: Governance processes should be reviewed periodically, ideally after each project or major phase, to incorporate lessons learned and adapt to changing needs.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Project Governance” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.