What is a Transaction Dispute?
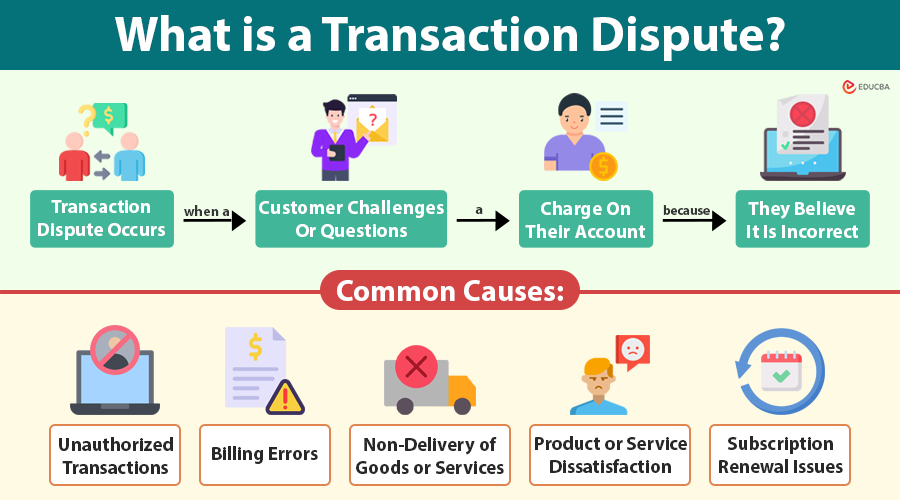
A transaction dispute occurs when a customer challenges or questions a charge on their account because they believe it is incorrect, unauthorized, or unsatisfactory. It is a formal request to review and reverse a transaction.
Transaction disputes are not limited to credit card transactions; they can happen with debit cards, bank transfers, mobile wallets, online payment gateways, and even point-of-sale purchases.
Customers, merchants, or banks can initiate disputes. For businesses, understanding and managing transaction disputes is vital to maintaining financial integrity and customer trust. For consumers, knowing how to file a dispute protects them from potential financial losses and fraudulent activities.
With an increasing number of people using e-commerce and online banking, disputes over transactions are becoming more common. This makes it crucial for both businesses and consumers to understand how to manage disputes effectively.
Table of Contents
Common Causes of Transaction Disputes
Understanding the underlying causes of transaction disputes is the first step toward resolving them effectively. Common causes include:
1. Unauthorized Transactions
Fraudulent activities, stolen credit card details, or phishing attacks often result in disputes. For example, a hacker may gain access to a customer’s credit card information and make purchases without consent, prompting the customer to report the transaction.
2. Billing Errors
Mistakes such as double charges, incorrect amounts, or unexpected fees can easily confuse customers. A minor typo or system glitch in the payment gateway can result in an overcharge, leading to disputes.
3. Non-Delivery of Goods or Services
Customers expect businesses to deliver products or services within the agreed-upon timelines. Customers often raise disputes when items arrive late, go missing, or when services are incomplete. This is particularly common in online shopping and subscription-based services.
4. Product or Service Dissatisfaction
If a customer receives a damaged, faulty, or incorrectly described product, or if a service fails to meet expectations, they will likely dispute the transaction. Quality assurance and clear product descriptions can reduce these disputes.
5. Subscription Renewal Issues
Automatic subscription renewals without clear customer consent can lead to disputes and conflicts. Many customers dispute charges when they are unaware of recurring payments or struggle to cancel subscriptions.
6. Technical or System Errors
Glitches in payment systems, website downtime during checkout, or app errors can trigger unintended charges or failed transactions. Customers often report these errors as disputes to recover their funds.
How to Handle a Transaction Dispute?
Proper handling of transaction disputes ensures resolution while maintaining customer trust. Here is a step-by-step approach:
1. Immediate Customer Communication
Responding promptly to a dispute can prevent escalation. Businesses should establish a dedicated customer support channel for resolving disputes. A timely response shows customers that you take their concerns seriously.
2. Documentation Review
Gather all supporting documentation, including receipts, invoices, transaction IDs, and communication logs. A well-documented record helps verify the transaction and supports your case in the event of disputes or chargebacks.
3. Contact the Payment Processor or Bank
For card-based transactions, please contact the payment processor or the issuing bank. They can mediate between the merchant and the customer, investigate claims, and determine whether a refund or reversal is warranted.
