Updated July 4, 2023
Introduction to SQL ROW_NUMBER
It is as simple as giving each row a unique number, like a roll call to identify it. Since ROW_NUMBER is a Windows function, it does not make any changes in the original data table. It is very helpful when we want to find answers to questions such as what is the nth highest/ lowest entry in the resultset. There are many uses of this function, like the RANK() function in SQL. We will learn about most of them in this post using some examples.
Syntax and Parameters:
The basic syntax for writing the ROW_NUMBER function in SQL is as follows :
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
[PARTITION BY partition_expression]
[ORDER BY order_expression [ASC | DESC]]
)The parameters used in the above syntax are as follows :
- partition_expression: The column or expression on the basis of which the entire dataset has to be divided. If you do not specify anything, by default, the entire result set is considered as a single window or partition.
- order_expression: The column or expression on the basis of which the rows in the partition set are ordered or sorted in a particular ascending or descending order.
Examples of SQL ROW_NUMBER
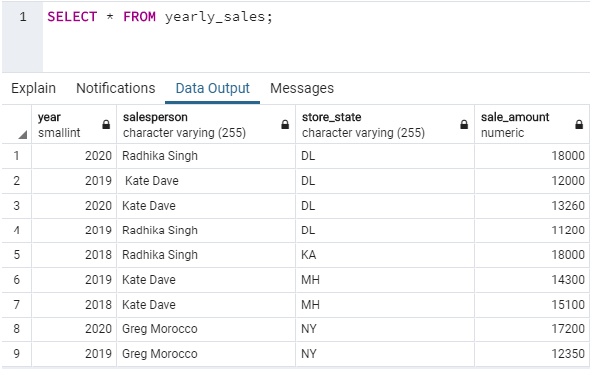
In order to illustrate ROW_NUMBER() function in great detail, let us create a table called “yearly_sales”.It contains details pertaining to sales made by a salesperson in a particular year. We can use the following code snippet to create the table.
CREATE TABLE public.yearly_sales (
year smallint NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) COLLATE pg_catalog."default" NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) COLLATE pg_catalog."default" NOT NULL,
sale_amount numeric NOT NULL
);We can use the following code snippet to insert values.
INSERT INTO public.yearly_sales(
year, salesperson, store_state, sale_amount)
VALUES (2020,'Radhika Singh','DL',18000),
(2019,' Kate Dave','DL',12000),
(2020,'Kate Dave','DL',13260),
(2019,'Radhika Singh','DL',11200),
(2018,'Radhika Singh','KA',18000),
(2019,'Kate Dave','MH',14300),
(2018,'Kate Dave','MH',15100),
(2020,'Greg Morocco','NY',17200),
(2019,'Greg Morocco','NY',12350);After the above-mentioned insertion operations, the data in the “yearly_sales” table looks something as shown below :
SELECT * FROM yearly_sales;Now we are all set to try a few examples based on the newly created “yearly_sales” table.
Example #1
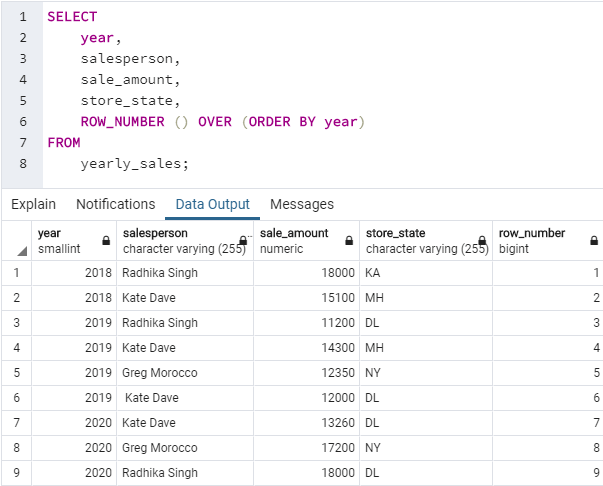
SQL query to illustrate the use of ROW_NUMBER() function to assign a sequential number to each row in the result set.
SELECT
year,
salesperson,
sale_amount,
store_state,
ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY year)
FROM
yearly_sales;In this example, since we have not created any partition, the entire result set by default is considered as a single partition. We can see in the data output that the row_number() function has sequentially assigned a unique integer number to each row in the partition, starting from 1 and ending at 9.
