What is a Liquidity Pool?
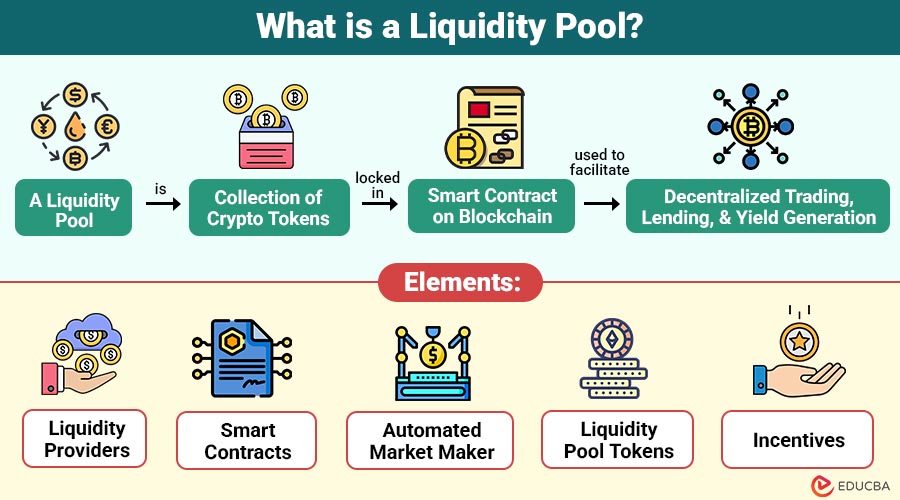
A liquidity pool is collection of crypto tokens locked in smart contract on a blockchain, typically used to facilitate decentralized trading, lending, and yield generation. These pools are created when liquidity providers (LPs) deposit pairs of tokens (such as ETH and USDC) into a smart contract. In return, LPs receive rewards, usually in the form of trading fees or governance tokens.
For example, users can swap ETH for USDC on Uniswap while liquidity providers earn fees and incentives.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Liquidity pools enable decentralized trading by allowing users to swap tokens directly and efficiently, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
- Rewards that encourage contributions and aid in the expansion of the DeFi ecosystem are given to participants in the form of transaction fees or governance tokens.
- Automated smart contracts manage deposits, withdrawals, and pricing, ensuring continuous liquidity and secure decentralized operations.
- Users must understand potential risks, including sudden price changes, protocol vulnerabilities, and loss of invested funds.
How Liquidity Pools Work?
It operates on automated market maker (AMM) models, rather than traditional order books.
1. Token Pairing
A liquidity pool typically consists of two tokens—for example, an ETH/USDC pool. Liquidity providers deposit both tokens in equal value.
2. Price Determination
Algorithms govern prices, most commonly the constant product
Formula: x×y=kx \times y = kx×y=k
Where:
- x = Quantity of Token A
- y = Quantity of Token B
- k = Constant (ensures balance)
3. Trading Process
When a trader swaps ETH for USDC, the pool automatically adjusts the token ratio, changing the price accordingly. The more tokens removed from one side, the more expensive they become due to supply-demand imbalance.
4. Rewards for Liquidity Providers
LPs earn a share of transaction fees (for example, 0.3% per trade on Uniswap). Some pools also provide governance tokens as additional rewards (yield farming).
Elements of Liquidity Pools
Here are the elements that make liquidity pools function effectively in decentralized finance (DeFi).
1. Liquidity Providers
Liquidity providers are individuals or institutions who deposit token pairs into pools, enabling decentralized trading and earning transaction-based rewards.
2. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are blockchain-based programs that automatically execute pool rules, securely handling deposits, withdrawals, token swaps, and reward distributions.
3. Automated Market Maker
An AMM utilizes mathematical formulas instead of traditional order books to determine token prices and autonomously provide continuous liquidity.
4. Liquidity Pool Tokens
Tokens represent ownership in a pool, allowing providers to redeem their deposited assets and accumulated fees or incentives at any time.