4. Investigation and Resolution
Thoroughly assess the validity of the dispute. If the customer’s claim is valid, process a refund, replacement, or service correction as necessary. If the dispute is invalid, provide clear evidence supporting the transaction. Ensuring accuracy and fairness is key.
5. Follow-Up
After resolving the dispute, follow up with the customer to confirm satisfaction. A clear and professional approach can transform a negative experience into a positive one, thereby fostering customer loyalty.
Steps to Prevent Transaction Disputes
Prevention is always better than managing disputes after the fact. Businesses can minimize disputes by adopting these best practices:
- Clear billing statements: Provide detailed and transparent invoices that are easy to understand. Include itemized charges, taxes, service fees, and subscription details. Clear billing reduces the chances of customers disputing transactions.
- Fraud prevention measures: Implement robust security protocols, including multi-factor authentication, secure payment gateways, and real-time monitoring of suspicious activities. Educate customers about safe online payment practices.
- Return and refund policies: Clearly outline return, refund, and cancellation policies on your website or product documentation. Clear policies reduce confusion and encourage customers to resolve issues directly with your support team, rather than initiating disputes.
- Accessible customer support: Offer responsive and multi-channel customer support, including chat, email, and phone options. Prompt assistance helps resolve problems before they escalate to formal disputes or chargebacks.
- Transaction alerts: Send real-time notifications to customers about purchases, withdrawals, or subscription renewals. Transparency in transaction communication reduces confusion and prevents disputes from occurring.
- Employee training: Train staff to handle disputes effectively and with empathy. Employees should understand dispute resolution protocols and the importance of customer satisfaction in maintaining trust.
Role of Banks and Payment Processors
Banks, credit card networks, and payment processors are critical intermediaries in dispute resolution. Their responsibilities include:
- Verification of transactions: Checking the validity of disputed transactions using merchant and customer records.
- Chargeback management: Facilitating refunds when disputes are justified.
- Regulatory compliance: They ensure that all disputes follow financial regulations and consumer protection laws.
- Support tools: Providing online portals or apps for customers to file disputes quickly and track their status.
By collaborating with banks and payment processors, businesses can ensure a smoother resolution process and maintain compliance with industry standards.
Impact of Transaction Disputes
Transaction disputes can affect both consumers and businesses:
- For consumers: Prolonged disputes can cause financial strain, result in frozen funds, or lead to delays in accessing services. Frequent disputes can also impact credit scores, particularly in cases involving unpaid amounts or chargebacks.
- For businesses: Disputes can lead to chargebacks, lost revenue, and reputational damage. They may also increase operational costs due to staff time, administrative processing, and potential penalties from payment processors.
Effective handling and proactive prevention of disputes are crucial for minimizing financial and reputational risks.
Final Thoughts
Transaction disputes are a common aspect of the digital financial landscape. They can result from errors, unauthorized transactions, or dissatisfaction with goods and services. Businesses that implement clear billing practices, robust fraud prevention measures, and strong customer support can significantly reduce disputes.
For consumers, understanding how to file a dispute, gather evidence, and communicate effectively with banks or merchants is key to protecting financial interests.
By fostering transparency, responsiveness, and trust, businesses and consumers can resolve disputes efficiently and maintain positive financial relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How long does a transaction dispute take to resolve?
Answer: The dispute process typically takes 7 to 90 days, depending on the payment method, bank guidelines, and complexity of the case. Some disputes, especially chargebacks, may take longer if additional investigation is required.
Q2. Does filing a transaction dispute affect my credit score?
Answer: Most disputes do not impact credit scores. However, if the dispute involves an outstanding loan payment or an unpaid credit card amount that remains unresolved, it may negatively impact your credit history.
Q3. Can a merchant refuse a refund during a dispute?
Answer: Yes, a merchant can refuse if they believe the transaction is valid. However, the final decision lies with the bank or card network, not the merchant.
Q4. What happens if the disputed amount is under investigation?
Answer: In many cases, banks issue a temporary credit to the customer’s account while they investigate the issue. This may be reversed later, depending on the final decision.
Q5. Can businesses blacklist customers who file frequent disputes?
Answer: Businesses are allowed to restrict or block customers who repeatedly file unjustified disputes, especially in cases of suspected abuse or fraud.
Q6. What is “friendly fraud”?
Answer: Friendly fraud occurs when a customer disputes a legitimate charge, even though they received the product or authorized the payment.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on transaction disputes helps you understand the causes, resolution methods, and preventive strategies. Explore related articles to learn more about chargeback management, fraud prevention, digital payment security, and effective payment dispute handling.
