Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL log_statement
The PostgreSQL log_statement parameter is related to error and reporting to log errors, warnings, and database queries, we can log_statement in PostgreSQL as per the options we configured in the configuration file. Default log_statement option in the PostgreSQL configuration file is none means nothing log anything into the error file. There are four options of log_statement of error and SQL query reporting, i.e., none, ddl, mod, and all, DDL specifies that log all ddl query into the error log. All options of log_statement are defined as log all database server queries. Log_statement is an important parameter in PostgreSQL.
Syntax
Given below is the syntax:
Set log_statement = options;Or
Log_statement (options or enum);Or
Alter system set log_statement = options;Parameters:
- Set: The keyword “SET” sets the log_statement parameter at the session level in PostgreSQL.
- log_statement: It is configuration parameter in PostgreSQL used to log specific statement in error log file. Log statement have four options which was we have configured in the configuration file.
- options: This parameter is defined as set options to log_statement. We can set four options with log_statement in PostgreSQL.
- Alter system: We have set the log_statement configuration parameter using alter system command in PostgreSQL. We have set this configuration parameter using alter system command at the global level.
- enum: The enum specifies the options we configure with the log_statement configuration parameter.
How log_statement work in PostgreSQL?
The log_statement parameter in PostgreSQL is a basic, important, and useful parameter that logs error logs, database warning messages, and SQL queries. To work the parameter of log_statement, we need to set the log_min_duration_statement configuration parameter to log queries.
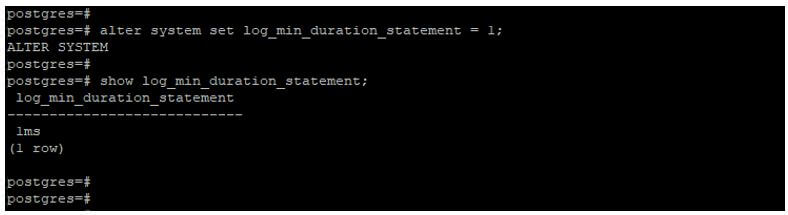
In the below example, we have set the log_min_duration_statement parameter as 1ms to work the log_statement parameter.
Code:
alter system set log_min_duration_statement = 1;
show log_min_duration_statement;Output:
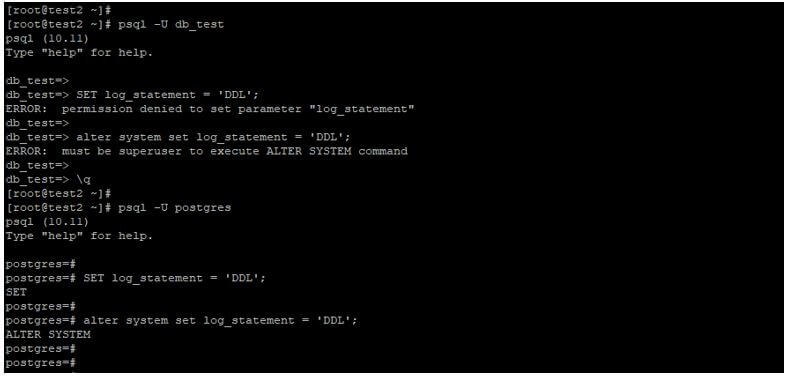
If we want to set the log_statement configuration parameter in PostgreSQL, we need to have super user privileges to set these options.
Below example shows that we need super user privileges to set the log_statement parameter in PostgreSQL.
Code:
psql -U db_test
SET log_statement = 'DDL';
alter system set log_statement = 'DDL';
psql -U postgres
SET log_statement = 'DDL';
alter system set log_statement = 'DDL';Output:
In the above first example, we are trying to set the log_statement configuration parameter using the db_test user, but the db_test user does not have privileges to set the options, so it will issues the error. In the second example, we are trying to set the log_statement configuration parameter using a postgres user, this user has super user privileges to set the parameter in PostgreSQL.
Log_statement has four options available in PostgreSQL:
- None: This option of log_statement is defined as doesn’t log any query in an error log file. This is the default configurations option of log_statement available. This is also defined as off the log_statement parameter.
- DDL: The log_statement option defines logging all queries that contain the DDL statement. The DDL query includes the create, alter, and drop statements.
- All: This option is defined as log all the statements executed by the user. It logs DDL, DML, and all the query languages in PostgreSQL. We cannot enable these options in the production environment because it will take a high overhead on the database to log all statements. It will log all queries which were fired from the database user.
- Mod: The log_statement parameter within the “mod” option logs not only DDL queries but also modifying statements, including delete, update, truncate, insert, copy, execute, and prepare. It will also log the analyze statement into the error log.
Logging in PostgreSQL into an error log file will occur when we have received a message from a database client or user. It will also include the bind parameter at the time of error reporting in PostgreSQL.
Examples
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
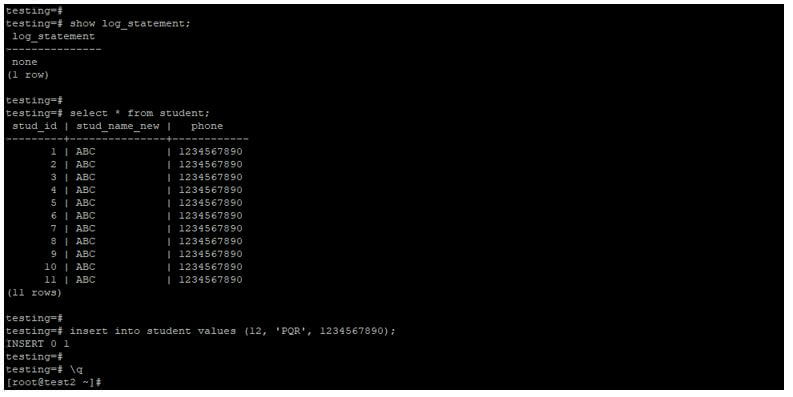
Log_statement using none options.