Example #2
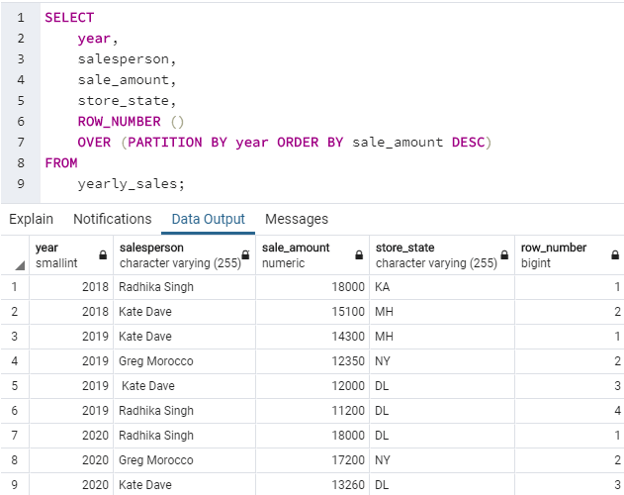
Use of ROW_NUMBER() function to assign a row number to each row in a partition created by year in the result set.
SELECT
year,
salesperson,
sale_amount,
store_state,
ROW_NUMBER ()
OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY sale_amount DESC)
FROM
yearly_sales;We can observe in the image that the ROW_NUMBER() function first created partitions by year (2018,2019, and 2020) and then uniquely numbered each row starting from 1 within each partition.
Example #3
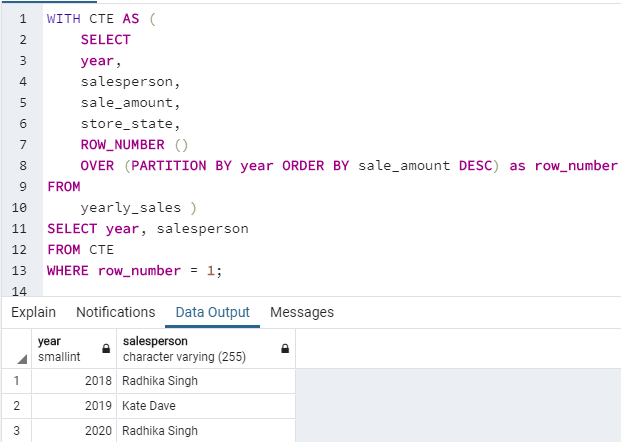
Use of ROW_NUMBER() function to find the name of the top salesperson
(the salesperson who made sales of the maximum amount) during the years 2018, 2019, and 2020.
WITH CTE AS (
SELECT
year,
salesperson,
sale_amount,
store_state,
ROW_NUMBER ()
OVER (PARTITION BY year ORDER BY sale_amount DESC) as row_number
FROM
yearly_sales )
SELECT year, salesperson
FROM CTE
WHERE row_number = 1;
In this example, we have created a CTE to illustrate the same. In the next example, we will use a subquery to illustrate the same further.
Example #4
SQL query to illustrate the use of the ROW_NUMBER() function to perform pagination of a huge result set.
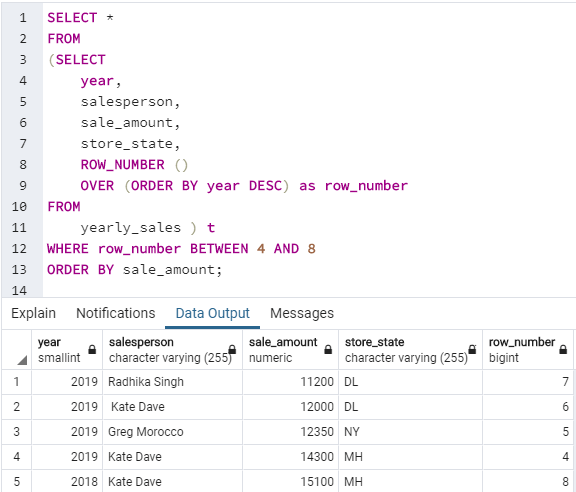
SELECT *
FROM
(SELECT
year,
salesperson,
sale_amount,
store_state,
ROW_NUMBER ()
OVER (ORDER BY year DESC) as row_number
FROM
yearly_sales ) t
WHERE row_number BETWEEN 4 AND 8
ORDER BY sale_amount;Many times, we might have to create dashboards or web applications where we cannot show the entire result set on a single page.
Conclusion
ROW_NUMBER () is a Windows function that is used to sequentially number the rows or data records in a result set or a partition of it. It is similar to the RANK() function in some aspects. It is helpful in performing pagination, finding nth highest/lowest entry in the dataset.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL ROW_NUMBER” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.