5. Incentives
Incentives, such as trading fees and yield farming rewards, motivate liquidity providers to contribute their assets, thereby ensuring deep liquidity and promoting the growth of the decentralized ecosystem.
Benefits of Liquidity Pools
Here are the benefits that liquidity pools bring to decentralized finance (DeFi).
1. Decentralization
Eliminate dependency on centralized exchanges, empowering users to trade freely through blockchain-based protocols without relying on traditional intermediaries.
2. Continuous Liquidity
Unlike traditional markets, liquidity pools ensure constant trading availability, allowing for instant token swaps without requiring matching buyers or sellers.
3. Passive Income
Liquidity providers provide long-term passive income prospects within DeFi by receiving a share of trading fees and possible yield farming rewards.
4. Accessibility
Anyone holding crypto tokens can easily become a liquidity provider, without requiring specialized expertise, large capital, or approval from centralized exchanges.
5. Innovation in DeFi
Liquidity pools power decentralized trading, lending, synthetic assets, and yield farming, fostering innovation and shaping the future of decentralized finance.
Risks of Liquidity Pool
Despite their benefits, it comes with risks:
1. Impermanent Loss
Liquidity providers risk reduced returns when token prices diverge significantly, making holding assets more profitable than providing liquidity to a pool.
2. Smart Contract Risks
Bugs, coding flaws, or exploits within smart contracts can cause unexpected losses of funds, jeopardizing liquidity providers’ contributions and overall trust.
3. Market Volatility
Sudden price swings in volatile cryptocurrencies may negatively impact liquidity providers, exposing them to substantial risks and unpredictable financial losses.
4. Regulatory Uncertainty
Evolving government regulations on decentralized finance could restrict liquidity pools, affecting participation, compliance requirements, and the future sustainability of DeFi platforms.
5. Rug Pulls and Exploits
Dishonest developers may create fraudulent pools, draining deposited assets and leaving liquidity providers powerless, holding worthless tokens with no recovery options.
Popular Use Cases of Liquidity Pools
Here are the most popular use cases of liquidity pools in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
1. Decentralized Exchanges
DEX platforms, such as Uniswap, PancakeSwap, and SushiSwap, utilize liquidity pools to enable seamless, decentralized, peer-to-peer token trading that occurs instantly.
2. Yield Farming
By contributing liquidity, users earn governance tokens and transaction fee rewards, incentivizing participation while maximizing returns within decentralized finance ecosystems.
3. Lending & Borrowing
Platforms like Aave and Compound utilize liquidity pools to offer collateralized loans, allowing users to borrow or lend assets efficiently.
4. Synthetic Assets
Liquidity pools support tokenized versions of real-world assets, enabling traders to access and trade synthetic derivatives without relying on traditional intermediaries.
5. Staking Pools
Pooling tokens collectively enables staking for blockchain validation, distributing network rewards proportionally to participants while securing decentralized networks.
Real-World Examples
Here are some well-known examples that showcase how liquidity pools operate in practice.
1. PancakeSwap (BSC)
DEX on Binance Smart Chain; BNB/CAKE and BUSD/USDT pools; LPs earn fees + CAKE tokens.
2. SushiSwap (Multi-Chain)
DEX across multiple blockchains; ETH/USDC and MATIC/USDT pools; LPs earn trading fees + SUSHI tokens.
3. Aave (Ethereum)
Aave is an Ethereum-based lending protocol where LPs earn interest by depositing assets for borrowers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How do liquidity providers earn money?
Answer: They earn a share of transaction fees and may receive additional incentives like governance tokens.
Q2. What is impermanent loss?
Answer: Impermanent loss occurs when the value of deposited assets changes compared to simply holding them, reducing potential returns.
Q3. Are liquidity pools safe?
Answer: They are generally safe on reputable platforms, but risks such as smart contract bugs, volatility, and scams still exist.
Q4. Can anyone create a liquidity pool?
Answer: Yes, most decentralized exchanges allow anyone to create a pool by depositing a token pair.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Liquidity Pool” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.