In the below example, we have used no options with the log_statement parameter. It will not log anything into the error log.
Code:
show log_statement;
select * from student;
insert into student values (12, 'PQR', 1234567890);Output:
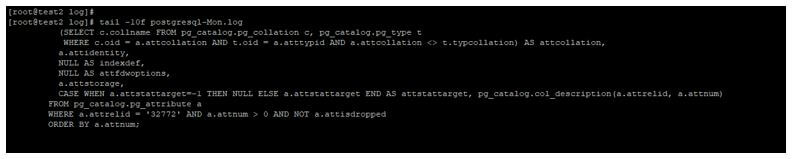
tail -10f postgresql-Mon.log
Example #2
Log_statement using DDL options.
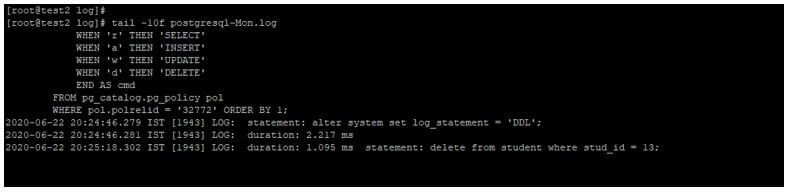
In the below example, we have used DDL options with the log_statement parameter. It will log only the DDL statement into the error log.
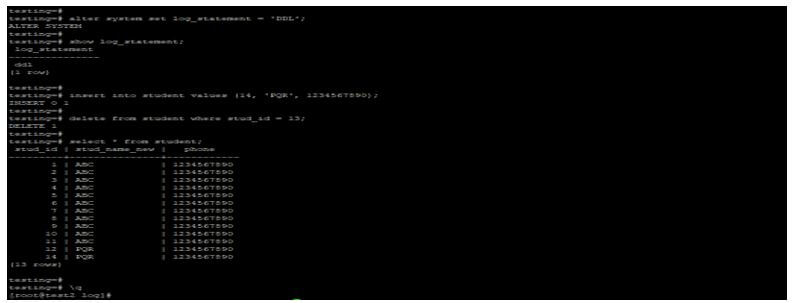
Code:
alter system set log_statement = 'DDL';
show log_statement;
insert into student values (14, 'PQR', 1234567890);id = 13;
delete from student where stud_id = 13;
select * from student;Output:
tail -10f postgresql-Mon.log
Example #3
Log_statement using ALL options.
In the below example, we have used ALL options with the log_statement parameter. It will log all statements into the error log.
Code:
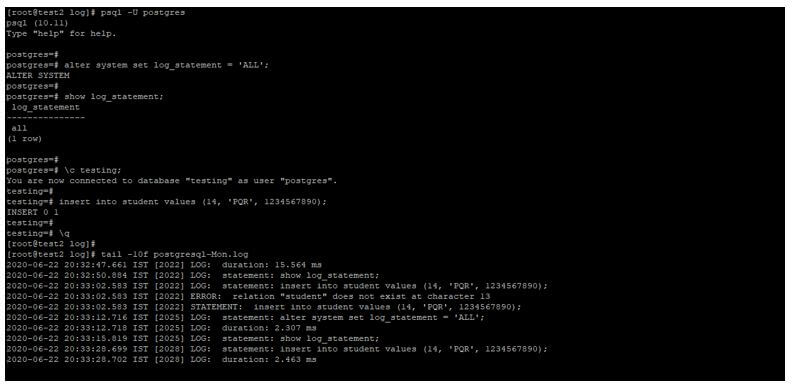
alter system set log_statement = 'ALL';
show log_statement;
insert into student values (14, 'PQR', 1234567890);
tail -10f postgresql-Mon.logOutput:
Example #4
Log_statement using mod options.
In the below example, we have used mod options with the log_statement parameter. It will log DDL and data modifying statement into an error log.
Code:
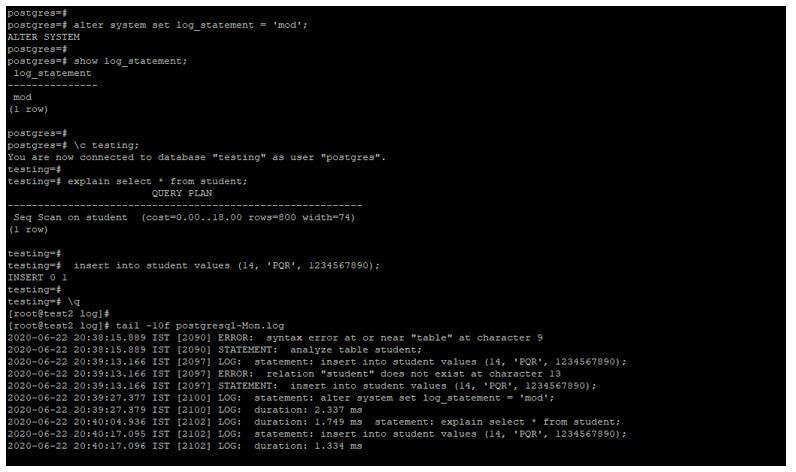
alter system set log_statement = 'mod';
show log_statement;
explain select * from student;
insert into student values (14, 'PQR', 1234567890);
tail -10f postgresql-Mon.logOutput:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL log_statement” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.